Review Cell Organelle - Catawba County Schools
advertisement

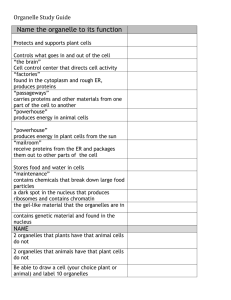
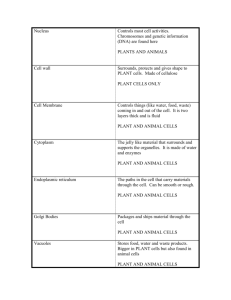
Cell Organelle Review Any organism composed of one or more cells, each of which contains a clearly defined nucleus enclosed by a membrane, along with organelles This is the command center and acts like the brain of the cell. It helps control eating, movement, and reproduction. If it happens in a cell, chances are the organelle knows about it. It is not always in the center of the cell. It will be a big dark spot somewhere in the middle of all of the cytoplasm (cytosol). Inside this organelle, you will find the Nucleolus These are the protein assemblers of a eukaryotic cell. They are typically composed of two subunits: a large subunit and a small subunit. These two units join together to produce proteins in a process called translation and are located along the Rough ER These organelles are the cell's power producers. They convert energy into forms that are usable by the cell. They are the sites of cellular respiration which ultimately generates fuel (ATP) for the cell's activities. ATP is mostly sugar and phosphates. The number of these organelles in a cell can range from a few to several thousand, depending on the type of cell. These are little digestion machines, they go to work when the cell absorbs or eats some food. Once the material is inside the cell, this organelle will attach and release their enzymes. The enzymes break down complex molecules that can include complex sugars and proteins These organelles are water-filled storage spaces found in cells. They are found in both animal and plant cells (but they are more common in plant cells they are also bigger in plant cells). They store food, collect waste products, and can help with cell shape and buoyancy. This part of a cell is located outside the cell membrane of a plant cell. The main purpose of it is to make the cell rigid and give the strength to protect itself against mechanical stress. It is found in cells of plant cell but not in animal cells. This type of cell is a very simple, single celled organisms. These cells have no nucleus, and very few organelles. They've got a loop of DNA in their center, along with some ribosomes floating around. This organelle produces ribosomes, which move out of the nucleus and take positions on the rough endoplasmic reticulum where they are critical in protein synthesis. These are the packaging for our genetic material, or DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and are located in the nucleus. DNA carries a specific code that gives instructions to our body on how to grow, develop and function. The instructions are organized into units called genes. This organelle, along with Ribosomes, is involved with the production of proteins. It is the transport system proteins use to travel through the cell. This organelle is like a shipping department of the factory we talked about. The proteins that are made by the ribosomes travel through the ER organelles and then are sorted and packaged in this orgnelle that will later send the proteins out of the cell This is the organelle of a plant that contains a pigment called chlorophyll. This chlorophyll absorbs the energy from sunlight and utilize this energy to make food from carbon dioxide and water. This is called photosynthesis. This is a thin semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell, enclosing its contents. Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell, while keeping other substances out.