Test Review Activity 1 & 2
advertisement

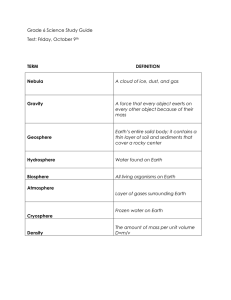
Test Review Activity 1 & 2 Open Response #1 • Describe the nebular theory of the formation of our solar system ON YOUR ANSWER SHEET. Use and underline these key terms in your writing (nebula, gravity, planetesimals (chunks), nuclear fusion, swirling/rotation, star/sun, mass/matter ) • Go to reading guide Solar System entry and look at the sequence of events in the nebular theory. Turn it into a paragraph. Define vocabulary terms as you use them. • DO NOT simply list the key terms without tying them together into an explanation. Example Answer • Restate question/ topic sentence: The Nebular theory describes the formation of the solar system. • First a supernova explodes and a cloud of gas and dust from the blown up star is formed – a nebula. Gravity pulls clumps of matter together and they form into chunks and grow bigger. As gravity causes the nebula to contract most of the mass is concentrated in the center and the cloud begins to spin or rotate. The clump of material in the center of the cloud becomes very hot as gravity continues to pull it inward. Eventually, nuclear fusion begins in the center of the cloud and becomes the sun. Meanwhile, in the outer parts of the cloud, clumps of matter stick together and form larger bodies called planetesimals that will become the planets. • Conclusion: The solar system has formed due to gravity and the planets revolve around the central sun. #2 Venn Diagram Inner VS Outer (Go to Reading Guide Solar System Entry) Inner : Smaller, warmer, rocky, molten metal cores, closer to sun, fewer moons, no rings, denser, shorter years, brighter Outer: larger, colder, gas /liquid hydrogen and methane, farther from sun, more moons, many rings, less dense, longer years, dimmer Both: same age, from same nebula, revolve around sun, rotate on axis, spherical #3 Hours Per Day Over Time Data A. The title of this graph is inappropriate. What would be the best title for this graph? • Titles had to refer to both axes: Changes in day length(days per year) over 600 million years (geologic time). B. What was the number of days in an Earth Year 550 million years ago? • 415-420 days per year (less points for 400-410 or no unit) Cite evidence from table or graph!! Time Period Precambrian Cambrian Ordovician Silurian Devonian Mississippian Pennsylvanian Permian Triassic Jurassic Cretaceous Present Date (millions years ago) 600 500 425 405 345 310 280 230 180 135 65 0 Length of Year (days) 424 412 404 402 396 393 390 385 381 377 371 365.25 C. State how the earth year has changed through time. Cite 2 pieces of specific evidence to support your claim. Topic sentence: The number of days in a year is decreasing over time. Cite 2 pieces of evidence: For example, 600 mya length of year was 424 days 290 million years later, at 310 mya the length of the year had decreased to 393 days per year. A decrease of 31 days in 290 million years a rate of 0.1 day every million years. What do you predict will happen to the length of an earth year in 100 million years from now? Why do you think that? (Reading Guide Moon Entry) • Extrapolate from the slope of the graph – approximately 350 days per year • You determined this by extending the line of the graph using a best fit line • You know that the Earth is slowing because of tidal friction caused by the moon’s pull on the Earth and its oceans y = 0.0961x + 363.87 R² = 0.996 Day Length Graph 440 400 380 360 340 320 700 600 500 400 300 Years before present (millions of years ago) 200 100 0 Number of Days in an Earth Year 420 #4 Scale Model of Asteroid Distance • What is a scale model and why are they useful? • Complete the table ON YOUR ANSWER SHEET to determine the distance from the sun of the very largest asteroid, Ceres – at 448,000,000 km– using the three different scale models in the chart provided. You may use a calculator (no sharing!). • If you had to actually place this asteroid on the rope model of our solar system, where – relative to the planets - would the asteroid be placed? Support your answer with specific evidence (numbers!) from your Activity 1. 4. A. Define Scale Model (Go to scale model activity entry) • General question not specific to our model • Don’t define it using its own name Ex: Scale is a particular type of model that is proportional to the actual object that it is representing. 2nd part to question- use Ex. Shows things too big or small to see for ourselves. 4. B & C Scale Calculations • Actual size divided by the scale 448,000,000 divided by 150,000,000 = 2.986 • Place the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter this is relative to the planets (explain the distance you calculated according to the scale)