Energy Sources Frayer Model Key
advertisement

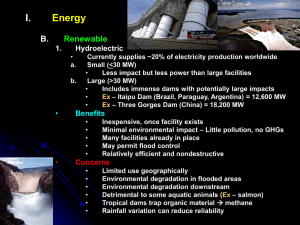
11 November 2015 All Classes: Begin reviewing for your Ecology and Environment CUBA, Monday, November 23rd Energy Sources Frayer Models Answer Key Use the following slides to check your Frayer model for the renewable and non-renewable energy sources Non-Renewable Uses • Generate electricity • Used to make steel • Used to make medicine and fertilizer • Heat Coal Advantages • Coal is plentiful • Easy to transport • When burned it produces a lot of energy • More efficient than other types of fuel • Supplies jobs • • • • Disadvantages Mining for coal can cause erosion Mining can be dangerous Runoff from coal mines can cause water pollution Creates air pollution Non-Renewable Uses • Fuel for vehicles • Heating homes • Making plastics and petroleum products Advantages • Accounts for 1/3 of all the • energy in the world • Can be easily transported • Make may products Oil Disadvantages • Hard to find • Takes millions of years to form • When oil spills it causes water pollution • Very deep underground Non-Renewable Uses • Heating homes • Generate electricity • Used for cooking Natural Gas Advantages • Can be compressed and stored in tanks/easy to transport • Produces a lot of energy with little air pollution • Less harmful than coal or oil when burned • • • • • Disadvantages Hard to find Highly flammable If leaking can cause sickness Can cause land pollution The pipes take up a lot of land space Renewable Uses • Create electricity • Heat water • Light Solar Advantages • Does not cause air pollution • Energy can be collected and • stored • Will not run out • • Can be used in area with a lot • of sun • Disadvantages Only works in areas that get a lot of sun Takes up a lot of space Expensive to buy panels Only available when sun is shining Renewable Uses • • • • Hydropower Advantages • No air pollution • Produced by flowing water/ water cycle • Inexpensive/cheapest way to generate electricity • Stores energy • • • • Generate electricity Control water flow Part the water cycle Power machines Disadvantages Only available in areas with water Change the environment by stopping the flow of water Can harm fish Causes floods Renewable Uses • • • • Wind Advantages • No pollution • • Generates electricity • • Renewable • • Less expensive than other • renewable resources Electricity Energy Heat Moves cool air Disadvantages Must have wind Cannot be owned by public Wind farms take up a lot of space Can be harmful to birds Renewable Uses • Electricity • Transportation • Fuel • Heating Biomass biodiesel Advantages • Can replace gasoline in cars • Less air pollution than fossil fuels • Can easily switch to without changing the current equipment • Non toxic • Low Nitrogen/Sulfur • Creates Ozone Disadvantages • Expensive • Not a lot of places to get this fuel • Land must grow a lot of soybeans and other biomass • Causes air pollution Renewable Uses • Energy • Provides hot water • Heats homes • Provides electricity Geothermal Advantages Disadvantages • Natural and easy to access in • Few places that can be used • Very expensive to drill wells certain areas • The technology is expensive to • No air pollution have in your home • Unlimited source of energy • Don’t need to transport fuel • Costs less than coal and natural gas Non-Renewable/Renewable Uses • Used to generate electricity Nuclear/ Uranium Advantages • No air pollution • Don’t need to drill/look for fuel • Very little impact on the environment unless there is an accident Disadvantages • Can be dangerous of explode or melt down • Uses a lot of water to cool; takes water from the environment • Creates radiation/Waste is challenging to store