Unit 2 Pacing Guide
advertisement

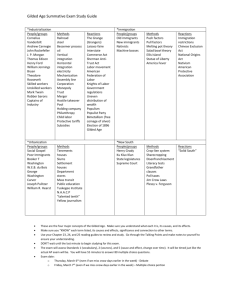
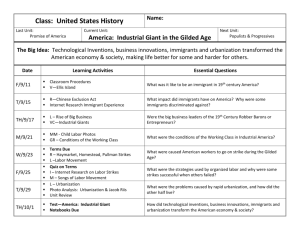
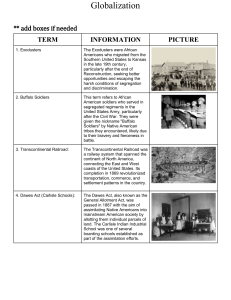
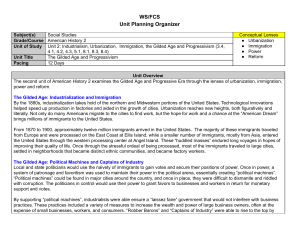
Unit 2 - Industrialism, Urbanization, Immigration, Gilded Age American History II Daily Schedule: 3 9 Innovators and New technology R Complete Reasons for Industrialization Rise of Big Business Old and New Immigrants F Nativism in the turn of the 20th Century Labor Unrest in the United States M Union Movement in United States Organized Labor / Strikes T Gilded Age Politics 10 W Gilded Age Politics 11 R 12 F 4 February W IN CLASS Post-test – WEBQUEST – Immigrants, Urbanization 5 8 HW/ READ 304-310 311-316 317-325 332-337 340-346 348-353 397-399 Rise of the Modern City Social and Cultural Trends in the late 19th Century Unit 2 Test Important terms, people, and ideas: (Remember – this is not a complete list) Industrialization inventions Edison Westinghouse Urbanization growth horizontal and vertical development of culture New Issues in Urban Life sanitation fires natural disasters Johnstown flood 1889 Galveston hurricane 1900 San Francisco earthquake of 1906 entertainment phonograph motion pictures mass entertainment Buffalo Bill’s Wild West saloons vaudeville spectator and team sports boxing professional baseball college football and basketball bicycle races leisure time city parks bicycles Coney Island Immigration reasons for immigration culture/ethnic groups Eastern and Southern Europeans Similarities and differences with Old Immigrants endurance of passage entry into USA port Ellis Island Angel Island huddled masses Lewis Hine photos from Ellis Island opportunity and mobility New York – garment industry Chicago – meat industry Cleveland – steel Mills ethnic neighborhoods naturalization views on American Dream and life in US Abraham Cahan Yekl: A Tale of the New York Ghetto Jacob Riis – How the Other Half Lives Tenements Working Conditions within various industries (garment, meat, steel) child labor Upton Sinclair, The Jungle Nativism toward Italians, Roman Catholics, Chinese Chinese Exclusion Act 1882 Gilded Age Political Machines corruption/graft Boss Tweed and Tammany Hall James Michael Curley and Boston Chicago/Cook County James Pendergast and Kansas City Ed Crump and Memphis immigrants for votes patronage and favoritism big business laissez-faire “robber barons” and “captains of industry” Rockefeller Carnegie “The Gospel of Wealth” Morgan Pullman Monopolies impact on workers and consumers Vertical and Horizontal integration Social Darwinism “survival of the fittest” Labor Unrest Formation of unions Knights of Labor and Terrence Powderly AFL and Samuel Gompers American Railway Union and Eugene Debs United Mine Workers and “Mother Jones” Eugene Debs and Socialist Party of America Union tactics Molly Maguires Railroad Strike 1877 Haymarket Affair Homestead Strike Pullman Strike Collective Bargaining Triangle Shirtwaist Fire Essential Thoughts/Questions 1. How did technological innovations enable urbanization and the horizontal and vertical growth of cities? 2. How did rapid urbanization impact the economic and cultural development of cities in the 19th Century? 3. How did the process of immigrating to the United States impact immigrants? 4. How did increased immigration impact the economic and cultural development of cities in the late 19th Century and early 20th Century? 5. How did the desire for power and the resulting political corruption impact government, economics, and society during the late 19th Century? 6. How did industrial leaders’ desire for power and money impact political, economic and cultural progress of the United States? 7. How did laborers respond to the tactics of industrialists and working conditions during the late 19th Century and early 20th Century?