Oxytocin - Pitocin
advertisement

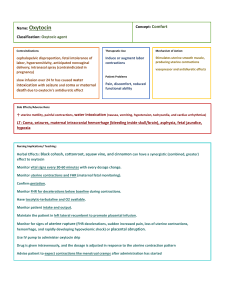
OXYTOCIN – PITOCIN OXYTOCIN – Stimulates uterine smooth muscle contractions. Increases excitability of muscle cells. Increases strength of muscle contractions. Supports the propagation of the contraction. HALF LIFE – Circulatory half-life is 3 – 5 minutes. Takes approximately 40 minutes to reach a steady-state plasma concentration. USES: Induction & Augmentation. Fourth stage to stimulate uterine contractions & control uterine atony. Not thought to cross placenta barrier because of molecular weight and oxytocinase in placenta. ROUTE/DOSAGE IM/IV Start induction at 0.5 – 1 mu/min until good contractions are achieved. MAXIMUM recommended dose usually = 10 mu/min (120ml/hr) Decrease oxytocin by similar increments when labor is well established & dilation has progressed to 5 – 6 cm. CONTRAINDICATIONS – same as for induction MATERNAL SIDE EFFECTS 1. CARDIOVASCULAR RESPONSEInitial decrease in BP, with prolonged administration 30% increase over baseline B/P may occur. Cardiac output and stroke volume increased. In doses > 20 mu/min, antidiuretic effect results in a decrease free water exchange in kidney & decrease UO. 2. HYPERSTIMULATION results in HYPERCONTRACTILITY, which may cause: a. abruption placenta b. impaired uterine blood flow c. rapid labor & birth – cervical, vaginal, or perineal lacerations, uterine atony. Fetal trauma. d. uterine rupture. e. H2O intoxication (n/ v, hypotension, tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmias) if given in an electrolyte – free solution or at a rate over 20 mu/ml (120ml/hr). f. hypotension with rapid IV bolus administered postpartially. FETAL/NEONATAL EFFECTS 1. Maternal hypercontractility causes a decreased oxygen supply to the fetus, which is reflected by irregularities and/or decreased FHR. 2. Hyperbilirubinemia 3. Trauma for rapid birth. AUGMENTATION – Prepare and administer as for induction. Flow rate is gradually increased at no less than every 30 minutes to a maximum of 10mu/min. FOURTH STAGE USE: One dose of 10 units Pitocin IM or added to IV fluids for continuous infusion. N/ADN/Spring 09/RNSG Oxytocin Pitocin Page 42 Revised 11/08