Experiment 5: Iodimetric Titration of Vitamin C 11
advertisement

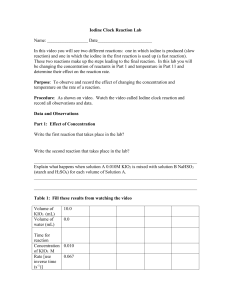
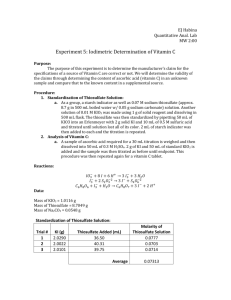
David Millard Naomi Bryner (partner) Experiment 5: Iodimetric Titation of Vitamin C11 Introduction: Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, in a supplemental source will be tested via titration. The amount of ascorbic acid will be compared to the manufacture’s label to determine if the amount is consistent. Reactions: IO3− + 8I + 6H + ↔ 3I3− + 3H2 O 2− − I3− + 2S2 O2− 3 ↔ 3I + S4 O6 C6 H8 O6 + I3− + H2 O ↔ C6 H8 O7 + 3I − + 2H + Procedure: Standardizing Thiosulfate Solution As a group, prepare a starch indicator solution. o Make paste, 5.0g of soluble starch in 50mL of water. o Pour paste into 500mL of boiling water, boil until clear. Prepare approximately 0.07M Na2S2O3 by dissolving about 8.70g of Na2S2O3∙H2O in 500mL of freshly boiled water containing 0.05g of Na2CO3. Store solution in a tightly amber bottle. Prepare approximately 0.01M KIO3 by weighing about 1.0g of solid reagent and dissolving it in a 500mL volumetric flask. Pipet 50.00mL of KIO3 solution into an erlenmeyer flask. Add 2.0g of solid KI and 10mL of 1M H2SO4. Immediately titrate with thiosulfate until the solution has lost almost all of its color (pale yellow) and then add 5mL of starch indicator and complete the titration to a clear endpoint. Repeat until you have three good trials. Analysis of Vitamin C Weigh out an appropriate amount of ascorbic acid for an approximate 30mL titration, and dissolve it in 50mL of 0.3M H2SO4 with stirring. Add 2.0g of solid KI and add 50mL of standard KIO3. Titrate with standard thiosulfate as above, adding 2.0mL of starch indicator just before the end point. Repeat procedure using two weighed vitamin C tablets. Data: Standardizing Thiosulfate KI (g) 2.0060 2.0047 2.0192 2.0010 Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3 Average Thiosulfate Molarity Thiosulfate (mL) 35.02 35.01 35.09 35.04 0.0562 Titrating Ascorbic Acid (used 150mL KIO3) KI (g) Thiosulfate (mL) Ascorbic Acid (g) Weight percent of ascorbic acid Sample 1 2.0056 30.61 0.5312 18.08 Sample 2 2.0308 30.40 0.5212 18.62 Sample 3 2.0018 31.28 0.5144 18.02 Average 2.0123 30.76 0.5223 18.24 KI (g) Thiosulfate (mL) Tablet mass (g) 2.0018 2.0018 2.0018 13.89 14.47 14.18 0.5057 0.5039 0.5048 Titrating Vitamin C (used 100mL KIO3) Sample 1 Sample 2 Average Weight percent of tablet 35.36 34.92 35.14 Calculations: Finding molarity of KIO3: g KIO3 ∗ mol KIO3 mol KIO3 = = Molarity KIO3 g KIO3 L Example: 1.0029g ∗ 1mol KIO3 0.004686mol KIO3 = = 0.0094M KIO3 214.00277g KIO3 0.50L Finding molarity of Thiosulfate: mol KIO3 mol I3− mol S2 O2− mol S2 O2− 3 3 g KIO3 ∗ ∗ ∗ = = Molarity S2 O2− 3 − g KIO3 mol KIO3 mol I3 L Example: 1.0029g KIO3 ∗ 1mol KIO3 3mol I3− 2mol S2 O2− 0.0281mol S2 O2− 3 3 ∗ ∗ = − 214.00277g KIO3 1mol KIO3 1mol I3 0.50L = 0.0562M S2 O2− 3 Finding grams of Ascorbic Acid: mol I3− mol AA g AA M Na2 S2 O3 ∗ L Na2 S2 O3 ∗ ∗ ∗ = g Ascorbic Acid mol I3− mol AA mol S2 O2− 3 Example: 3mol I3− 1mol AA 176.12g AA 0.0562M Na2 S2 O3 ∗ 0.03504L Na2 S2 O3 ∗ 2− ∗ 1mol I − ∗ 1mol AA 2mol S2 O3 3 = 0.5204g Ascorbic Acid Finding weight percent of ascorbic Acid Excess I3-: mol S2 O2− mol I3− 3 M Na2 S2 O3 ∗ L Na2 S2 O3 = mol Na2 S2 O3 ∗ ∗ = I3− excuess moles 2− mol Na2 S2 O3 mol S2 O3 Example: 0.0562M Na2 S2 O3 ∗ 0.03061L Na2 S2 O3 ∗ 1mol S2 O2− 1mol I3− 3 ∗ 1mol Na2 S2 O3 2mol S2 O2− 3 = 0.000860I3− excess moles Moles of I3-: mol I3− M KIO3 ∗ LKIO3 = mol KIO3 ∗ = mol I3− mol KIO3 Example: 3mol I3− 0.0094M KIO3 ∗ 0.050LKIO3 = 0.00047mol KIO3 ∗ = 0.00141mol I3− 1mol KIO3 Moles of I3-: mol I3− − excess mol I3− = mol I3− Example: 0.00141mol I3− − 0.000860mol I3− = 0.00055mol I3− Finding Mass of Ascorbic Acid: mol I3− ∗ mol AA g AA = g AA mol I3− mol AA Example: 0.00055mol I3− ∗ 1mol AA 176.12g AA ∗ = 0.0969g AA 1mol I3− 1mol AA Finding weight percent of Ascorbic Acid: g AA in tablet ∗ 100 = wt% g tablet Example: 0.0969g ∗ 100 = 18.08% 0.5223g Finding weight percent from tablet: g Ascorbic Acid ∗ 100 = wt% Ascorbic Acid g tablet Example: 0.500g AA ∗ 100 = 80.33% 0.6224g Finding standard deviation: 2 √∑(xi − xavg ) = Standard Deviation n−1 Conclusion: The overall objective of this lab was to determine the amount of ascorbic acid in a tablet and compare it to the manufacturers claim. We found the amount in the vitamin C tablet to be on average 35.14% (±0.3137) compared to the claim of the pills containing 80.33%. This is a significant difference. However, there were many errors in this lab. First, the amount of H2SO4 was not consistent with the molarity. Also, the formula used to determine the molarity of thiosulfate was later determined to be incorrect, but the incorrect number was used to carry out the remainder of the lab. This error accounted for a larger amount of ascorbic acid to be used in the second titration. The undissolved solids from the tables could have been any kind of impurity from the manufacture such as dirt or some kind of additive to help with the taste or the digestion of the pill.