Study Guide
advertisement
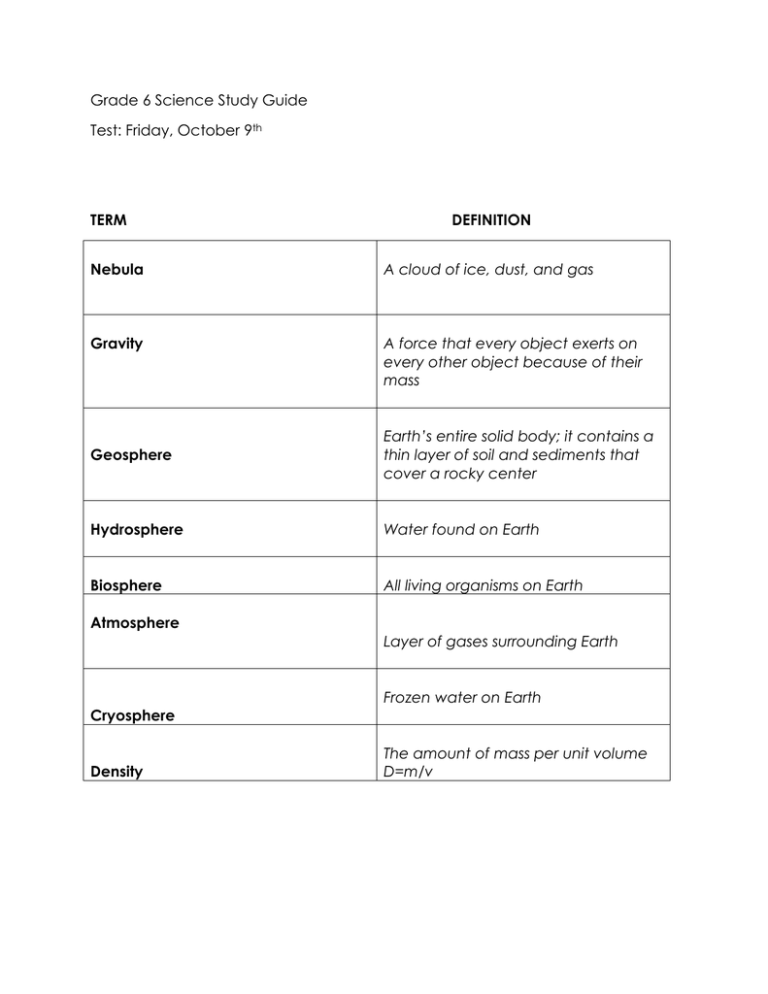
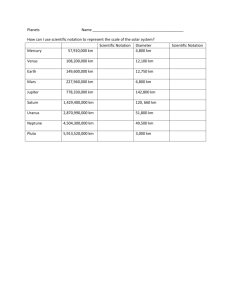
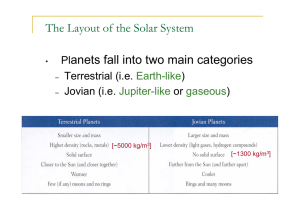
Grade 6 Science Study Guide Test: Friday, October 9th TERM DEFINITION Nebula A cloud of ice, dust, and gas Gravity A force that every object exerts on every other object because of their mass Geosphere Earth’s entire solid body; it contains a thin layer of soil and sediments that cover a rocky center Hydrosphere Water found on Earth Biosphere All living organisms on Earth Atmosphere Layer of gases surrounding Earth Frozen water on Earth Cryosphere Density The amount of mass per unit volume D=m/v TERM Mass Weight DEFINITION The amount of matter within a constant The sum of the gravitation pull between two objects Makes up all matter Atoms Particles that make up atoms Protons, neutrons, electrons Objects made up of atoms Matter Sphere System A ball shape with all points on its surface at an equal distance from the center A group of related objects or parts that work together to form a whole Important facts to know: Size and shape of the Earth The Earth is shaped as a sphere; it has a bulge around the equator Early Earth beliefs People believed Earth was a flat disk with land in the center and water at the edges Order of the planets Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Rocky planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars Gaseous planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Earth’s systems Atmosphere Hydrosphere Geosphere Biosphere Cryosphere Types of water found on Earth: Fresh (lake, pond, river) Marine (ocean) Ice (frozen fresh) Brackish (salt + fresh) 1. The nebula formed The Big Bang Theory 2. Gravity pulled the particles of the nebula close together 3. Nebula got smaller and formed a disk 4. The disk began to turn- our star formed our sun 5. Material started to clump together and planets formed 6. The more gravity pulled particles together 7. Other matter collected to form objects