8th Grade Science Final Exam Review Sheet
advertisement

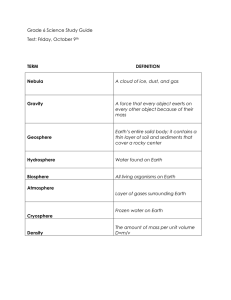
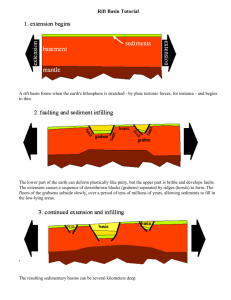
Name ______________________________________ Period _________ Teacher P, C or B 5/20/14 REVIEW FOR: 8th GRADE SCIENCE FINAL EXAM Option one: Do the review at home on your own time for extra credit and go to Mr Peters/Mr Cacciatore rooms for Jeopardy and other review styles Option two: Do the review in Ms Bennight’s room. (Read directions; we will find info together) Due Tuesday May 27, for extra credit. If you don’t have the review completed, you will have NOTHING to study for the final exam. Directions: Get your ISN and title the page(s) “Final Exam Review”. Answer the following questions in your ISN in complete sentences, labeled pictures, etc. This paper is a work cited page; write down where you found the answer in the space provided below each review term (book & page number, etc). To get a 100%, show this paper completed and show your ISN with all 41 topics answered, drawn, defined, etc. Those working at home: use your ISN, the online textbook and any class work from this year to answer topics. 1. Be able to balance equations. Give an example of a balanced equation 2. Define and give examples of qualitative and quantitative 3. Define Gravity 4. Define these variables: independent, dependent and control. Give examples of each 5. Define inference and give an example? 6. Define the 3 types of galaxies and draw a picture of all 3 types. 7. Define weathering and erosion 8. Define: Subduction Zone, Trench, Rift Valley and Volcano 9. Describe Wegener’s theory of the Continental Drift 10. Draw a picture of Earth with its Axis. What is the degree of tilt? 11. Draw a picture of the Earth position to the Sun for each season and label 12. Draw an illustration on the electromagnetic spectrum, label it and know what ROYGBIV is. 13. Draw pictures and label: Rift Valley, Trench, and Mountain 14. Draw pictures to show the moon cycle; know the quarters 15. Galaxies are all made up of? 16. How do we know that our sun is a main sequence star? 17. How do you calculate speed? 18. How do you develop a hypothesis? 19. How do you read a topographical map? 20. How do you read a triple balance beam and a test tube or beaker? 21. How many days does it take for the Earth to orbit the Sun? 22. How many hours does it take the Earth to rotate? 23. Know how to read an H-R diagram 24. Know the size of these waves (high=>low frequency) for: gamma, inferred, visible, unltraviolet, x-ray and radio 25. Review Lab Safety Rules 26. What are the differences in: a block hole, a neutron star and a black dwarf 27. What are the types of plate movements and draw each type with arrows. 28. What does a Red Shift have to do with the Big Bang? 29. What does it mean to interpret data? 30. What does it mean to transfer energy? Give 3 examples of different types. 31. What is a lunar eclipse? Solar eclipse? 32. What is a Nebula? 33. What is displacement and how would you use it to measure a rocks volume? 34. What is folding and faulting? 35. What is gravity’s role in a nebula? 36. What is MSDS? Why do we need them? 37. What kind of wave transfer energy from the Sun to the Earth? 38. What types of energy can you find in your notes/book, etc? ex: thermal, electrical, etc. 39. Which waves can humans see? 40. Why are models important? 41. Why are topographical maps helpful?