Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You
advertisement

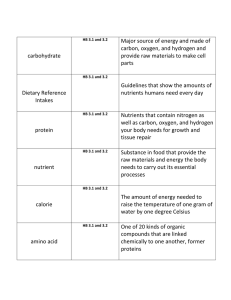
7 Chapter 7 Nutrients: Nutrients: From Food to You Food to You Chapter From Nutrients provide energy, build and repair body cells, and keep your body working. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 1 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Content Vocabulary Academic Vocabulary nutrient appropriate carbohydrate process sugar starch fiber proteins vitamins minerals Recommended Dietary Allowances malnutrition supplement Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 2 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Nutrients for Wellness More than 40 nutrients belong in six groups: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and water. nutrient A substance that perform a job in your body. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 3 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You What Nutrients Do for You Give you energy: your body uses energy even when you sleep Build and repair body cells: Proteins help build and repair cells and help you grow process Regulate body processes: Body processes include breathing, digesting food, and building red blood cells A function Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 4 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You How Digestion and Absorption Work Mouth Large Intestine Esophagus Stomach Liver Small Intestine Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 5 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Meet the Nutrients Carbohydrates: Your Main Energy Source A carbohydrate is an important nutrient that helps proteins and fats do their regular jobs. carbohydrate A nutrient that serves as the body’s main energy source. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 6 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Meet the Nutrients Sugar is a simple carbohydrate because it is made of one or two sugar units. sugar A simple carbohydrate that are digested quickly. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 7 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Meet the Nutrients Starch is broken down during the digestion process into single sugars, which are used to make energy. starch Many sugar units attached together. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 8 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Meet the Nutrients Complex carbohydrates are starches and fiber. fiber Plant material that cannot be digested. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 9 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Foods with Carbohydrates • Grain products • Starchy vegetables • Legumes Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 10 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Fats: Nutrients Essential to Your Health Fats provide energy, insulate you from heat and cold, and cushion vital organs. Fats are naturally present in meat, poultry, fish, dairy foods, and nuts. Eating too much fat increases your risk of heart disease. Saturated Fats Wellness Trans Fats Types of Fats Unsaturated Fats Cholesterol is a fat-like substance found in body cells. High levels in the bloodstream have been linked to heart disease. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 11 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Proteins: Your Body’s Building Blocks Proteins are needed for growth and fighting disease, are made of many small units called amino acids, and help give you energy if you do not take in enough carbohydrates and fats. Types and Sources of Protein: Complete proteins Incomplete proteins proteins Substances that the body uses to build new cells and repair injured ones. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 12 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Water is a Nutrient! Every body cell contains water. Water helps digestive process by eliminating waste. Water carries nutrients. Water helps regulate body temperature. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 13 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Vital Vitamins Vitamins do not provide energy or build body tissue, but your body cannot produce energy without them. Fat-soluble vitamins—A, D, E, and K—dissolve in fat. Excess amounts can build up to harmful levels in your body. vitamins Nutrients that help regulate body processes and help other nutrients do their work. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 14 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Mighty Minerals Your body uses minerals for many processes. minerals Inorganic nutrients that are essential for health and growth. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 15 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Build Strong Bones for Life Bones grow with the help of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium. Your need for calcium is highest during your teen years. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 16 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Eat Right for Healthy Blood Iron helps red blood cells carry oxygen to all your cells. If you do not eat enough foods with iron, you many develop anemia. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 17 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Nutrients and Energy What are Calories? Calories are not a food ingredient or nutrient, instead, they are units the measure energy. Energy in Food Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins provide energy. Food provides energy so your body can do its work, even for sleep. When you balance the energy from your food and drinks with the amount your body uses, you maintain your weight. Energy Your Body Uses Energy in Balance Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 18 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Nutrient Advice The Recommended Dietary Allowances are part of the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) from the Institute of Medicine. Poor nutrition can cause malnutrition. Recommended Dietary Allowance Governmental advice about daily nutrient needs for most healthy people. Malnutrition Poor nutrition. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 19 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Nutrient Advice Dietary supplements may be sold as pills, capsules, liquids, or powders. With wise food choices, you probably do not need a supplement. supplements Contains nutrients or other food substances that add to your diet. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 20 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You After You Read Review Key Concepts List the three main nutrient functions. The six categories of nutrients are: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and water. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 21 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You After You Read Review Key Concepts List food sources of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and water. Food sources of carbohydrates are grain products, such as breads, cereal, rice, grits, and pasta; starchy vegetables, such as squash, potatoes, and corn; and legumes, such as beans, peas, and lentils. Food sources of fat are meat, poultry, fish, dairy foods, and nuts. Food sources of proteins are food from animal sources, such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products or from soy for complete proteins, or plant sources such as beans, peas, grains, and nuts for incomplete proteins. Water can come from plain water, juice, milk, and soups, as well as most foods. Vitamins and minerals come from a variety of foods. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 22 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You After You Read Review Key Concepts Explain energy balance. Energy balance is consuming the same amount of energy, or calories, as your body uses. When you balance the energy from your food and drinks with the amount your body uses, you maintain your weight. If you eat more food and drinks than the amount your body uses, you gain weight. If you eat less food or drinks than the amount your body uses, you lose weight. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 23 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You After You Read Review Key Concepts Describe the possible effects of getting too few or too many nutrients. Getting too few nutrients may result in poor health or a lack of energy. If you get too much of a nutrient, the body gets rid of extra water-soluble vitamins as waste. Extra energy from carbohydrates, proteins, or fats turns into body fat. If you take too many fat-soluble vitamins, as well as some minerals, they can build up in the body and create health problems. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 24 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You After You Read Review Key Concepts Describe the safe use of dietary supplements. Health professionals may recommend supplements for specific reasons including calcium supplements for people who are allergic to milk, or to some elderly people, pregnant or nursing women, people on certain medications, or those recovering from illness. Taking large amounts of these vitamins may cause health problems. Some watersoluble supplements can cause your kidneys to work too hard to remove the excess, while others may harm your liver and other organs. Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 25 Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You End of Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You Glencoe Food, Nutrition & Wellness Chapter 7 Nutrients: From Food to You 26