Commodity Products - Pustaka Asep MuSa

Commodity Products
CHEMICAL PRODUCT ENGINEERING
ASEP MUHAMAD SAMSUDIN
Chemical Products
Category of
Product
Class of Product
Specialty chemicals Surfactant
Example
Ammonium lauryl sulfate
Exfoliating gel Formulated products
Cosmetic
Bio-based concepts Drug
Devices
Alendronate sodium
Biomedical device Blood oxygenator
Virtual chemical products
Technology-based consumer goods
Key Attribute
Molecular structure
Microstructure
Biological activity
Software to simulate chemical processes
Health care consumer goods
Aspen Plus
Disposable diaper
Materials and assembly
Computational performance
Materials and assembly
R. Costa and G. D. Moggridge
R. Costa, G. D. Moggridge, P. M. Saraiva. Chemical Product Engineering: An Emerging Paradigm Within Chemical Engineering. AIChE Journal, 52 (2006) :1979
Chemical Products
Based on the characteristic size scale which is critical to their performance
Examples
Scale
Key
Basis
Risk
Commodities Chemical Devices
Artificial kidneys
Meters
Molecular
Products
Penicillin
Microstructures
Products
Sunscreen Ethylene, ammonia
Continuum
Cost Convenience
Nanometers Micrometers
Discovery
Reaction Engineering,
Unit operations
Feedstock
Reaction Engineering,
Unit operations
Chemistry
Intellectual Property Discovery
Function
Recipe
Science
Cussler and Moggridge
Cussler EL, Moggridge GD. Chemical product design. 2 nd edition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2011.
Critical size of Chemical
Products
Commodity Products
The core of the chemical industry. Simple molecules produced in large quantities (over 10,000 tons/year) at the lowest possible cost.
Fewer than 50 of the more than 30,000,000 compounds which are known.
The molecular weights are typically less than 100 daltons.
The king of these product is liquid fuel: gasoline, petrol, diesel
The key chemical and physical properties of the commodity products : key scale, chemical reactivities and volatilities.
We can use the same design template of needs, ideas, selection and manufacture to improve manufacturing itself.
Product Design Procedures
Cussler & Moggridge, 2011
Example 1
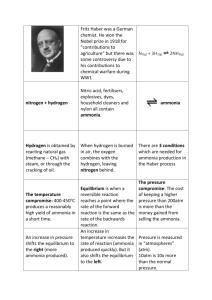
Ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen
Needs
A product purity above 95%.
An amount over 10,000 tons/year.
Price already defined by the market.
A production cost perhaps 20% less than the price
Example 1
Ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen
Ideas
Derive from the four step outline suggested by Douglas (1988)
Batch Vs. Continuous
Process
Inputs and Outputs
Reactors and Recycles
Separation and Heat
Integration
Example
Ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen
First : decide weather we use a batch of continuous one
Experience suggests that for commodities a continuous process will almost always be cheaper.
Second : draw a flow diagram. A chart illustrating the flow of different chemical stream in the reactor.
𝑁
2
+ 3𝐻
2
↔ 2𝑁𝐻
3
Example
Ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen
Third: recognize that this process will not involve complete reaction
For the conventional Haber process, only get perhaps 20% conversion.
The process must have a reactor followed by some sort of separator.
Example
Ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen
Fourth: Douglas suggests more detailed identification of separation required.
The gases from the reactor are chilled to 10 o C to condense liquid ammonia, and the non-condensables are recycled.
Part of this recycle is purged to get rid of the argon.
Significant amounts of nitrogen and hydrogen dissolve in the liquid ammonia.
One the pressure is released (to about 20 bar), the dissolved gases can be removed by simple distillation for recycle and recompression.
Example
Ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen
IDEAS.
1.
2.
3.
Seek better catalyst.
Get rid the argon and so not waste the hydrogen and nitrogen necessarily discarded with the purge.
Invent a better, more selective separation
Example
Ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen
SELECTION
The catalyst, the firs area for study, has received the greatest effort. The original Iron oxides used by Haber as catalyst.
The activity of catalyst can be enhanced by trace quantities of many metals, especially ruthenium.
Removing argon, which is the second area of interest, would certainty possible by liquefying air and distilling off the nitrogen. While the separation of argon from oxygen is difficult because the difference in boiling points is so small.
We can infer that this distillation is too expensive, costing much more than purging the argon and wasting some nitrogen and hydrogen.
Example
Ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen
SELECTION
We may decide to focus on the third area, a better separation of ammonia from the other gases.
We may select three good idea : A membrane 100 times more permeable to ammonia than to nitrogen and hydrogen at room temperature
A similar membrane selective and stable at reactors temperature
An adsorbent selective for ammonia at reactor conditions.
Example
Ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen
MANUFACTURE