College and Career Terms
advertisement

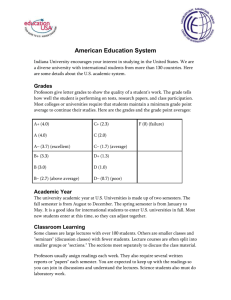
College and Career Terms Leadership and Career Development Miss Mann 2014 Technical School AKA: Vocational Education • 1-2 year school Example Programs: • Cosmetology • Automotive Technology • HV/AC • Culinary Arts • Photography • Technical School Programs • Technical Careers Benefits of Technical Schools • • • • • Skill-Specific Education Day/Night Classes Lower Tuition Costs Open Admissions Policy More one-on-one instruction and hands-on experience. Community College • 2 year school offering an Associate’s Degree Benefits: • Low Tuition • Live at Home • Enter workforce sooner Option 2: • Transfer to a University for a Bachelor’s Degree Example: 2 years at BC3, 2 years at PITT Bachelor/Baccalaureate (B.A. or B.S.) A degree awarded by a college or university to a person who has completed __4 years__ of undergraduate studies. *2 years of liberal studies courses *2 years of major courses Examples: • Education • Engineering • Marketing • Pre-med What are Liberal Studies? • • • • • • College Writing • Research Writing Humanities and Literature • Fine Art Elective Denotes a curriculum that imparts general knowledge and develops the student’s rational thought and intellectual capabilities. • • • • Math Science with Lab History and Geography Psychology Sociology Philosophy Technology Course Other Electives Majors Explored Social Sciences – Study of Human Society and Social Relationships • Psychology, Anthropology, Philosophy, Geography, Sociology, Criminology Humanities/Fine Arts – Imaginative, Aesthetic, or Intellectual Content • Art, Dance, Theater, Music, Visual Arts, Foreign Languages, Cultural courses, Poetry, Literature, Religion Natural Sciences – Deals with the physical world • Biology, Chemistry, Physics, Meteorology, Archaeology, Geology Art vs. Science Bachelor of Arts 1. General Education 2. Core Courses 3. Foreign language 4. Theoretical Research 5. Less Rigid Psychology, Sociology, History, Law Well-Rounded Graduate Bachelor of Science 1. General Education 2. Core Courses 3. Lab work w/ Accurate Results 4. Computer and Technology Oriented Math, Science, Computers, Medicine Highly Knowledgeable in Field of Study 4 year Universities Private • Often Costs More • Sometimes Affiliated w/ Religions • Funding from Alumni and Businesses Public • Often Costs Less for Instate students • Funded by Local and State Governments Bachelor’s Degree Graduation Requirements • 120 credits • Average 4 years Example Exams to become licensed or certified: • Teacher – 5 Praxis exams - Math, Reading, Writing, 2 content area exams • Engineer – FE exam (8 hours) and PE Exam (8 hours) • Nurse – National Council Licensure Exam (NCLEX-RN) • Architect – Architect Registration Exam – 7 exams Master’s Degree (M.A. or M.S.) An academic degree given after completion of about __2 years__ of study beyond the bachelor's degree. • • • • Masters of Business Administration, MBA Masters of Physical Therapy, MPA (changing to Doctorate) Physician’s Assistant, P.A. Masters in Education, M.Ed. Master’s Degree Requirements BEFORE: Take the entrance exam: GRE – Graduate Record Examination -analogy, antonym, reading comprehension, sentence completion, problem solving, and quantitative comparison. DURING: Complete 30-36 credits, or 1-2 years of work AFTER: Write a Thesis – a 30-50 page research paper *not always required Law Degree An academic degree given after completion of __3 years __ of study beyond the bachelor's degree. Steps to becoming a lawyer: 1. Obtain any 4 year Bachelor’s degree 2. Pass the L-SAT – Law School Admission Test 3. Complete the 3 year law school 4. Pass the Bar Exam to obtain licensure Minimum # of years to become a lawyer: 7 years Jurisdiction Doctorate • 4 years beyond Law School • Dissertation Required • Terminal Degree – highest level of law education possible 4 year Bachelor’s Degree 3 year Law Degree 4 year Jurisdiction Doctorate Degree 11 years total (sometimes completed in less time) Research Doctorate Degree • Granted upon completion of extensive academic work in a field of study. • It takes about __4__ years to complete the Ph.D ___Dissertation___ • An original work ranging in length, per discipline, from 50 to 800 pages • Published in Scholarly Journals or as a Book • Doctor of Philosophy, Ph.D. • Doctor of Education, Ed. D. • Doctor of Engineering, Eng. D. Research Doctorates What steps are necessary to earn a Ph.D.? 1. Attend a 4 year university (Bachelors) 2. Attend a 2 year graduate school (Masters) 3. Complete a 4 year doctoral program 4. Complete a Dissertation (_50-800_ pages) How many total years? About 10 years Professional Doctorate Degrees • Research doctorates with a focus on applied research for professional purposes. • Typically earned in _4_ years. • Most often do not require the Master’s Degree! • • • • • Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine, D.O. Doctor of Medicine, M.D. Doctor of Dental Medicine, D.M.D. Doctor of Dental Surgery, D.D.S. Doctor of Pharmacy, Pharm.D. Residency • In-depth training for physicians after medical school. • Focuses on specific branches such as: • Neurosurgery • Pediatrics • Cardiology • Additional __2-7 years__ of training after obtaining the M.D. ***You are a paid physician at this time but it is still training, like an internship is for business students. Attending Physician Requirements Steps to becoming a Physician/Surgeon: 1. Obtain a Bachelor’s degree in a Science Field 2. Pass the M-CAT – Medical College Admission Test 3. Complete the 4 year medical school 4. Complete the 2-7 year residency 5. Pass the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) to obtain licensure, also known as the “Boards” exam Minimum # of years to become an Attending: 10-17 years What to consider when choosing a career: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Passion for the Field Related Skills Nature of the Work Working Conditions Job Outlook Salary/Benefits Degrees Required Nature of the Work • • What will you be doing? What are your job responsibilities? Example: Nurse 1. Treat Patients 2. Educating patients and the public about various medical conditions 3. Record patients’ medical histories and symptoms 4. Help to perform diagnostic tests and analyze results 5. Operate medical machinery 6. Administer treatment and medications Example Working Conditions Registered Nurse • Well-lighted, comfortable health care facilities • Considerable time walking and standing • 24-hour care • May work nights, weekends, and holidays • May be on call—available to work on short notice • Must observe rigid, standardized guidelines to guard against disease and other dangers • May suffer emotional strain from observing patient suffering Job Outlook • Is there a good chance you will get a job right after graduating from school? • Is the field competitive? • Is there a high turnover rate? (people quit often) Example: Nurse • Job opportunities for RNs in all specialties are expected to be excellent. • Registered nurses are projected to create the second largest number of new jobs among all occupations. Salary (Earnings) / Benefits Salary • a fixed compensation periodically paid to a person for regular work or services • May be paid once a week, every other week, or once a month. Fringe Benefits • compensation that is not in the form of direct cash to a worker • Health insurance, vision and dental insurance, life and disability insurance, sick days, paid vacations, holidays, 401K, stocks, gas mileage, cell phone usage, company car, flexible work schedules, child care, tuition reimbursement, and bonuses WEB RESOURCES • Occupational Outlook Handbook www.bls.gov/oco BOOKS • Occupational Outlook Handbook • America’s Top Jobs • America’s Career Info Net www.acinet.org • Career Journal www.careerjournal.com • Career Builder www.careerbuilder.com • Careers and Colleges www.careersandcolleges.com • America’s Fasting Growing Jobs • 101 Careers • Outdoor Careers • America’s Federal Jobs • Encyclopedia of Careers • 200 Best Jobs for College Graduates Assignment: • Complete the OCO Assignment using the online Occupational Outlook Handbook • Due: