File - Mechatronics 2k14

Annexure – I
Cupola & Electric Furnaces
Cupola
• The selection of the melting unit depends on
1) The temperature required to melt the alloy.
2) Quantity of metal required
3) Economy of installation and operation
4) Environmental and wastage disposal
• The most commonly used furnaces in foundries are
1) Cupola furnace
2) Electric arc furnace
3) Induction furnace
Cupola
• Cupola is the primary method of melting iron in foundries.
• The primary objective in cupola is to produce iron with desired composition, temperature and properties at the required rate in the economical manner..
• In recent times the usage of cupola is reduced in favor of induction furnace which offer very precision control of melt chemistry and temperature and much lower emission.
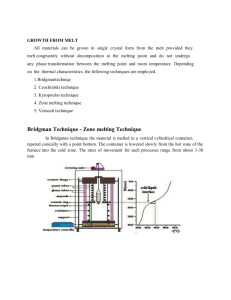
Cupola Construction
Cupola Operation
The four stages in the cupola melting process are
1) Preparing the cupola – Height of sand bed 200mm
2) Firing the cupola
3) Charging and Melting –
Coke is fuel, Lime stone is to remove impurities
(thorough mixing of molten metal)
25 : 1 (Pig iron to limestone)
10 : 1 (Pig iron to coke)
4) Tapping metal
Advantages
• Continuous operation
• Low cost
• Easy to operate
• Composition of temperature of melt can be controlled
Direct electric arc furnace
Description
• 7% of total steel produced in US
• Larger % of steel melted in steel foundries
• Acid linings
• Graphite electrodes
• Temperature is about 11000
F
• Life of roof may of 100 heats
Advantages
Heat application can be closely controlled
High thermal efficiency (70%)
Metal loss is minimum
Indirect electric arc furnace
Description
• Arc between electrodes
• Rollers allow the furnace to rock during melting
• Rocking provides faster melting
• Low temperature than direct arc furnace.
• Cast iron and non ferrous metals
Induction Furnace
Annexure – II
Questions
1) Name the various parts of cupola.
2) List the various stages in cupola.
3) What is the purpose of adding flux during melting?
4) What is the purpose of using fire clay in cupola?
5) What are the advantages of electric furnace as compared to cupola?
Key words
1) Slag – A film forms on the top of the molten metal
2) Spout - Pouring passage
3) Crucible – Container for molten metal
Annexure – III Mind map
Annexure – IV
Summary
The selection of the melting unit depends on
1) The temperature required to melt the alloy.
2) Quantity of metal required
3) Economy of installation and operation
4) Environmental and wastage disposal
The most commonly used furnaces in foundries are
1) Cupola furnace
2) Electric arc furnace
3) Induction furnace
Summary
• The primary objective in cupola is to produce iron with desired composition, temperature and properties at the required rate in the economical manner..
• In recent times the usage of cupola is reduced in favor of induction furnace which offer very precision control of melt chemistry and temperature and much lower emission.
Annexure – V
MCQ
1) Tuyeres are used
(a) to feed the charge in the cupola
(b) to allow the air in the combustion zone of cupola
(c) to collect the molten metal
(d) to throw the exhaust from the cupola
2. Charging in a cupola consists of
(a) alternate layers of lime stone and coke
(b) alternate layers of iron and coke
(c) alternate layers of limestone, iron and coke
(d) alternate layers of limestone and iron
MCQ
3) Which of the following refractory materials is recommended for steel furnaces ?
(a) Alumina (b) Silica (c) Magnesia d) Fireclay
4) The following furnace is suitable for melting steel a) Cupola b) Induction furnace c) Crucible d) All of the above
5) Coke is used in a) Cupola b) Induction furnace c) Crucible d) All of the above