File
advertisement

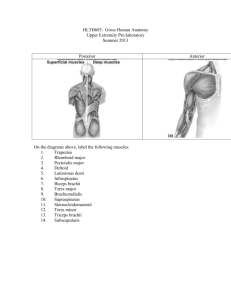
Muscles of the Body Muscles of the Neck and Vertebral Column Trunk extension Deep muscles of the back Maintain normal curvatures of the spine Form a column from sacrum to the skull Erector spinae group Largest of the deep back muscles Deep Muscles of the Thorax—Breathing Deep muscles provide movements for breathing External intercostal muscles Lift the rib cage Internal intercostal muscles Aid expiration during heavy breathing Diaphragm Most important muscle of respiration Flattens as it contracts Increases the volume of the thoracic cavity Muscles of the Abdominal Wall Lateral and anterior abdominal wall Formed from three flat muscle sheets External oblique Internal oblique Transversus abdominis Fourth muscle pair Rectus abdominis Inserts at the linea alba Superficial Muscles of the Anterior Thorax Movements of the scapula Pectoralis major Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior Subclavius Superficial Muscles of the Posterior Thorax Movements of the scapula Trapezius Levator scapulae Rhomboid major Rhomboid minor Muscles Crossing the Shoulder Joint Movements of the arm Deltoid Pectoralis major Muscles Crossing the Elbow Joint Posterior muscles—extensors of the forearm Triceps brachii Anconeus Anterior muscles—flexors of the forearm Biceps brachii—also supinates the forearm Brachialis Brachioradialis Muscles of the Forearm Movements of the wrist, hand, and fingers Tendons are anchored by Flexor and extensor retinacula Most forearm muscles arise from the distal humerus Movements at the wrist include Flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction Wrist and fingers are “operated” by muscles in the forearm Flexors Anterior flexor compartment Innervated by median and ulnar nerves Originate from a common tendon Medial epicondyle of the humerus Superficial Anterior Muscles of the Forearm Pronator teres Flexor carpi radialis Palmaris longus Flexor carpi ulnaris Flexor digitorum superficialis Deep Anterior Muscles of the Forearm Flexor pollicis longus Flexor digitorum profundus Pronator quadratus Muscles of the Forearm Extensors Posterior compartment of the forearm Innervated by the radial nerve Originate at a common tendon Lateral epicondyle of the humerus Superficial Posterior Muscles of the Forearm Brachioradialis— flexes forearm Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor carpi radialis brevis Extensor digitorum Extensor carpi ulnaris Deep Posterior Muscles of the Forearm Supinator Abductor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis brevis and longus Extensor indicus Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand Fine movement of the fingers All located in the palm Control precise movements Include muscles of Adduction, abduction, and opposition Muscles Crossing the Hip and Knee Joints Thigh and leg movements Anterior muscles Flex the thigh and extend the leg at the knee Posterior muscles Extend the thigh and flex the leg Muscles Crossing the Hip and Knee Joints Thigh and leg movements Adductor muscles—on medial aspect of thigh Adduct the thigh only Deep fascia of the thigh Surrounds and encloses all three groups Movements at the hip joint Muscles that flex the thigh Originate on vertebral column or pelvis Muscles that extend the thigh Arise posterior to the hip joint Adductors originate medial to the hip joint Abductors originate lateral to the hip joint Anterior and Medial Muscles Origin on pelvis or vertebral column Iliacus Psoas major Sartorius Muscles of the medial compartment Adductor longus Adductor brevis Adductor magnus Pectineus Muscles of the Anterior Compartment of the Thigh Quadriceps femoris Has four separate heads Has a common insertion at the quadriceps tendon Powerful knee extensors Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus medialis Vastus intermedius Tensor fasciae latae Posterior Muscles Origin on pelvis or sacrum Gluteus maximus Gluteus medius Gluteus minimus Lateral rotators Piriformis Obturator externus Obturator internus Superior and inferior gemellus Quadratus femoris Muscles of the Leg Fascia lata of the leg surrounds muscles Tightly binds muscles Prevents swelling during exercise Aids venous return Divides leg into three compartments Tendons are held in place by Extensor, fibular, and flexor retinacula Muscle movement at ankle and intertarsal joints Muscles of the Posterior Compartment Superficial muscles Triceps surae Gastrocnemius Soleus Plantaris Surface Anatomy Palpation—feeling internal structures through the skin “Living anatomy”—provides information about Palpation of arterial pulses Skeleton, muscles, and blood vessels Sounds of the heart and lungs Where to give injections The Abdomen Structures felt through the skin Iliac crest Anterior superior iliac spine Inguinal ligament Runs medially from anterior superior iliac spine to the pubic tubercle Pubic crest Muscles of the Back Trapezius Latissimus dorsi Erector spinae The Shoulder Acromion—lateral end of the spine of the scapula Acromioclavicular joint Deltoid muscle Covers the greater tubercle of the humerus The Arm The region between the shoulder and elbow Humerus Palpated through skin along its entire length Biceps brachii Medial bicipital groove The medial boundary of the biceps brachii Triceps brachii The Elbow Lateral and medial epicondyles of the humerus Ulnar nerve—“funny bone” runs across medial epicondyle Olecranon process of the ulna Cubital fossa—(antecubital fossa) Forms anterior surface of forearm Forearm Bones Ulna—palpate entire length Styloid process and head—distal end Radius—partly covered in muscle Head of the radius—proximal end Styloid process—distal end Muscles of the Forearm Flexor muscles—anterior forearm Flexor carpi radialis Palmaris longus This muscle is absent in about 30% of people Extensor muscles—posterior forearm Other Structures of the Forearm Anatomical snuff box bordered by Extensor pollicis brevis Extensor pollicis longus The Hand Dorsum of hand Dorsal venous network Tendons of extensor digitorum Gluteal Region Iliac crests Posterior superior iliac spine Sacroiliac joint Prominences of the buttocks “Cheeks” of the buttocks Formed from subcutaneous fat and the gluteal muscles Thigh Medial and lateral condyles of the femur Patella Three groups of muscles Quadriceps femoris—anterior thigh Vastus lateralis—injection site Adductors—medial thigh Hamstrings—posterior thigh The Thigh The femoral triangle Superior border—inguinal ligament Inferior borders Sartorius Adductor longus Popliteal fossa Diamond-shaped hollow on posterior knee Defined by borders of “hamstring” tendons and gastrocnemius Leg and Foot Palpate patella to find the patellar ligament Structures of the proximal leg Tibial tuberosity Lateral and medial condyles of the tibia Head of the fibula Structures of the distal leg Medial malleolus Lateral malleolus Muscle Groups of the Leg Posterior calf muscles Gastrocnemius and soleus Calcaneal tendon—inferior end of the soleus and gastrocnemius Anterior compartment muscles Tibialis anterior Extensor digitorum Fibularis