Biology Unit 3 revision
advertisement

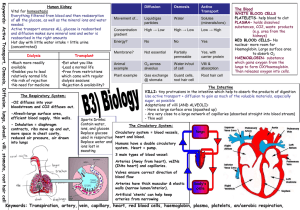
Keywords: Active Transport, Osmosis, Diffusion, lungs, alveoli, villi, stomata, root hair cell Human Kidney Vital for homeostasis Everything filtered from blood and then reabsorption of all the glucose, as well as the mineral ions and water needed. Active transport ensures ALL glucose is reabsorbed and diffusion makes sure mineral ions and water is reabsorbed in the right amounts Hot day with little water intake = little urine (concentrated) Dialysis •Much more readily available •Enables you to lead relatively normal life •No risk of rejection •No need for medicine Transplant •Eat what you like •Lead a normal life •Free from restrictions which come with regular dialysis sessions •Rejection & availability? The Respiratory System: -O2 diffuses into your bloodstream and CO2 diffuses out. -Alveoli=large surface area, efficient blood supply, thin walls. - Inhalation = diaphragm contracts, ribs move up and out, more space in chest cavity, reduced air pressure, air drawn into lungs Sports Drinks: Contain water, ions, and glucose Replace glucose used in respiration Replace water and ions lost in sweating Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport Movement of... Liquid/gas particles Water Solutes (minerals/ions) Concentration gradient High → Low High → Low Low → High Energy? No No Yes Membrane? Not essential Partially permeable Yes, with carrier protein Animal example O2 across alveolus Water in/out of cell Villi & absorption Plant example Gas exchange @ stomata Guard cells, root hair cell Root hair cell The Blood WHITE BLOOD CELLS PLATELETS- help blood to clot PLASMA- holds dissolved substances, CO2, waste products (e.g. urea from the kidneys) RED BLOOD CELLS- No nucleus- more room for Haemoglobin. Large surface area to absorb O2 HAEMOGLOBIN- substance which gains oxygen from the lungs to form OXYhaemoglobin. Then releases oxygen into cells. The Intestine VILLI= tiny protrusions in the intestine which help to absorb the products of digestion Use active transport + diffusion to gain as much of the valuable materials, especially sugar, as possible Adaptations of villi (AND ALVEOLI): - Have a large surface area (squashed up) - Are very close to a large network of capillaries (absorbed straight into blood stream) - Thin wall The Circulatory System: Circulatory system = blood vessels, heart and blood. lungs Humans have a double circulatory system. Heart = pump. 3 main types of blood vessel: Arteries (Away from heart), veINs (INto heart) and capillaries. Valves ensure correct direction of blood flow Arteries have thick muscular & elastic walls (narrow lumen/interior). body’s cells Artificial ‘stents’ can help keep arteries from narrowing Keywords: Transpiration, artery, vein, capillary, heart, red blood cells, haemoglobin, plasma, platelets, an/aerobic respiration, Keywords: Biogas, biofuels, mycoprotein, insulin, glucagon, glucose, glycogen, vasodilation Transpiration is the loss of water by evaporation from plants. Plants lose water when they open the stomata in the leaves to let in carbon dioxide (controlled by guard cells). Transpiration happens faster in hot, dry, windy conditions. Wilting - when Type I diabetes: Not enough more water is insulin produced, insulin lost than can injected be replaced Type II: body not responsive to insulin. Diet carefully Xylem – controlled. transports water & ions, Blood sugar regulation: roots to leaves If high: pancreas releases & stem insulin, glucose → glycogen in Phloem – liver. transports If low: pancreas releases sugars, biglucagon, glycogen → glucose directional Thermoregulation: If hot: sweating (heat lost when evaporates), hairs flat, vasodilation (increase blood flow to skin, heat lost through radiation). If cold: shivering, vasoconstriction Biogas – mainly methane – produced by anaerobic fermentation of a wide range of plants and waste materials that contain carbohydrates Gets rid of waste, solves energy needs and is renewable, however hard to do it on a large scale Fermenters Microbes can be grown on a large scale using fermenters Fermenters have features such as an oxgen supply, stirrer to keep microorganisms in suspension and maintain an even temp, water-cooler jacket to remove excess heat and measuring instruments such as pH and temperature gauges Mycoprotein is produced by allowing the fungus ‘Fusarium’ to grow on sugar syrup in aerobic conditions Food production: Energy lost at each stage in a food chain (due to respiration, movement waste materials etc.). Improving efficiency in food production: decrease no. of stages, limit movement, control temp. Biofuels Ethanol based fuels can be produced from anaerobic fermentation of sugar cane juices by the enzyme carbohydrase. +Adv. = does’nt produce toxic gases, much cleaner and can be mixed with petrol, carbon neutral Disadv. = needs lots of space, poor countries grow cash crops instead of feeding people starvation. Pollution: Greenhouse gases: methane, CO2 Water pollutants: fertilisers, sewage, pesticides Acid rain: sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides (cars, power stations) Human impacts: deforestation (loss of biodiversity), removal of peat lands, building Exchange in Plants Need osmosis in roots (for water) and diffusion near stomata (for CO2) Leaves thin + flat to increase SA for light and a waxy cuticle to prevent evaporation Root hair cells increase SA because of long, thin hairs Most minerals + ions needed taken through roots Anaerobic Respiration Your everyday muscle movements are made possible by AEROBIC respiration If heart rate is increased, blood cannot supply O2 quick enough Anaerobic respiration = incomplete breakdown of glucose, releasing less energy Glucose Lactic Acid (+ energy) Lactic acid needs to be got rid of (by reacting with O2 to form CO2 + water) = OXYGEN DEBT Keywords: kidney, dialysis, transplant, immunosuppressant drugs, microbes, fermentation, alcohol, bacteria, lactic acid 1. The table below shows the amounts of some substances that are processed by the kidneys each day. a) Calculate the amount of water filtered each day [1mark] 2. Plant roots absorb some of their mineral salts from the soil by active transport. What is involved in active transport? [4marks] 3. a) Describe the function of the pigment found in red blood cells [2marks] b) Calculate the % of sodium reabsorbed [1mark] b) Explain how red blood cells are adapted to perform their function [3marks] Substanc e water urea sodium Amount filtered 56 g 25 200 units Amount reabsorbed 178.5 litres 28 g 25 050 units Percentage reabsorbed 99.2 % 50 % Amount excreted 1.5 litres 28 g 150 units 4. Kidney transplants can be treated or dialysis using a kidney ‘machine’. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using dialysis or kidney transplants to keep people alive [5marks] 5. Why is glucose found in the blood but not in the urine? Explain as fully as you can [3marks] 6. A fresh fruit salad is made by cutting up fruits and placing them in a bowl with layers of sugar in between. After 2hrs the fruit is surrounded by syrup (concentrated sugar solution). Explain why the syrup was produced after 2hrs [4marks] 8. The table below shows the composition of blood entering and leaving the lungs. Describe in detail the changes that take place as blood passes through the lungs [3marks] 7. Oxygen is absorbed through the alveoli of the lungs. How are the alveoli adapted to perform this function? [3marks] Gas O2 CO2 Concentration in arbitrary units Blood entering Blood leaving lungs lungs 40 100 46 40 1. The table below shows the economic costs and benefits of using a particular type of biogas generator. Using the table, discuss the adv. and disadv. Of using this type of generator [4marks] Feature Cost of generator and fitting Annual maintenance costs Annual profit from gas produced Annual profit from fertiliser produced 2. During exercise the process of respiration produces excess heat. Explain how the body prevents this heat from causing a rise in core body temp. [4marks] Cost or profit (£) 250 40 30 40 6. Use the table below to explain how a cactus is better adapted to living in hot, dry conditions [4marks] 5. Describe, in as much detail as you can, how the body responds to an increase in blood sugar concentration [3marks] 4. For this question write your answer on a separate sheet. The information in the table compares two farms. a) Use this information to work out the average daily human energy requirement in kilojoules (kJ) per day [2marks] Name Farm A Farm B Grows… Food for humans Food for animals which are food for us Energy value of food for humans made in 1 year 3285 million kJ No. of people whose energy needs are met by this food 720 365 million kJ 80 b) Explain why Farm A is much more efficient at meeting human food energy requirements [3marks] c) The human population has been increasing rapidly throughout this century. It is now about 6 billion and is still growing. What does the information in this question suggest about likely changes in the human diet which may need to occur during the coming century? Explain your answer [4marks] 3. Describe the process of transpiration in plants [3marks] Feature Thickness of waxy cuticle Total leaf surface area (cm 2) % of water storage tissue in stem No. of stomata per mm2 Time of day when stomata open Horizontal spread of roots (m) Geranium 5 1800 50 59 daylight 0.2 Cactus 15 150 85 13 night 5 7. Explain, as fully as you can, how agricultural activities are contributing to global warming [5marks] 8. Explain why after exercise, despite sitting down to rest, breathing rate and oxygen consumption remain high [4] Side 1 Mark Scheme 1.. a. 180 OR 179.9 b. 99.4 2. Molecules/ions (named example) [1], move across membrane/cell wall [1], against a concentration gradient [1], using a carrier protein [1], requires energy [1], obtained through respiration [1] 3.. a. Carries oxygen / forms oxyhaemoglobin [1], from lungs to cells/tissues [1] OR remove carbon dioxide [1] b. No nucleus [1] therefore more space for oxygen [1], large surface area [1] for efficient oxygen absorption [or similar] [1] 4. Comparison of cost (dialysis more expensive long term) [1], lifestyle restrictions e.g. diet with dialysis [1], independent after transplant [1], low availability of transplant [1], donated kidney may be rejected / immunosuppressant drugs required [1] 5. Glucose enters the blood from digestive system/intestine etc. [1], glucose is filtered [1], reabsorbed [1] by active transport [1] 6. Ideas that: sugar has dissolved in moisture (on surface of fruit) [1], this solution more concentrated than solution inside fruit [1], osmosis [1], movement of water out of fruit [1], through partially permeable membrane (of fruit cells) [1]. any four for 1 mark each; allow explanations in terms of concentrations of water molecules for full marks 7. Large surface area [1], thin walls [1] therefore short diffusion distance [1], highly vascularised / good blood supply etc. [1]; all to maximise efficiency of gas exchange [1] 8. Oxygen more concentrated in blood leaving the lungs [1], 2.5x more [1]; carbon dioxide more concentrated in blood entering lungs [1], 1.125x more [1] (allow converse arguments) Side 2 Mark Scheme 1.Advantages (max 3): reduced use of fossil fuels [1], less smoke produced [1], cheaper long-term [1], fertiliser produced [1], means of waste disposal [1], energy self sufficient [1]. Disadvantages (max 3): high initial cost [1], explosion risk [1], training required [1] 2.Increased sweat production [1], evaporation cools body [1]; vasodilation [1], heat loss (by radiation) [1] 3.Evaporation of water [1], from the leaves [1], through the stomata [1], causing a pull [1], so that water moves up the plant [1], = transpiration stream [1], water enters through roots [1] 4.. a. 12500 [2] 1 mark for correct working if answer incorrect b. Any three linked points from, less: links in food chain [1], energy lost at each link [1], energy lost in respiration [1], energy used to maintain body temp. [1], energy used in movement [1] c. People will eat more food from plants (or converse) [1]; land available for food production is limited [1], meat will become more expensive [1], more people = less land for food production [1], land more expensive [1], demand for food will rise [1], greater demand for factory farming [1], farmers will need to improve efficiency [1] 5.Insulin released [1], by pancreas [1]; glucose converted to glycogen [1] in liver [1] 6.Any 4 features + explanation from: thicker cuticle to retain water [1], smaller surface area to reduce water loss/heat absorption [1], fewer stomata and closed in day to reduce water loss [2], widespread roots for water absorption [1], more water storage tissue [1] 7.Any five from: methane produced [1] by cattle [1] and rice fields [1]; more greenhouse gases [1], increased CO2 from transport/machinery etc. [1], deforestation releases CO2 [1] due to burning / less photosynthesis [1]; heat radiated from Earth is absorbed/reflected [1] 8.Need to remove extra CO2 [1], remove heat / cool down [1], anaerobic respiration has occurred [1], lactic acid produced [1], oxygen required to breakdown lactic acid [1] into CO2 and water [1]