Ratio Definition
advertisement

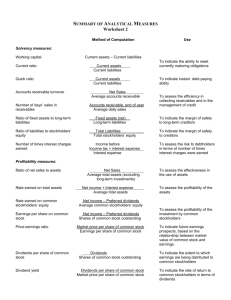
Cornerstones of Managerial Accounting 2e Chapter Sixteen Financial Statement Analysis Mowen/Hansen Copyright © 2008 Thomson South-Western, a part of the Thomson Corporation. Thomson, the Star logo, and South-Western are trademarks used herein under license. 1 Common-Size Analysis • • • Compares two financial statement periods or items within one financial statement period Line items expressed as percentages ◦ Eliminates the effects of size Two major forms: ◦ Horizontal analysis ∙ ∙ ◦ Expresses a line item as a percentage of some priorperiod amount Allows the trend over time to be assessed Vertical analysis ∙ ∙ ∙ Concerned with relationships among items within a particular time period Line items on income statement are expressed as a percentage of net sales Line items on the balance sheet are expressed as a percentage of total assets 2 Ratio Analysis • Fractions or percentages computed by dividing one account or line-item amount by another Help explain the financial well-being of a company when used as a comparison Common comparison standards: • • ◦ ◦ Company historical amounts Industry averages ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ Key Business Ratios Standard and Poor’s Industry Survey Annual Statement Studies The Almanac of Business and Industrial Financial Ratios Dow Jones-Irwin Business and Investment Almanac 3 Classification of Ratios • Liquidity Ratios ◦ • Measure the ability of a company to meet its current obligations Leverage Ratios ◦ ◦ • Measure the ability of a company to meets its long- and short-term obligations Provide a measure of the degree of protection provided to a company’s creditors Profitability Ratios ◦ ◦ Measure the earning ability of a company Allow investors, creditors, and managers to evaluate the extent to which invested funds are being used efficiently 4 Liquidity Ratios • Current Ratio ◦ ◦ ◦ Current Assets ÷ Current Liabilities Measure of the ability of a company to pay its short-term liabilities using short-term assets Rule of thumb ◦ • 2.0 ratio is needed to provide good debt-paying ability Quick or Acid-Test Ratios ◦ ◦ Compares only the most liquid assets with current liabilities Usual standard is ratio of 1.0 5 Liquidity Ratios • Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio ◦ ◦ • Measures how long it takes the company to turn its receivables into cash Net Sales ÷ Average Accounts Receivable Inventory Turnover Ratio ◦ ◦ Cost of Goods Sold ÷ Average Inventory Measures how many times the average inventory turns over (sold) during the year 6 Ratio Definition Current ratio = Current assets ÷ Current liabilities 7 Ratio Definition Quick ratio = (Cash + Marketable Securities + Receivables) ÷ Current liabilities 8 Ratio Definition Average Accounts Receivable = (Beginning Receivables + Ending Receivables) ÷ 2 9 Ratio Definition Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio = Net Sales ÷ Average Accounts Receivable 10 Ratio Definition Accounts Receivable in Days = Days in a year ÷ Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio 11 Ratio Definition Average Inventory = (Beginning Inventory + Ending Inventory) ÷ 2 12 Ratio Definition Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of Goods Sold ÷ Average Inventory 13 Ratio Definition Inventory Turnover in Days = Days in a year ÷ Inventory Turnover Ratio 14 Leverage Ratios • • • Times-Interest-Earned Ratio ◦ (Income before taxes + Interest Expense) ÷ Interest Expense ◦ Uses the income statement to assess a company’s ability to service its debt Debt Ratio ◦ Measures the degree of protection afforded creditors in case of insolvency ◦ Reflects the percentage of assets financed by creditors ◦ Total Liabilities ÷ Total Assets Debt to Equity Ratio ◦ Total Liabilities ÷ Total Stockholders’ Equity ◦ Measures the amount of debt that is financed by 15 stockholders Ratio Definition Times-Interest-Earned Ratio = (Income Before Taxes + Interest Expense) ÷ Interest Expense 16 Ratio Definition Debt Ratio = Total liabilities ÷ Total assets 17 Ratio Definition Debt to Equity Ratio = Total liabilities ÷ Total stockholders’ equity 18 Profitability Ratios • • Return on Sales ◦ Net Income ÷ Sales ◦ Measures the efficiency of a firm ◦ Tells what percentage of each sales dollar is earned as net income Return on Total Assets ◦ Operating Income After Taxes ÷ Average Total Assets ◦ Measures how efficiently total assets are used to generate profits 19 Profitability Ratios • • Return on Common Stockholders’ Equity ◦ (Net Income – Preferred Dividends) ÷ Average Common Stockholders’ Equity ◦ Measures the return the company generated on the common shareholders’ investment Earnings Per Share ◦ (Net Income – Preferred Dividends) ÷ Average Common Shares ◦ Measures the profit earned by the company for each share of common stock outstanding 20 Profitability Ratios • • • Price-Earnings Ratio ◦ Market Price Per Share ÷ Earnings Per Share ◦ Measures the investors’ perceptions of a company’s future growth prospects Dividend Yield ◦ Dividends Per Common Share ÷ Market Price Per Share ◦ Measures a reasonable approximation of the total return accruing to an investor Payout Ratio ◦ Common Dividends ÷ (Net Income – Preferred Dividends) ◦ Tells an investor the proportion of earnings that a company pays in dividends 21 Ratio Definition Return on Sales = Net Income ÷ Sales 22 Ratio Definition Average Total Assets = (Beginning Total Assets + Ending Total Assets) ÷ 2 23 Ratio Definition Return on Total Assets = [Net Income + Interest Expense (1 – Tax Rate)] ÷ Average Total Assets 24 Ratio Definition Average Common Stockholders’ Equity = (Beginning Common Stockholders’ Equity + Ending Common Stockholders’ Equity) ÷2 25 Ratio Definition Return on Stockholders’ Equity = (Net Income – Preferred Dividends) ÷ Average Common Stockholders’ Equity 26 Ratio Definition Return on Stockholders’ Equity = (Net Income – Preferred Dividends) ÷ Average Common Stockholders’ Equity 27 Ratio Definition Preferred Dividends = Preferred Stock × Dividend Rate 28 Ratio Definition Number of Common Shares = Common Stock ÷ Par Value per share 29 Ratio Definition Earnings Per Share = (Net Income – Preferred Dividends) ÷ Number of Common Shares 30 Ratio Definition Price-Earnings Ratio = Price per share ÷ Earnings Per Share 31 Ratio Definition Dividends Per Share = Dividends to Common Shareholders ÷ Number of Common Shares 32 Ratio Definition Dividends Yield = Dividends per share ÷ Market Price per share 33 Ratio Definition Dividend Payout Ratio = Common Dividends ÷ (Net Income – Preferred Dividends) 34 Just-in-Time Manufacturing Environment • • Goals: ◦ Reduce inventories ◦ Increase quality If goals are being met: ◦ Inventory turnover ratio should increase dramatically ◦ Current ratio will drop ◦ Quality costs as a percentage of sales should decrease 35