Where does our energy come from?
advertisement

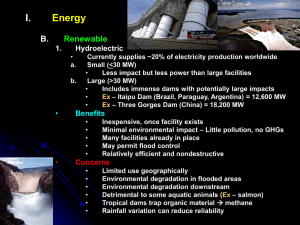
ENERGY Where does our Energy come from? Where does our energy come from for…? • • • • • Electric light Mobile phones Power for your mp3 TV Hot Water Energy for these things come from Energy Resources, that are converted into energy that we can easily use. Electricity is the main form of energy that we use and can power or charge what we need energy for. Energy in Northern Ireland There are 3 power stations: 1. Coolkeeragh Power Station, near Londonderry. Uses gas to generate electricity 2. Ballylumford Power Station, Island Magee. Uses gas to generate electricity 3. Kilroot Power Station, Carrickfergus. Uses coal to generate electricity To generate electricity… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. You need an energy source, e.g. coal This is burnt to produce heat or steam The heat or steam then drives a turbine The turbine then can drive a generator The generator then produces electricity The electricity is then transported in cables to where it is needed Energy Resources can be divided into 2 categories: 1. Non-Renewable Resources For example – coal, oil, gas, uranium or lignite Once used these resources CANNOT be used again 2. Renewable Resources For example – wind, water or solar These resources can be used over and over again Non-Renewable Resources: COAL What is it? • Formed underground from decaying plant material How much left in the world? • About 200 years Advantages? • Plenty left • Mining is getting more efficient Disadvantages? • Pollution: CO2 emissions (linked to global warming), SO2 (linked to acid rain) • Heavy & bulky to transport Non-Renewable Resources: What is it? OIL • Formed underground from decaying animal and plant material How much left in the world? • About 40 years! Advantages? • Quite easy to transport • Efficient in producing energy • Less pollution than coal Disadvantages? • Not much left • Pollution: air and danger of water pollution through spills Non-Renewable Resources: NATURAL GAS What is it? • Formed underground from decaying animal and plant material How much left in the world? • About 60 years Advantages? • Clean, least polluting of all non-renewables • Easy to transport Disadvantages? • Some air pollution • Danger of explosions Non-Renewable Resources: NUCLEAR What is it? • Uses uranium, naturally found in some rocks How much left in the world? • Not known Advantages? • Not much waste and few CO2 emissions released, as well as, few other greenhouse gases Disadvantages? • High cost to build and close down power stations. • Waste is radioactive. Problem with getting rid of waste safely Non-Renewable Resources: LIGNITE What is it? • Formed underground from decaying plant material How much left in the world? • In Northern Ireland, it is thought at least 30 years (SOURCE: www.geographyinaction.co.uk/Issues/Lignite) Advantages? • For Northern Ireland: a local resource, good for generating electricity Disadvantages? • Air pollution, scarring of landscape through open-cast mining • High moisture content Why is the term, FOSSIL FUEL used for coal, oil, gas and lignite? Renewable Resources: WIND What is it? It the movement of air from high to low pressure How much left? Endless Advantages? No pollution Disadvantages? Winds change all the time, not predictable Renewable Resources: SOLAR What is it? Energy from the sun How much left? Endless Advantages? No pollution, can be used in remote areas Disadvantages? Can be expensive, needs sunlight At night it doesn’t work Renewable Resources: BIO-ENERGY What is it? Biomass and Biogas – • fermented animal or plant waste • vegetation from sustainable sources How much left? Endless Advantages? Good availability Disadvantages? Can be expensive to set up Renewable Resources: HYDRO What is it? Movement of water drives a turbine How much left? Endless Advantages? No CO2 emissions, can control flooding and provide a good water supply to an area Disadvantages? Large areas maybe flooded. Visual and water pollution Renewable Resources: GEOTHERMAL What is it? Heat from the ground – often used to heat water How much left? A lot Advantages? No CO2 emissions Disadvantages? Expensive and can only be used in certain parts of the world Renewable Resources: WATER & TIDAL What is it? Movement of sea drives turbines How much left? Endless Advantages? Can produce a lot of electricity, no CO2 emissions Disadvantages? Not many suitable sites Renewable Energy is increasing in Northern Ireland TARGET: In Northern Ireland, 12% of electricity generated by renewables by 2012 NOW: Wind energy supplies from between 3-7% of our energy needs Where does our Energy come from? • From renewable and non-renewable energy sources • Renewable energy sources are now increasingly being used • Renewable energy: The future of energy, today!