The Layout of the Solar System Planets fall into two main categories
advertisement
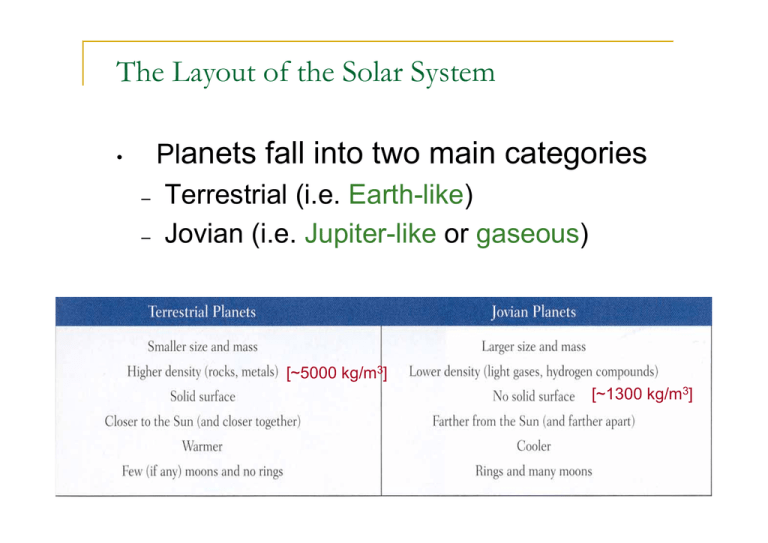
The Layout of the Solar System • Planets fall into two main categories – Terrestrial (i.e. Earth-like) – Jovian (i.e. Jupiter-like or gaseous) [~5000 kg/m3] [~1300 kg/m3] What is density? Average density = mass/volume typical units: [kg/m3] Density of water is 1000 kg/m3. Useful formula: Volume of a sphere = r = radius Mars Neptune Terrestrial Jovian 1 g/cm3 = 1000 kg/m3 Some facts about the Solar System • Planets orbit the Sun under the influence of gravity. • The planets all go around the Sun in the same direction. • Most of the planets spin in the same direction as their orbit. • The orbits of all planets are aligned within a few degrees of each other. (Pluto is no longer considered a planet) The orbits of all the planets, as seen from directly above the Sun’s equator, 100 AU away. Only Pluto’s orbit is more than 7 degrees away from the rest. Pluto’s orbit A Few Exceptions to the Rules… Uranus is tilted on its side. Venus rotates “backwards” (i.e. clockwise). Triton orbits Neptune “backwards.” Earth is the only terrestrial planet with a relatively large moon. Origin of the Solar System Theory must explain the data: Large bodies in the Solar System have orderly motions. There are two types of planets. small, rocky terrestrial planets large, hydrogen-rich Jovian planets Asteroids & comets exist in certain regions of the Solar System The exceptions to the general patterns need to be explained Close-encounter theory Sun had a close encounter with another star Fails to explain why the orbits are almost circular Fails to explain the terrestrial/Jovian split Close encounters are rare Gravity pulled matter off the surface of the Sun Predicts that extra-solar planets should be very rare Doesn’t work Nebular Theory Solar System formed from a giant, swirling cloud of gas & dust Depends on two principles of Physics: Law of Gravity gravitational potential energy ⇒ heat Conservation of angular momentum And basic chemistry Heating, spinning, flattening…. The Solar Nebula The nebular theory holds that our Solar System formed out of a nebula which collapsed under its own gravity. observational evidence We observe stars in the process of forming today. The are always found within interstellar clouds of gas. 10,000 AU newly born stars in the Orion Nebula solar nebula – name given to the cloud of gas from which our own Solar System formed Gravitational Collapse • The solar nebular was initially fairly spherical and a few light years in diameter. – very cold – rotating slightly • It was given a “push” by some event. – perhaps the shock wave from a nearby supernova • As the nebula shrank, gravity increased, causing collapse. • As the nebula “falls” inward, gravitational potential energy is converted to heat. – Conservation of Energy • As the nebula’s radius decreases, it rotates faster – Conservation of Angular Momentum Collapse of the Solar Nebula Orderly Motions in the Solar System The Sun formed in the very centre of the nebula. temperature & density were high enough for nuclear fusion reactions to begin The planets formed in the rest of the disk. This would explain the following: all planets lie along one plane (in the disk) all planets orbit in one direction (the spin direction of the disk) the Sun rotates in the same direction the planets would tend to rotate in this same direction most moons orbit in this direction most planetary orbits are near circular (collisions in the disk) More Support for the Nebular Theory We have observed disks around other stars. These could be new planetary systems in formation. β Pictoris AB Aurigae Ok the theory seems to pass the first test…. How about explaining the existence of planets? And in particular 2 type of planets? • What key fact explains why there are two types of planet? • Describe the basic steps by which the terrestrial planets formed. • Describe the basic steps by which the Jovian planets formed. Making planets The gravity of the gas in the Solar Nebula was too weak to form planets Needs some ‘seeds’ to form another way Metal/rocky seeds form close in; hydrogen compounds form further out, by condensation Condensation Elements & compounds began to condense (i.e. solidify) out of the nebula…. depending on temperature Building the Planets So only rocks & metals condensed within 3.5 AU of the Sun… the so-called frost line. Hydrogen compounds (ices) condensed beyond the frost line. Building the Planets accretion -- small grains stick to one another via electromagnetic force until they are massive enough to attract via gravity to form... …planetesimals which will: • • • combine near the Sun to form rocky planets combine beyond the frostline to form icy planetesimals which… capture H/He far from Sun to form gas planets Evidence for condensation Impacts happen even today (but rare) July, 1994: Comet Shoemaker-Levy/9 collided with Jupiter Why the outer planets are big Basic idea: the Hill Sphere: Slightly stronger pull of Sun on this side Nebular gas Sun Planet Pull of gravity We need the planet’s gravity to be stronger than the extra Sun’s gravity, in order to pull in the nebular material How big a region can the planet accrete from?