Postpartum Haemorrhage
advertisement

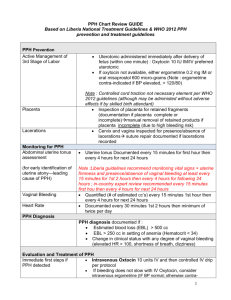
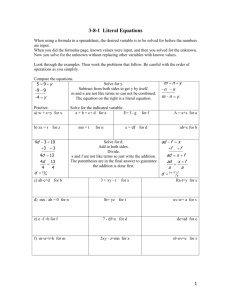
Postpartum Haemorrhage Definitions • Primary PPH – blood loss of 500ml or more within 24hours of delivery. • Secondary PPH – significant blood loss between 24 hours and 6 weeks after birth. Why do we care? Major obstetric haemorrhage – more than 1000ml Very rapidly lead to maternal death • 3rd highest cause of direct maternal death in the UK and Ireland (2003-2005) • 58% of these cases care was “seriously substandard” • Major cause of severe maternal morbidity in “near-miss audits” Risk Factors Most cases have no risk factors • • • • • • • • Previous PPH Antepartum haemorrhage Grand multiparity Multiple pregnancy Polyhydramnios Fibroids Placenta praevia Prolonged labour (&oxytocin) Prevention • Be aware of risk factors – may present antenatally or intrapartum • Treat anaemia antenatally • Active management of the 3rd stage • Prophylactic oxytocics reduce the risk of PPH by 60% (oxytocin or oxytocin & ergometrine) • 5IU IM for vaginal delivery • 5IU IV for LSCS • Consider oxytocin infusions 4 T’s Tone Tissue Thrombin Trauma Causes Tone Previous PPH Prolonged labour Age > 40 years Big baby Multiple pregnancy Placenta praevia Obesity Asian ethnicity Tissue Retained placenta/ membrane/clot Thrombin Abruption PET Pyrexia Intrauterine death Amniotic fluid embolism DIC Trauma Caesarean section (emergency > elective) Perineal trauma Operative delivery Vaginal and cervical tears Uterine rupture • Blood loss is commonly underestimated • Loss may be well-tolerated • Beware the “trickle” and the “moderate lochia” • Minor PPH can easily progress to major PPH. Management • Has the placenta been delivered and is it complete? • Is the uterus well-contracted? • Is the bleeding due to trauma? Resuscitation A & B – 10 -15l/min O2 by facemask C2 14 gauge cannulae blood for Hb, U&E, LFTs, clotting crossmatch 4 units 2 litres of crystalloid rapidly transfuse as soon as possible – consider O – ve blood if any delays. Uterine Contraction-First Line Drugs • • • • Oxytocin 5IU Oxtocin infusion – 40IU in 500mls Ergometrine 0.5mg Carboprost (Haemabate©) 0.25mg IM every 15 minutes x 8 doses • Misoprostol 600 mcg sublingually Uterine Contraction – non-pharm • • • • • • • • • Empty uterus Foley catheter Rub up a contraction Bimanual compression Balloon tamponade Brace suture Uterine artery ligation Internal iliac artery ligation Interventional radiology • Hysterectomy – before it’s too late B-Lynch Suture Balloon Tamponade Haematological Management • • • • DIC Transfuse without delay Involve haematology service at an early stage Correct coagulopathy Liase with consultant haematologist re use of recombinant Factor V11 (Novoseven©) and Fibrinogen. • Traumatic for patient, family and staff. • Debriefing for patient and staff. • Case analysed to ensure care was of good standard and any substandard care can be improved. Secondary PPH • • • • • Infection Retained placenta Trophoblastic disease Antibiotics Evacuation of retained products if bleeding persistent or significant amount of tissue retained.