PROBLEM-SOLVING and DECISION
advertisement

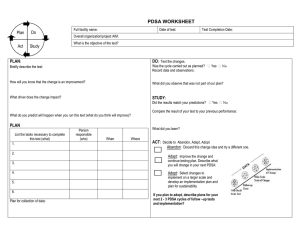
PROBLEM-SOLVING and DECISION-MAKING TOOLS Presented by: Karen Deering, Jon Ross, Mark Kesler THE PDSA CYCLE CONTINUOUS PROCESS IMPROVEMENT CYCLE THE SEVEN PHASES TO THE PROBLEM SOLVING METHOD 6 PRINCIPLES OF TQM Mark… Leadership and Customer Service Jon… Employee Involvement and Continuous Process Improvement Karen… Supplier Partnerships and Performance Measures LEADERSHIP As organizations are searching for new and/or better ways to be successful, more attention and accountability are being placed on those responsible for charting the course, navigating the changes, and keeping the organization afloat. The forces and factors impacting organizations in the new millennium are more interdependent, dramatic, fast paced, and unpredictable. The complexity of what decision makers in organizations must know and be able to do if organizations survive and thrive is being influenced by its leaders… Leadership…Why, What and How? Why…to motivate and inspire to a common goal or purpose. Providing direction, engagement, and encouragement What…ethical, realistic, consistent, responsible, courageous, visionary How…”know where to go”. Have a vision and create cohesion of the team Empower your employees to allow them to have the confidence, ability, and commitment to take the responsibility and ownership to improve the process and initiate the necessary steps to satisfy customer expectations – within well-defined boundaries in order to achieve organizational values and goals TEAM PROBLEM-SOLVING Is a process that uses a group of people in a team setting with the objective of resolving a problem or improving an existing process at any level of the organization Six Sigma Refers to the number of standard deviations found between the process central tendency and the closest specifications. Six Sigma Methodology Disciplined team problem solving approach using metrics and measurements to track loss…statistical tools to ensure best results “8D” 8 Disciplines in problem solving which follows a fact based approach that fits well with Decision – Making and PDSA models DO - Prepare for the 8D Process D1 - Establish the team D2 – Describe the problem D3 – Develop the Interim Containment Action and Verification D4 – Define and Verify Root Cause and Escape Point D5 – Choose and Verify Permanent Corrective Actions for Root Cause and Escape Point D6 – Implement and Validate Permanent Corrective Action D7 – Prevent Recurrence D8 – Recognize Team and Individual Contributions OTHER LEADERSHIP TOOLS Psychological Type Theory (MBTI) ORJI Left – hand Column Herman’s Brain Model Dialogue MODELS and THEORIES THE NORMATIVE DECISION MODEL THE SITUATION LEADERSHIP THEORY THE CONTINGENCY MODEL THE PATH GOAL THEORY POST-HEROIC LEADERSHIP TRANSACTIONAL AND TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP 7 HABITS OF HIGHLY EFFECTIVE PEOPLE CUSTOMER SERVICE WHY FOCUS ON CUSTOMERS? WHO ARE OUR CUSTOMERS? WHAT DO CUSTOMERS WANT? HOW DO WE BETTER UNDERSTAND OUR CUSTOMERS? HOW DO WE TRANSLATE CUSTOMER NEEDS INTO SPECIFICATIONS/STANDARDS? CUSTOMER SERVICE Why? Customers are the most important asset. They determine the “bottom line”. Who? External and Internal Customers What? Quality, durability, and price. Most critical or important… function or reliability How? Standards such as ISO 9000 HOW DO WE BETTER UNDERSTAND OUR CUSTOMER Comment cards Surveys Focus Groups Telephone Customer Visits Report Cards Internet Employee Feedback MEET SID THE CAB DRIVER Academic Assessment Employee participation and continuous improvement What is Academic Assessment? (Employee involvement) A continuous improvement tool Involving all employees and management Not a method to grade student work Students and employees grade course or program How do we assess academics (Continuous improvement cycle) Review mission and purpose statement Review program goals Identify assessment methods / intended outcomes Gather data – or make the measurement Analyze the information Take Action Review of mission and purpose / Program goals Courses and programs must be aligned with mission and purpose of the entire organization Changes should be made at this level if alignment is not found Measurement tools Timing of assessment – – – Pre enrollment data Process – (during course) data Post enrollment data Assessment tools – – Direct measures Indirect measures Direct Measurement Assessment Tools Pre/post test Course embedded tests Portfolios Capstone exam/project Standardized exams Performance assessment Primary trait analysis Professional certification Indirect Measurement Assessment Tools Focus groups Graduate survey / interview Employer/faculty survey Interpretation of measurements What did you measure? Are the results what you predicted? Can you use the data? What other factors may have influenced the data? Help in statistical measurement maybe needed Use the data to make changes Slight variation may require small changes Larger variations require new curriculum or further study Repeated large variations may require new focus in mission or purpose. Variations of assessment plans Plans and methods will vary between institutions Plans and methods will vary internal to the institution Plans will vary based on needs and resources How to be sure assessment successful Why is assessment being done? Management must support and provide resources for assessment Employees must understand the benefits and use the method Multiple sections of a course and multiple instructors will complicate method Communication is vital Success should be rewarded Review Assessment (PSDA) cycles are not just for manufacturing business Assessment methods can be used on small scale projects or large scale operations Find a process and follow it. Several cycles will be needed to have valid data Tools for Solving Problems and Making Decisions Supplier Partnerships and Performance Measures Supplier Partnerships Long Term Commitment Mutual Trust Goals and Objectives Expectations and Values Increased Efficiency Lower Costs Innovation Continuous Improvement Equal Quality Standards Cost, Quality, Overall Value Added Understand Philosophy Dependent & Independent Performance Measures Set Performance Expectations Benchmark Continuously Improve the Process Customer Satisfaction, On-time Delivery, Absenteeism, and Turnover Customer Focused East to Interpret Valued by the Employee Vision, Mission, Quality Policy Statements Baseline - Benchmark Record Findings Analyze Results Review and Update Making Decisions Solving Problems The PDSA Cycle PLAN carefully what is to be done. DO carry out the plan. STUDY the results. ACT on the results. Act Study Plan Do Continuous Process Improvement Cycle Phase 1: Identify the Opportunity Phase 7: Plan for the Future Phase 2: Analyze the Process Phase 6: Standardize the Solution Act Phase 3: Develop the Optimal Solution(s) Study Phase 5: Study the Results Plan Do Phase 4: Implement Using a systematic, orderly approach will yield the highest probability of success.