Nonsilicate minerals
advertisement

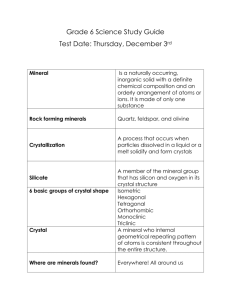
Bell Work: 9/16/10 Observe the photo on pgs. 334 & 335 in your textbook. Read the caption titled, “About the Photo.” Answer the following questions: ◦ What is a mineral? ◦ What does the caption tell you about minerals? What is a mineral? A _________is a naturally formed, mineral inorganic solid that has a definite crystalline structure. ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ naturally inorganic solid crystalline (structure) Mineral Structure By answering these four questions, you can tell whether an object is a mineral: 1. Is _________________ it nonliving material?- A mineral is inorganic, meaning it isn’t make of living things. Is it a solid?2. __________Minerals can’t be gases or liquids. 3. Does ___________________________Minerals it have a crystalline structure?are crystals, which have a repeating inner structure that is often reflected in the shape of a crystal. it formed in nature?-Crystalline materials 4. Is ________________ made by people aren’t classified as minerals. Identifying Minerals The following pictures are in your group: wood, fossil, bone, granite, quartz crystal Observe the pictures and determine which ones are minerals by using the four questions. Write down the names of each item and “yes” if it is a mineral and “no” if it is not a mineral. Mineral Structure _________ Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. All minerals contain one or more of the 92 naturally occurring elements. Atoms and Compounds Each element is made of only one kind of _______. atom An atom is the _________ smallest part of an element that has all the properties of that element. Some properties of aluminum are: shiny, silver colored, fragile, and thin. Each element has its own type of properties. Most minerals are made of __________ compounds of several different elements. A compound is a substance made of two ___ or more elements that have been chemically joined or ________. bonded A Carrot The smallest particles of matter are called atoms. Let’s take a carrot for example. If you continue to chop a carrot into smaller and smaller pieces, eventually you would reach a point where you could not cut up the carrot anymore, but still have carrot. You would then have molecules of carrot. The same applies to elements. If you continually cut up a piece of aluminum, you will reach a point that you could no longer divide it. These are aluminum atoms. Atoms Atoms E ME lements Crystals Solid, geometric forms of minerals produced by a repeating pattern of atoms or molecules that is present throughout the mineral are called ________. crystals A crystal’s shape is determined by the arrangement of the atoms within the crystal. Two Groups of Minerals Silicate minerals are minerals that contain a combination of silicon, oxygen, and one or more metals. Nonsilicate minerals are minerals that do not contain compounds of silicon and oxygen. There are six main classes of nonsilicate minerals. Two Groups of Minerals Write the names of the two groups on the front of the foldable (one on each side). Inside (on the notebook paper) use Figures 4 & 5 on pages 338-339 to take notes on the two groups. Include the definition of the two groups and examples with descriptions. Silicate Nonsilicate Minerals Minerals