Module 4 Tips – Learning & Language
advertisement
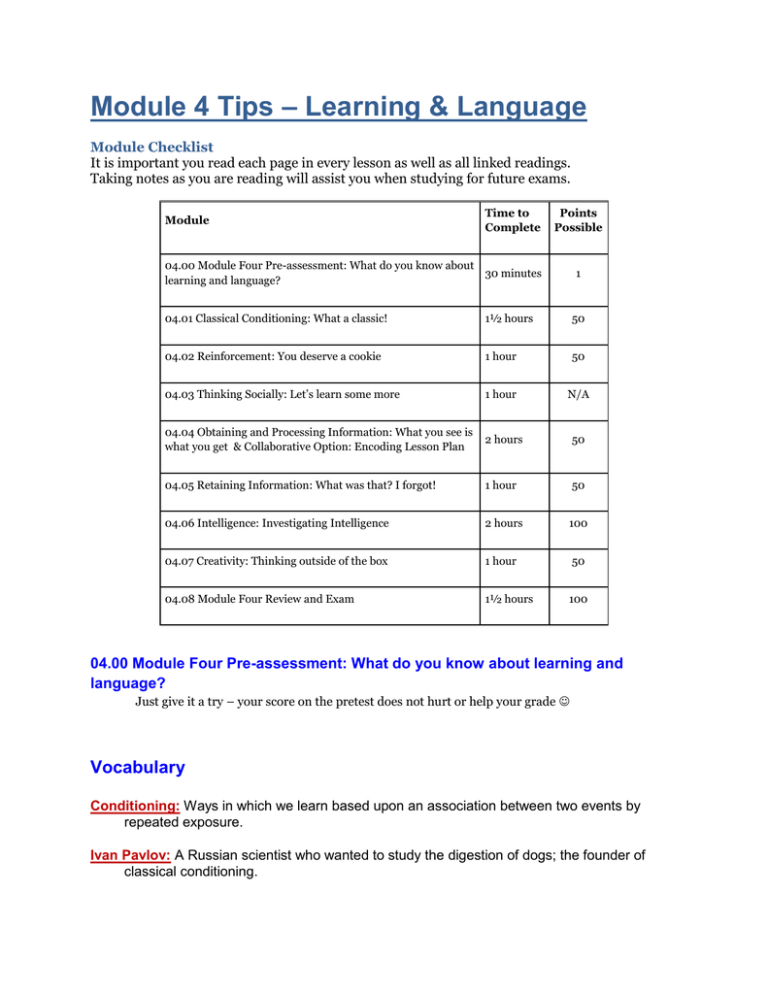
Module 4 Tips – Learning & Language Module Checklist It is important you read each page in every lesson as well as all linked readings. Taking notes as you are reading will assist you when studying for future exams. Module Time to Complete Points Possible 04.00 Module Four Pre-assessment: What do you know about 30 minutes learning and language? 1 04.01 Classical Conditioning: What a classic! 1½ hours 50 04.02 Reinforcement: You deserve a cookie 1 hour 50 04.03 Thinking Socially: Let’s learn some more 1 hour N/A 04.04 Obtaining and Processing Information: What you see is what you get & Collaborative Option: Encoding Lesson Plan 2 hours 50 04.05 Retaining Information: What was that? I forgot! 1 hour 50 04.06 Intelligence: Investigating Intelligence 2 hours 100 04.07 Creativity: Thinking outside of the box 1 hour 50 04.08 Module Four Review and Exam 1½ hours 100 04.00 Module Four Pre-assessment: What do you know about learning and language? Just give it a try – your score on the pretest does not hurt or help your grade Vocabulary Conditioning: Ways in which we learn based upon an association between two events by repeated exposure. Ivan Pavlov: A Russian scientist who wanted to study the digestion of dogs; the founder of classical conditioning. Classical Conditioning: A method of conditioning in which associations are made between a natural stimulus and a learned, neutral stimulus. John B. Watson: An American psychologist who established the psychological school of behaviorism, conducted the controversial 'Little Albert' experiment, and become a popular author on child rearing. Mary Cover Jones - A pioneer of behavior therapy within a scientific field dominated throughout much of the 20th century by male scientists. She pioneered the removal of fears using behavioral classical conditioning. Stimulus Generalization: The theory that a response can spread from one specific stimulus to a resembling stimuli. Phobia: an exaggerated, usually illogical fear, such as heights, animals, the dark, etc., that causes much anxiety. Operant Conditioning: Conditioning that results from actions and consequences resulted from the actions. Primary Reinforcement: Something necessary for psychological/physical survival that is used as a reward. Examples include love, food, water, and shelter. Secondary Reinforcement: Anything that comes to represent a primary reinforcer. One example is money. Positive Reinforcement: Strengthening the possibility to repeat a response by following it with something that is pleasant. Negative Reinforcement: Strengthening a response by following it with taking away or avoiding something unpleasant. Punishment: The process of weakening a response by imposing unpleasant consequences. Transfer of Training: A learning process in which learning is moved from one task to another based on resemblance between the two tasks. Amnesia: The blocking of old memories and/or the loss of the new memories. Intelligence: The ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations. Mental Set: The tendency to use the same old solution over and over again even when it does not work. Schema: A mental codification of experience that includes a particular organized way of perceiving cognitively and responding to a complex situation or set of stimuli. Forgetting: An increase in errors in trying to retrieve information. Aptitude: Capacity for learning. Intelligence Quotient: A measure of intelligence originally obtained by comparing the mental age with the chronological age and dividing this sum by 100.







