Quality Improvement
advertisement

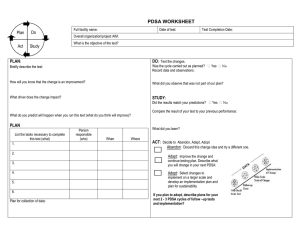
Quality Improvement Objectives To gain an understanding of what quality improvement is To present the Model for Improvement and PDSA cycle To introduce measurement in quality improvement To introduce flowcharts What is Quality Improvement? A formal approach to the analysis of performance and systematic efforts to improve it Different from Quality Assurance Quality Improvement versus Quality Assurance Quality Improvement Quality Assurance What can we do to improve? What went wrong? Proactive Reactive Avoids blame Often Punitive Fosters System change Tries to find who was at fault Focuses on the entire system Focuses on the specific incident What is quality? Definition of quality depends on stakeholders The client/customer (the patient) The provider/employer (health care providers) Management (hospital management) Payer (Ministry of Health) 6 Pillars of Quality Safety Timely Access Equitable Efficacy Efficient Patient Centered “Every system is perfectly designed to get the results it gets” How can you improve a system to achieve better results in the 6 pillars of quality? To improve a system… You need a good understanding of the system You need to understand where it is failing Identify what is wrong Make sure it is the step that needs fixing Then you can implement a change to the “system” What is a system? System = any assembly of procedures, resources and routines to carry out a specific activity System To understand a system and identify what is wrong with it Map it out! How do you map out a system? Use a flow chart/diagram Use different perspectives (a doctor’s perspective is different to a nurse’s or a porter’s to a patient’s perspective) Quality Improvement Models Model for Improvement = Three questions + PDSA cycle FADE = Focus, Analyze, Develop, Execute and Evaluate Six Sigma CQI = Continuous Quality Improvement TQI = Total Quality Management 7 step method Model for Improvement = Three questions + PDSA cycle The Three Questions The Model for Improvement begins with three fundamental questions 1. The Aim: What are we trying to accomplish? (How good do we want to get and by when?) 2. The Measures: How will we know a change is an improvement? 3. The Changes: What change can we make that will result in improvement? PDSA Cycle Plan a change Do the change Study the results Act on the results ACT STUDY PLAN DO PDSA Cycle Enables rapid testing and learning Allows for incremental testing Instead of spending weeks or months planning out a comprehensive change, then putting it into practice only to find that it is fundamentally flawed PDSA Cycle Can aid you in: Developing a change Testing a change Implementing a change What are we trying to accomplish? How will we know that a change is an improvement? What change can we make that will result in improvement? ACT STUDY PLAN DO MODEL FOR IMPROVEMENT Executing the Model for Improvement Let’s do an example The Problem Patient’s at emergency department are often in pain We want to change that how do we do that? Executing the Model for Improvement Form a team Three Questions: The Aim, The Measures, The changes Test changes - PDSA Cycle Implement changes that work Spread the changes to other areas The Aim The Measure The Change ACT STUDY PLAN DO You need a team Why? Need different perspectives It’s a lot of work Increased buy-in by staff Different levels of support (e.g. management) To come up with the right team you have to have an idea of what your aim is… The Aim A good aim: Is Specific Is Measurable Determines a time frame Addresses who the change is for, and what has to be achieved Is Sustainable The Aim Back to the Problem: Patients at emergency department are often in pain We decide to focus on emergency department patients with fractures The Aim All emergency department patients with fractures We will provide analgesia to 100% of our patients with a suspected fracture within 15 minutes of arrival to the emergency department by the end of December 2014. Choose your team Consider the system that relates to the aim i.e. what processes will be affected by the improvement efforts Involve members familiar with all different parts of processes Back to our example All emergency department patients with fractures What processes will be affected? Nursing/Triage Pharmacy Stocking Doctors Registration ED chief/director/ manager We will provide analgesia to 100% of our patients with a suspected fracture within 15 minutes of arrival to the emergency department by the end of December 2014. Choose your team Effective teams require three kinds of expertise System leadership Clinical -Technical expertise Day to day leadership - Project leader Your team Team leader: Medical director of the emergency department Technical expert: Hospital Quality Management member Day to day leader (project leader): an emergency doctor or nurse Additional team members: pharmacist, person responsible for stocking, charge nurse, registration clerk Revisit the Aim Once you have chosen your team, review and modify the aim based on their input Measurement How will we know that a change is an improvement? Measurement Measurement is critical for testing and implementing changes The Aim The Measure Different from measurement for research The Change ACT STUDY PLAN DO Measurement Measurement for Research Measurement for Improvement Purpose To discover new knowledge To bring new knowledge into daily practice Tests One large blind test Many sequential, observable tests Biases Control for as many biases as possible Stabilize the biases from test to test Data Gather as much data as possible, just in case Gather just enough data to learn and complete another cycle Duration Can take a long time Short duration Measurement 3 types of measures for quality improvement Outcome measures Process measures Balancing measures (+/- Structure Measures) Outcome Measure = Where are we ultimately trying to go Are your changes actually leading to improvement Process Measures = Are we doing the right things to get there? To affect an outcome you have to improve your processes Are the parts/steps in the system performing as planned Balancing Measures Tells you if changes designed to improve one part of the system are causing new problems in other parts of the system Structure Measures “Physical” measures Human resources, equipment, facilities Often included in Process Measures Measurement For any improvement project you want to identify a family of measures Measurement Aim = Decrease sepsis mortality by 20% by January 2011 Outcome Measure Process Measure Balancing Measures Measurement Aim = Decrease sepsis mortality by 20% by January 2011 Outcome Measure Process Measure Balancing Measures Mortality rates -Time it takes to register and triage -% of patients being appropriately triaged -Time from triage to initiation of resuscitation -% of patients getting properly fluid resuscitated -% of patients getting antibiotics -Availability of medications and supplies -Time to antibiotics -Delay to getting to hospital Costs Neglect of other patients (e.g. increase in mortality for another patient population) (e.g. increase in time to be seen for other patients) The Change What change can we make that will lead to improvement? Developing Changes Depends what you are trying to change The Aim The Measure The Change ACT STUDY PLAN DO Basic techniques Critical Thinking Benchmarking Barcodes for medications Creative Thinking Compare to best practice Using Technology Flow Chart/Diagram Become a patient for a day Using Change Concepts Basic techniques Critical Thinking Benchmarking Barcodes for medications Creative Thinking Compare to best practice Using Technology Flow Chart/Diagram Become a patient for a day Using Change Concepts Critical Thinking Use a Flow Chart/Diagram A flow chart allows to “visualize” the system you are trying to change Allows ALL to see the system the same way Flow Chart/Diagram It helps to clarify complex processes It identifies steps that do not add value to the internal or external customer, including: Delays Needless storage and transportation Unnecessary work, duplication, and added expense Breakdowns in communication Flow Chart/Diagram It helps team members gain a shared understanding of the process and use this knowledge to collect data, identify problems, focus discussions, and identify resources. It serves as a basis for designing new processes. Flow Chart/Diagram High-level flowchart, showing six to 12 steps, gives a panoramic view of a process Detailed flowchart is a close-up view of the process, typically showing dozens of steps. These flowcharts make it easy to identify rework loops and complexity in a process. Example: High Level Flow Chart From: http://www.hciproject.org/improvement_tools/improvement_methods/analytical_tools/flowchart Example: Detailed Flow Chart From: http://www.hciproject.org/improvement_tools/improvement_methods/analytical_tools/flowchart Change Concepts Eliminate Waste - an activity or resource that does not add value Improve Work Flow Optimize Inventory - is your work being held up because items are not properly organized or available Change Concepts Change the Work Environment (does the work culture enhance or impede change) Manage Time Focus on Variation - what aspect of the system vary and make your outcomes unpredictable Focus on Error Proofing (checklist) Testing Changes: PDSA Cycle All improvement will require change, but not all change will result in improvement. Testing Changes Why test changes (even if they are already proven elsewhere)? To learn how to adapt the change to the particular conditions in your setting To evaluate the costs and side effects To minimize resistance when implementing the change in the organization Increase your belief that the change will result in improvement PDSA Cycle Plan Objectives Questions and predictions Plan to carry out the cycle (who, what, where, when) Plan for data collection The Aim The Measure The Change ACT STUDY PLAN DO PDSA Cycle Do Carry out the plan Document problems and unexpected results Begin Analysis The Aim The Measure The Change ACT STUDY PLAN DO PDSA Cycle Study Complete analysis of the data Compare data to prediction Summarize what was learned The Aim The Measure The Change ACT STUDY PLAN DO PDSA Cycle Act What changes are to be made Next cycle? The Aim The Measure The Change ACT STUDY PLAN DO Testing Changes Much can be learnt from a failed test ACT STUDY ACT PLAN DO PLAN PDSA STUDY ACT STUDY DO PDSA PLAN PDSA DO PDSA PDSA What happens when you identify what works? Are you done? How easily is change adopted? Process of “Normalization” People have a tendency to fall into old habits People have a tendency to resist change People may feel threatened by a change Executing the Model for Improvement Form a team Three Questions: The Aim, The Measures, The changes Test changes - PDSA Cycle Implement changes that work Spread the changes The Aim The Measure The Change ACT STUDY PLAN DO Implementation Usually comes after a series of successful tests It requires that staff and leaders build the change into formal plans, job definitions, training, and explicit reviews The change does not depend on the individuals doing the work, but on the way the work is organized - as part of the system. Implementing Change “Hard-wire” the change into the system Hardwire Change Market your change Train everyone involved Make changes to job descriptions, policies, procedures, forms Addressing supply and equipment issues Assigning day-to-day ownership for the maintenance of the new process Have senior leaders remove any barriers Social System Social System - understand the relationship among the people who will be adopting the new ideas Remember there is an emotional component to change Stress of learning and executing something new Initial disruption to workflow Maybe they feel their job/position is threatened Social System Those who are supportive Those who are not supportive Enlist on your side Don’t try to change their attitude Listen to what concerns them, identify barriers Those who don’t really care, and will follow when others do Implementation PDSA in Pilot PDSA in Phase Implementation Phase Support Requirements Low High Tolerance for failure High Low Number affected by a test Low High Resistance Low Potentially high Time for each cycle Short Longer Summary In this modules we have presented an introduction to: Quality Improvement The Model of Improvement 3 questions (What is your aim, measures, change) and PDSA cycle Types of Measures Change and Implementation