Chapter 13

Systems
Processes
(IPP)
1
Learning Objectives
• Appreciate contemporary production trends.
• Understand role of ERPs in integrating total manufacturing environment.
• Know principal components of Integrated
Production Processes (IPP).
• Recognize effects of automation on IPP.
• Understand key inputs, outputs, files, processes.
• Identify principal challenges/opportunities.
• Introduce supply chain management software
ERPs - SAP Automotive Modules
•
Business Planning
•
Controlling
•
Finance & Accounting
•
Suppliers
•
Original Equipment Manufacturers
•
Aftermarket
3
Managing Throughput Times
•
Push Manufacturing
–
Sales forecast drives production plan
–
Goods produced in large batches
–
Jobs wait until machines ready
•
Pull Manufacturing
–
Idle machine pulls job from previous machine
– Theoretically, job = “batch” of one unit
4
Features of Pull Approach
•
Short production runs
•
Continuous flow operations
•
Factory cells - all machines together
– workers run more than 1 machine
•
Reduced WIP & FG inventories
•
Reduced floor space
– improved layout/less inventory
5
Trends - Cost Management/
Accounting
•
Shift to reporting to assist strategic planning/decision making
•
Increased emphasis - managing costs v. accounting for costs
•
Attack waste Vs. reporting variances
•
Flexible cost systems - responsive to change
•
Shift - cost structure - variable to fixed costs
6
Trends - Cost Management/
Accounting (2)
•
Less DL - less use of DL to apply OH
•
Increase in OH component of total cost
•
4th category (direct technology) added to DM,
DL, OH
•
Use of Activity Based Costing (ABC) systems
•
Real-time data capture in factory
•
Shift from Std. cost systems to actual
•
Reduction in data-gathering costs
•
Collecting statistical + financial data
7
Trends - Cost Management/
Accounting (3)
•
Replace detail reporting by shop order and/or operation with actg. for cell throughput time
•
Use cell throughput time v. DL to apply OH
•
Trend towards process cost systems v. job order systems
•
For mgt. purposes, abandonment of absorption costing
•
Accumulation of costs for decision making vs. valuing inventories
8
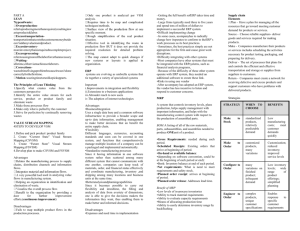
Overview–ERP-Driven Manufacturing
En gi n e e ri n g
ERP Database
Man u factu ri n g
Bu si n e s s
Re porti n g
ERP Data management modules
ERP Data management
Engineering Flexible Manufacturing System Production, Planning and Control
Floor Control
Logistics Process Control and Planning
Product Design
CAM GT
MPS
MRP
MRP SFC
CAD/
CAE
CAPP
CRP DRP
CNC
Robotics
AGVS &
AS/RS
Automated
Data
Collection
Bar code readers
VDTs
JIT
Quality
Management
Business Reporting
OE/S
B/AR/
CR
P/AP/
CD
HR
Product costing
Inventory control
Performance measurement
9
Communication and Messaging (i.e., change orders, new designs, etc.)
Production Planning/Control
Systems
•
Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP)
–
Master production schedule
–
Materials requirements planning (mrp)
–
Shop floor control
•
Just-in-time
10
Just-in-time Objectives
•
Zero defects
•
Zero setup times
•
Small lot sizes
•
Zero lead times
•
Zero inventories
11
JIT Implementation Features
•
Arrange factory in U-shaped work cells
•
Assign 1 worker to multiple machines
•
Give production workers authority to stop the line if they are behind schedule or if they discover defective parts
•
Require nearly constant parts production schedule
•
Develop vendor cooperation re deliveries
•
Simplify system for tracking movement of goods through factory
12
Flexible Mfg. Systems Components
•
Group Technology
•
Computer-aided manufacturing
•
Computer-aided process planning
– computer numerical control
• robotics
• automated guided vehicles
• automated storage/retrieval systems
• digital image processors
•
Automated data collection devices
13
A
Start
Master production schedule (MPS)
Materials requirements planning
(little mrp)
Parts master
Time-phased order requirements
BOM*
Detailed capacity requirements planning
(DCRP)
Open
MO*
Open
PO*
RM
Status*
FG
Status*
Time-phased order requirements
A
Released
POs
Production schedule
Routing*
Work center master*
Work center status*
Raw materials requisitions
Completed move tickets
Production work centers
Job time tickets
Shop floor control (SFC)
Cost accounting
Open
MO*
Overview: Production planning & control & cost accounting.
Vendors
Production supervisor
Inventory control
Completed mfg. orders notice
Released mfg. orders
Printed move tickets
Production work centers
Cost variances
GL updates
Various managers
RM issued notice
Inventory control RM returned notice
Standard costs master*
WIP
Inventory*
General
Ledger*
Budget master*
Payroll master*
GL system
BOM = Bill of materials; MO = Manufacturing orders; PO = Purchase orders; RM = Raw materials; WIP =
Work in Process; FG = Finished Goods * = ERP database component
14
15
16
17
18
19
Inventory system controls
•
Effectiveness of operations
– maintain sufficient inventory to prevent stockouts
– maintain sufficient inventory to maintain operational efficiency
– minimize cost of carrying inventory
•
Efficiency of system operations
– JIT materials acquisition
–
Warehouse bin locations
•
Resource security
– periodic physical inventory counts
– locked storerooms
20
Learning Objectives
• Appreciate contemporary production trends.
• Understand role of ERPs in integrating total manufacturing environment.
• Know principal components of Integrated
Production Processes (IPP).
• Recognize effects of automation on IPP.
• Understand key inputs, outputs, files, processes.
• Identify principal challenges/opportunities.
• Introduce supply chain management software