File
advertisement

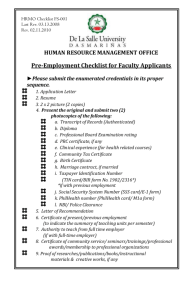
LCVP LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAM SECTION A – AUDIO-VISUAL Compulsory and worth 30 marks Answer all 8 questions on: What you see? What you hear? Application of LCVP Knowledge, learning and skills 25 minutes AUDIO-VISUAL TIPS Read the eight questions carefully before the DVD commences. Use the BUG* technique Ensure to take notes on the rough work sheet on the inside cover of the answer booklet. Questions 7 & 8 are worth 12 marks. They require detail. Ensure to elaborate and always give examples if appropriate. *BUG Technique = Box Underline Glance Back SECTION B – CASE STUDY Compulsory and worth 30 marks Answer all 3 questions Questions may be sub-divided into parts Study your pre-prepared answers in your copy and look at last weeks handout CASE STUDY ANALYSIS TIPS Use the case study to revise the entire course by posing relevant questions. The case study mind map can be a vehicle to revise all the specific learning outcomes. WRITE EVERYTHING YOU KNOW ABOUT: Safety, Health and Welfare at work Act The Employment Equality Act The protection of Young Persons Act Planning Evaluating Skills CASE STUDY – TIPS FOR EXAM Read the questions carefully. Stop and think. Use the BUG technique. Ensure detail and always elaborate. 25 minutes SECTION C 23 minutes per question Answer 4 out of 6 questions that cover the entire syllabus. Questions may be sub-divided into parts. Choose questions that may deliver the most marks for you. Ensure you can answer all parts of the question. Take account of mark allocations for questions and parts of questions and plan the use of time accordingly. Always state your answer, explain your answer with at least two different points and give an example supporting your answer. Do not leave blank spaces or give one word answers. Use BUG technique. SECTION C Use your “Comprehensive Notes for the LCVP exam” PowerPoint – this has the notes for all 8 units. Refer to your “General Questions Topic by Topic” Word Document – this goes through each single topic from 1996-2013 and it outlines the types of questions that come up in each area. BUG TECHNIQUE BOX, UNDERLINE & GLANCE BACK Explain three objectives that the class might have for organising the visit. This is a prompt to students that they needed to explain three objectives for organising a visit rather than misinterpreting the question and focusing solely on visiting the organisation. Keep Glancing Back at the question to ensure that you’re answering it correctly COMPARE & CONTRAST QUESTIONS Differences Differences Similarities Compare - what is common to both and what is different to both Contrast - distinguish what is unique to each INTEGRAL THEMES IN LCVP Planning Evaluation Skills My Own Place Legislation Activities PLANNING Ensure to cover all areas of Planning: Define planning, Why Plan? The advantages and challenges of a plan. Can you draft a Business plan? What are the main headings? Can you draft an Enterprise/ Action Plan? EVALUATING Why evaluate? The advantages and challenges of evaluating. How to evaluate? Advantages and disadvantages of methods. When evaluating use the DAR approach. Describe: Reflect on the experience, What happened? What did you do? Did you meet your objectives? Assess: Think back on the experience, what went well?, what did not work? Was it useful? What subjects were useful? What about teamwork? Recommend: What would you recommend for future activities? Are there any follow on activities. SKILLS Be able to articulate the following: Communication Skills Team Work Skills Organisation Skills Research Skills Administrative Skills Presentation Skills Information Technology Skills Skills of Analysis MY OWN PLACE Be aware of employment, social services, job creation agencies, transport , financial institutions, industrial relations, economic activities, tourism, Business Enterprises, voluntary/ community enterprises and issues in your local area. LEGISLATION 1. 2. 3. Safety, Health and Welfare at work Act The Employment Equality Act The protection of Young Persons Act 1. SAFETY, HEALTH AND WELFARE AT WORK ACT 2005 The Safety, Health and Welfare at Work Act 2005 sets out rights and duties for both employers and employees. Employees have the right to be safe at work and employers must provide a safe place of work and safe systems and equipment in the place of work. Did you know that in 2012 forty seven people were killed in Irish workplaces? Health and Safety at Work is everyone’s responsibility. The Health and Safety Authority is the state body which has overall responsibility for the administration and enforcement of health and safety at work. The authority monitors compliance with health and safety legislation in the workplace and can offer information and advice to employers, employees and the self-employed in all aspects of workplace health and safety. The Health and Safety Authority is not just a regulatory enforcement agency but also encourages efforts to improve occupational safety and health. 1. SAFETY, HEALTH AND WELFARE AT WORK ACT 2005 Responsibilities of Employees Co-operate with an employer or other people to ensure that health and safety law is implemented Don’t engage in improper conduct that will endanger themselves or anyone else Attend health and safety training and correctly use any equipment at work Use protective clothing and equipment provided Report any dangerous practices or situations that they are aware of to an appropriate person Don’t interfere with or misuse any safety equipment at the workplace 1. SAFETY, HEALTH AND WELFARE AT WORK ACT 2005 Responsibilities of Employers Provide and maintain a workplace that is safe and do likewise for all machinery, equipment, etc. Manage work activities to ensure the safety, health and welfare of employees Ensure that risks are assessed and a safety statement is prepared and updated Provide and maintain decent welfare facilities for employees Prepare and update procedures to deal with an emergency situation Provide training and information to workers in a format and language that is appropriate Report serious accidents to the Health and Safety Authority7 2. EMPLOYMENT EQUALITY ACT 1998 The Employment Equality Act 1998 provides for the promotion of equality between employed persons and it outlaws discrimination in relation to employment on nine grounds: Gender Marital status Family status Sexual orientation Religious belief Age Disability Race Membership of the traveller community 2. EMPLOYMENT EQUALITY ACT 1998 The Act describes discrimination as treating one person in a less favourable way than another person in all aspects of employment such as pay, training, promotion, etc. The Act also provides for equal pay for equal work. The Equality Authority was established under the Employment Equality Act and the Authority has the statutory remit to work towards the elimination of discrimination and the promotion of equal opportunities in employment. Sexual Harassment and Harassment across the nine grounds is discrimination and it is outlawed in the workplace, and outside the workplace in the course of one’s employment. Harassment may be caused by any of the following: The employer Another employer A client A customer A business contact of the employer It is a defence for the employer to prove that he/she took such steps as are reasonably practicable to prevent harassment and to prevent different treatment and to reverse the effects of such different treatment if it has occurred. 3. PROTECTION OF YOUNG PERSONS (EMPLOYMENT) ACT 1996 The Protection of Young Persons (Employment) Act 1996 is designed to protect young workers under the age of 18 and takes account of international rules on protecting young workers drawn up by the International Labour Organisation and the European Union. It is designed to protect the health of young workers and to ensure that work during school years does not put a young person’s education at risk. The law sets out: Minimum age limits for employment Rest intervals Maximum working hours The act regards a “young person” as a person who has reached 16 years but has not reached 18 years. The act refers to a person who has not reached the age of 16 as a “child”. Employers may not employ those aged under 16 in a regular full-time job and the act prohibits the employment of under 18s on late night work. Employers are required to keep specific records for their workers who are under the age of 18. Before employing a young person or child, an employer must see a copy of the birth certificate or other evidence of age and before employing under 16s, an employer must get the written permission of a parent or guardian. 3. PROTECTION OF YOUNG PERSONS (EMPLOYMENT) ACT 1996 For 16 and 17 year olds the maximum working day is 8 hours and the maximum working week is 40 hours. Persons aged 15 may be employed as part of an approved training programme and an employer may employ a 14 or 15 year old who is a full-time second level student as part of a work experience or educational programme. These placements are for a maximum of 8 hours a day or 40 hours a week. The act also deals with exceptions that arise where children are employed in cultural, artistic, sports or advertising activities. ACTIVITIES Visit to a Training Scheme/Business Enterprise /Voluntary Organisation My Own Place Investigation Simulated Job Interviews Career Investigations Work Placements Presentations/Interviews Local business investigations Visitors to the classroom Voluntary/ Community organisation investigations Use of ICT An Enterprise Activity. OUTCOME VERBS Ensure you understand the difference between terms like: State, Explain, Outline, Describe, Analyse, Discuss, Evaluate, Illustrate. PEP approach: Pre-experience, experience and Post experience COMMON MISINTERPRETATIONS Is the question on a Visit in or a Visit out? Are you asked to evaluate the organising of an event or evaluate the organisation? Are you evaluating the Career or the Activity itself, i.e. the Career Investigation? Why evaluate an activity v’s evaluating an activity. Work experience v’s work shadowing. Ensuring you know the differences between Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats. Ensure you can draft a SWOT analysis for an Entrepreneur, Business or Voluntary organisation that you studied. COMMON MISINTERPRETATIONS What makes an Activity successful v’s discussing the Activity. The role of the entrepreneur v’s the role of the manager. How to improve on a skill v’s rather than describing the skill. Entrepreneur skills, qualities and characteristics. Personal risks v Business risks when establishing a Business. Business Plan and Enterprise/Action Plan. Obligations of an Employer and Employee. What makes a business successful v’s measuring the success of a Business? FINAL TIPS Be aware of all 93 Specific learning outcomes Revise your Portfolio as this is an excellent revision tool and refer to the learning, skills and knowledge gained Read all questions carefully and answer all the required parts Always State, Explain, at least two different points and give an example Ensure that all work is neat and legible Ensure to develop points made and give meaningful evaluations if required. FINAL TIPS Take a critical look at each answer before leaving it to ensure that all relevant details are included Ensure to use the learning gained through the completion of the Portfolio Take account of mark allocations for questions and parts of questions and plan the use of time accordingly Use the published marking scheme as a resource and a guide when preparing for the Written Examination. These are available at the State Examinations Commission’s website www.examinations.ie SPECIFIC LEARNING OUTCOMES LINK MODULE I Preparation for the World of Work UNIT 1-Introduction to working life UNIT 2-Job seeking skills UNIT 3-Career Investigation UNIT 4- Work Placement LINK MODULE II Enterprise Education UNIT 1-Enterprise skills UNIT 2-Local Business Enterprises UNIT 3-Local Voluntary Organisations /Community Enterprises UNIT 4-An Enterprise Activity LINK MODULE I PREPARATION FOR THE WORLD OF WORK UNIT 1-Introduction to working life 1.1 identify the main sources of employment in the local area 1.2 identify the main social services and job creation agencies in the local area 1.3 identify the main agencies that provide transport in the local area 1.4 identify the main financial institutions servicing the needs of the local area 1.5 identify the main agencies involved in industrial relations in the local area 1.6 identify the principal economic activities in the local area 1.7 evaluate the potential for tourism in the local area 1.8 identify and understand the main differences between school and work 1.9 describe the intrinsic value of various forms of work including self employment and voluntary work 1.10 understand current regulations/legislation relating to the employment of young workers 1.11 understand current Health and Safety regulations in workplaces 1.12 role-play a situation that could give rise to a dispute in the workplace 1.13 understand issues related to diversity in the workplace 1.14 list the different forms of assistance for unemployed people 1.15 arrange a visit to a training scheme in the locality and/or invite an appropriate speaker from such an organisation to visit the group in the school 1.16 link the activities in this unit to learning in relevant Leaving Certificate subjects LINK MODULE I PREPARATION FOR THE WORLD OF WORK UNIT 2-Job seeking skills 2.1 recognise the different ways in which job vacancies are advertised 2.2 apply for a job by letter, telephone and e-mail 2.3 complete an application form 2.4 compile and create a curriculum vitae in word processed format 2.5 explain how to prepare for a job interview 2.6 engage in a simulated job interview LINK MODULE I PREPARATION FOR THE WORLD OF WORK UNIT 3-Career Investigation 3.1 identify personal aptitudes and interests 3.2 investigate a range of careers appropriate to personal aptitude and interests 3.3 identify and analyse the aptitude and skills required to pursue a specific career 3.4 describe relevant qualifications and training required for entry to the selected career 3.5 identify available opportunities to pursue a selected career locally, nationally, and where possible, at international level 3.6plan and set up an opportunity to interview and/or work shadow a person in a selected career 3.7 integrate information from a variety of sources to prepare a final report on a career investigation 3.8 reflect on and evaluate the experience of undertaking a career investigation 3.9 link the activities in this unit to learning in relevant Leaving Certificate subjects LINK MODULE I PREPARATION FOR THE WORLD OF WORK UNIT 4- Work Placement 4.1 specify personal goals in relation to a work placement 4.2 plan and organise a work placement 4.3 attend punctually for a specific placement 4.4 dress appropriately for a specific placement 4.5 follow a set of procedures in accordance with specific instructions 4.6 communicate effectively with other workers in a particular placement 4.7 follow a specific set of instructions relating to Health & Safety 4.8 review personal experiences in relation to a work placement 4.9 analyse reports by adults of personal performance in a workplace 4.10 reflect on and evaluate a specific work placement in the light of career aspirations 4.11 describe how what has been learned can be applied to work at home, in school and in the community 4.12 present a diary/written/verbal report on a specific work placement 4.13 link the activities in this unit to learning in relevant Leaving Certificate subjects LINK MODULE II ENTERPRISE EDUCATION UNIT 1-Enterprise skills 1.1 describe the qualities and skills of enterprising people 1.2 recognise examples of personal, community and entrepreneurial enterprise 1.3 identify personal strengths and weaknesses 1.4 suggest a course of action appropriate to improving personal enterprise skills 1.5 work co-operatively with others as part of a team 1.6 appreciate the value of teamwork in generating ideas, assessing risks, solving problems and completing tasks 1.7 undertake leadership of a group in an appropriate activity 1.8 plan and organise a meeting 1.9 make a presentation to peers and to adults 1.10 link the activities in this unit to learning in relevant Leaving Certificate subjects 1.11 evaluate the successes achieved and problems encountered in this unit LINK MODULE II ENTERPRISE EDUCATION UNIT 2-Local Business Enterprises 2.1 identify a range of enterprises in the local community 2.2 understand how an enterprise starts up and what support/training is available 2.3 describe the steps required to plan and carry out an investigation of a local enterprise 2.4 use learning from relevant Leaving Certificate subjects to formulate questions about aspects of a local enterprise 2.5 organise a visit to a local enterprise and invite appropriate speakers to visit the group in school 2.6 carry out a SWOT analysis of a business 2.7 report accurately on a visit by an entrepreneur to the classroom and on a class visit to a local enterprise 2.8 compare and contrast information gathered on a group visit to a local enterprise 2.9 describe a local enterprise with particular reference to products, services, markets and workforce 2.10 understand and describe the different roles of adults working in a business environment 2.11 describe the impact of the Single European Market on a specific enterprise 2.12 describe and evaluate the use of information and communication technologies in a business enterprise 2.13 understand the importance of education and training in the development of a business enterprise 2.14 link the activities in this unit to learning in relevant Leaving Certificate subjects 2.15 evaluate the successes achieved and problems encountered in this unit LINK MODULE 11 ENTERPRISE EDUCATION UNIT 3-Local Voluntary Organisations /Community Enterprises 3.1 identify the voluntary bodies that carry out community work in the locality 3.2 describe the work carried out by a range of voluntary groups in the locality 3.3 understand and describe the different roles of adults working in voluntary community organisations 3.4 organise a visit to a local community enterprise and/or invite an appropriate speaker to visit the group in school 3.5 use learning from relevant Leaving Certificate subjects to formulate questions about aspects of a community enterprise 3.6 integrate information from a variety of sources to prepare a report, plan or presentation on an aspect of community development 3.7 link the activities in this unit to learning in relevant Leaving Certificate subjects 3.8 evaluate the successes achieved and problems encountered in this unit LINK MODULE 11 ENTERPRISE EDUCATION UNIT 4-An Enterprise Activity 4.1 work co-operatively with others to generate a range of ideas 4.2 prepare a plan for the selected enterprise activity 4.3 identify available resources to support an enterprise activity 4.4 integrate information from a variety of sources including relevant Leaving Certificate subjects 4.5 assess personal and group skills and identify possible training needs 4.6 identify and recruit consultants willing to advise on a selected enterprise activity 4.7 understand the practical importance of market research and marketing mix 4.8 be aware of the concepts of publicity and promotion 4.9 actively participate in group work in a variety of roles-owner, worker, team leader 4.10 take responsibility to ensure that targets are reached 4.11 participate in a review of group performance 4.12 review personal performance in an enterprise activity 4.13 prepare and present a written or verbal report on an enterprise report 4.14 link the activities in this unit to learning in relevant Leaving Certificate subjects 4.15 evaluate the successes achieved and problems encountered in this unit FINALLY The very very very best of luck! The main thing is not to panic. But remember “Fail to prepare…prepare to fail” Over 81% of students use LCVP as one of their 6 subjects for points – next Wednesday is a Leaving Certificate exam – prepare yourself for that!!!!