Egypt History and Politics

Egypt
World History & Geography to 1500 AD
PowerPoint Slides
Mr. Mable
Tucker High School
2012
SOL Standards Chapter 1
STANDARD WHI.2a
The student will demonstrate knowledge of ancient river valley civilizations, including those of Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus River Valley, and China and the civilizations of the Hebrews, Phoenicians, and Nubians, by b) describing the development of social, political, and economic patterns, including slavery.
Development of social patterns
• Hereditary rulers: Dynasties of kings, pharaohs
• Rigid class system where slavery was accepted
Development of political patterns
• World’s first states (i.e., city-states, kingdoms, empires)
• Centralized government, often based on religious authority
• Written law codes (e.g., Ten Commandments, Code of Hammurabi)
Development of economic patterns
• Use of metal (e.g., bronze, iron) tools and weapons
• Increasing agricultural surplus: Better tools, plows, irrigation
• Development of the world’s first cities
• Development of the practice of slavery within most cultures in the ancient world, taking various forms
Three Major Time periods of
Ancient Egypt
Achievements
Old Kingdom
2650-2134 BC
Built enormous tombs & pyramids .
Decline Power struggles, crop failures, & cost of pyramids.
Middle Kingdom
2040-1640 BC
Land drained for farming.
Hyksos invaded & conquered.
New Kingdom
1550-1070 BC
Sea Trade &
Became an empire.
Conquered much of
Near East
Nubians, Persian,
Greeks, & Romans invaded.
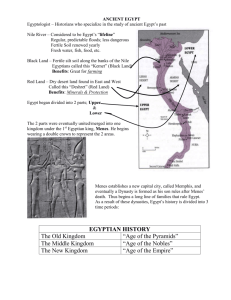
Egyptian History is divided into three main periods
•The Old Kingdom
•The Middle Kingdom
•The New Kingdom
Menes is Narmer
He changed his name after he unified Egypt!
The History of Egypt begins with Menes
Menes Unites upper Egypt and Lower
Egypt, joining the two into a united kingdom
In doing this, Menes establishes the first Egyptian Dynasty
Lower Egypt
Upper Egypt
Union of Two Crowns
• Red Crown
– Upper Egypt
• White Crown
– Lower Egypt
• Menes
– Overthrew the king of
Lower Egypt
– Wore a Double Crown
• Unification
– Joining of separate parts into one whole
Crown of Lower Egypt
• Red Crown
• Upper Egypt
• Symbol: Vulture
Crown of Upper Egypt
• White Crown
• Lower Egypt
• Symbol: Cobra
Double Crown
• King Tut’s Death
Mask
• Notice Double
Crown
• Vulture and Cobra
The Pharaoh
• God -King
• Pharaoh Means “ BIG HOUSE ”
• owns all the land and people and what people posses
• Pharaoh's will is the law
• irrigation
• no city walls
The Pharaoh
• God-King (Therefore a Theocracy )
• Religious
• direct descendant of the Sun god
• HE IS THE LIVING GOD !
• controls access to the afterlife
• July-Sept, during floods life is controlled by the
Pharaoh
– 365 day calendar.
Role played by size in Egyptian Artwork
IV. Social Order
Priests
Nobles/Warriors
Scribes
Merchants
Peasants/Slaves
The Old Kingdom 2700-2200 B.C.
The Old Kingdom was a period of great prosperity.
• Time of Great Pyramid Building
• Kings became Pharaohs.
• The Pharaoh was seen as divine , or godlike.
• The Pharaoh wielded absolute power, but used advisors to help them.
• The Chief advisor to the Pharaoh was the
Vizier .
• Social order and customs were established in the OLD KINGDOM
First Intermediate Period
• civil wars
• Famine
• Drought
• Loss of trade
• Pharaohs became weak
• Open to foreign Invasions
• After the fall of the Old Kingdom there was a period of chaos for about 150 years
• A new dynasty brought stability.
• The Pharaoh was still on top…
• But the Nobles were more powerful and ruled things
• The dynasties of the middle kingdom were weak and disorganized.
• No strong CENTRAL power; Power was Diffused!!!
Middle Kingdom 2050-1750 BCE
• End of civil wars , & farming and trade return
• move capital south to Upper Egypt
(Thebes)
• public improvements
– drain swamps, canal to Red Sea
• belief in afterlife expands to include common people
• tombs instead of pyramids
– better protection for mummies.
Second Intermediate Period
• The Middle Kingdom ended with the invasion of a people called the
Hyksos
• The Hyksos had Chariots and bronze weapons to the Egyptians.
The Egyptians were easily defeated.
• Eventually the Egyptians overthrew the Hyksos and established the New Kingdom
Hyksos
• Hyksos is Egyptian for FOREIGN
RULERS
• Chariots &Bronze weapons
VI. New Kingdom 1550-1075 BCE
• Ahmose I expelled the invading Hyksos and reunited Egypt
• Known as the Empire period
• development of “public” and “private” zones at temples.
Ahmose I leading Egyptians against the
Hyksos
New Kingdom 1567-1085 BCE
• Egyptian Threw out Foreign Invaders
• The Pharaohs of the New Kingdom took a more aggressive ruling style
• Egypt became the most powerful state in Southwest Asia.
• Egypt became an Empire! Ruled
Territory outside its own.
• Golden Age of Egypt
VI. New Kingdom 1550-1075 BCE
• Characterized by a more militaristic and imperialistic nature
– incorporated chariot, bronze working, horses
– development of a professional army
• became a slave based economy fueled by war and expansion
She was the first woman to be Pharaoh
She took power for herself
She had to pose as a man to cement her authority.
She built many monuments and temples.
VI. Threats to Tradition
• Amenhotep IV (c. 1362-1347
B.C.) introduced the worship of
Aton, god of the sun disk , as the chief god and pursued his worship with enthusiasm.
• Changed name to Akhenaten (“It is well with Aton”)
• He closed the temples of other gods and especially endeavored to lessen the power of Amon-Re and his priesthood at Thebes.
Aten
• Unifying deity, lord of all
• Akhenaten ( heretic king) tried to unify religions and kingdoms
• No physical form – just sun rays
VI. Threats to Tradition
1355-1335 BCE
• Nefertiti
– Wife of Akhenaton the only pharaoh to even partially reject polytheism
– political move against priests of Amon-Re
– moved capital to Amarna
– worshipped Aton, the sun disk
• royal inbreeding.
Akhenaton
• Amomhotep IV became Akhneaton
• Aton was the sun god
• Ankh was the symbol for LIFE
• Therefore, he was the LIVING Sun God!!!
Influences????
Remember that the Hebrews were enslaved in Egypt at this time!
Influences????
Amen or Amun was the overall god of the Egyptians.
Christians say AMEN after their prayers
Brief Period of Monotheism
• The Belief in
ONE god
Mono = one
Theism or theistic
= religion
The sun disc Aten shining on the names of the royal family
Tutankhamen
1335-1325 BCE
• Tut = The King
• Ahnk = Living
• Amun = god
King Tut:Tutankhamen
• Became Pharaoh after the death of Akhenaton.
• Restored the old religious practices
• Has the only tomb to be found intact
VI. Tutankhamen
1335-1325 BCE
• (King Tut)
• child ruler
• ruled nine years, died at
18
• young death meant burial in the tomb of a lesser person (noble) resulting in preservation
Ramses II
He fathered over 100 children
Some think he’s the Pharaoh of Hebrew Exodus
Think he is the face of the Sphinx
Abu Simbel : Temple of Ramses the Great
VI. Ramses II (1279-1213)
• greatest New Kingdom ruler
• military leader of Egypt
• expanded into southern
Turkey
• built many monuments to himself
• last gasp of Egyptian power.
VI. Ramses II (1279-1213)
Ramses the Great today
Abu Simble: Ramses II (1279-1213)
Invasion of the “Sea Peoples”
Decline
• Egypt fell into a period of decline and foreign invasion.
• Conquered by the Greeks,
Persians, & Romans.
• The last Pharaoh was Cleopatra
VII
• committed suicide rather than surrender to the Romans.
1
Three Kingdoms of Ancient Egypt
OLD
KINGDOM
Pharaohs organized a strong central state, were absolute rulers, and were considered gods.
Egyptians built pyramids at Giza.
Power struggles, crop failures, and cost of pyramids contributed to the collapse of the Old
Kingdom.
MIDDLE
KINGDOM
Large drainage project created arable farmland.
NEW
KINGDOM
Powerful pharaohs created a large empire that reached the
Euphrates River. Traders had contacts with Middle East and
Crete. Hatshepsut encouraged trade.
Corruption and rebellions were common.
Ramses II expanded
Egyptian rule to Syria.
Hyksos invaded and occupied the delta region.
Egyptian power declined.