Articulations
advertisement

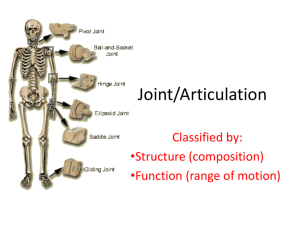
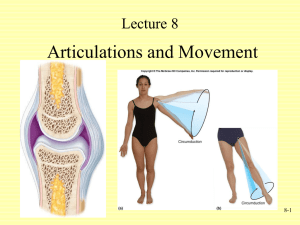
Articulations Introduction Classification of Joints Articular Form & Function Representative Articulations Introduction • Articulation • Articular Components Learning Objectives • Articulation: Define what an articulation is an provide several examples • Tissue Components: List three tissue components that contribute to the structure of joints Articulations • Articulation (a.k.a., joint) The site of contact between bones or cartilage & bone Joints permit growth & movement Not all joints are movable joints Articular Tissue Components • Bone • Cartilage • Connective tissue ligaments tendons membranes lubricating fluids Classification of Joints • Functional Classification: Degree of Movement • Structural Classification Learning Objectives • Joints: Contrast the major categories of joints, and explain the relationship between structure & function for each category Provide examples for each category of articulation • Synovial Joints: Describe the basic structure of a synovial joint and identify accessory structures & their functions Provide examples for each category of synovial joint Functional Classification: Degree of Movement • Synarthroses: immovable may involve fusion of bones • Amphiarthroses: slightly movable • Diarthroses: freely movable Structural Classification • Bony fusion: synarthroses • Fibrous joints: synarthroses amphiarthroses • Cartilaginous joints: synarthroses amphiarthroses • Synovial joints: diarthroses Synarthroses (No Movement) • Fibrous: Suture interdigitated projections dense connective tissue bonds ex: btw/ bones of the skull Gomphosis bony sockets fibrous connective tissue bonds ex: btw/ teeth & jaw bones Synarthroses • Cartilaginous: Synchondrosis interposition of cartilage plate ex: epiphyseal plates Synostosis conversion of articular cartilage causing fusion of bones: totally rigid ex: portions of skull & epiphyseal lines Amphiarthroses (Little Movement) • Fibrous: Syndesmosis ligamentous connection ex: btw/ tibia & fibula Symphysis bonded by fibrocartilage pad ex: btw/ right & left halves of pelvis & btw/ adjacent vertebrae Diarthroses (Free Movement) • Synovial: – complex joint bounded by joint capsule & containing synovial fluid Monaxial permits movement along 1 axis ex: elbow; ankle Biaxial permits movement along 2 axes ex: wrist-radius; thumb-metacarpal; ribvertebrae Triaxial permits movement along 3 axes (angular & rotational) ex: shoulder; hip Components of Synovial Joints • Articular capsule synovial membrane surrounds synovial cavity secretes synovial fluid • Articular cartilage hyaline-like covering of bone surface w/in joint slick, smooth surface reduces friction Components of Synovial Joints • Synovial fluid similar to interstitial fluid w/ ↑ [proteoglycans] secreted by fibroblast of synovial membrane functions: lubrication of articular cartilage nutrient distribution to articular cartilage shock absorption when joints are compressed Components of Synovial Joints • Accessory structures menisci (sing. meniscus) structure – fibrocartilage pads function – channel fluid flow; packing fat pads structure – adipose tissue function – antishock & pack joint capsule to fill gaps during movement accessory ligaments structure – localized thickenings of capsule function – reinforce & strengthen; limit rotation Components of Synovial Joints • Accessory structures (cont) tendons structure – collagen fibers of dense regular connective tissue not technically part of articulation function – limit range of motion & provide mechanical support bursae structure – small, synovial fluid-filled connective tissue pockets function – form where ligaments &/or tendons rub against other tissues: reduce friction Synovial Joint: Stabilizing Factors • Factors: collagen fibers of joint capsule & accessory ligaments articular surface shapes of bones presence of other bones, skeletal muscles, &/or fat pads tension in tendons attached to the articulating bones • Functions: limit range of motion to reduce chance of injury stabilize joint Shoulder Joint – Stabilization • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • MOV Video plays about 32 sec Articular Form & Function (Synovial Joints) • Describing Dynamic Motion • Types of Movements • Structural Classification of Synovial Joints Learning Objectives • Dynamic Movement: Describe the dynamic movements of the skeleton • Synovial Joints: List the different types of synovial joints, & discuss how characteristic motions are related to anatomical structure Dynamic Motion • Linear motion movement away from point of origin: forward/backward & left/right • Angular motion change in degree from vertical: movement away from point of origin: forward/backward & left/right circumduction – complex angular motion • Rotation movement around a vertical axis Types of Movements: Linear Motion • Gliding Opposing surfaces slide past one another ex: btw/ carpal & tarsal bones; btw/ clavicles & sternum Wrist: Gliding Motion • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • MOV Video plays about 2 sec Types of Movements: Angular Motion • Flexion & Extension Flexion – reduces angle btw/ articulating elements Extension – increases angle btw/ articulating elements ex: movement at elbow • Abduction & Adduction Abduction – movement away from the longitudinal axis of the body Adduction – movement toward the longitudinal axis of the body ex: movement of arm laterally or medially Elbow: Flexion & Extension • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • MOV Video plays about 3 sec Hyper-extension • Extension beyond the range of normal motion May result in injury: “Extension” to Knee this position Elbow Wrist Interphalangeal joints • Normal for many joints in motion: Hip Wrist Shoulder: Adduction & Abduction • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • MOV Video plays about 3 sec Types of Movements: Rotation • Rotation - Pivoting around an axis Left rotation & right rotation ex: shaking head “no” Medial rotation – internal or inward rotation ex: rotating arm across front of body Lateral rotation – external or outward rotation ex: rotating arm across front of body Shoulder: Rotation • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • MOV Video plays about 3 sec Types of Movements: Rotation • Rotation (cont) Pronation ex: palm front to palm back Supination ex: palm back to palm front Types of Movements: Complex Angular Motion • Circumduction Describing a circle Combination of flexion, extension, adduction, & abduction ex: movement of arm at shoulder to draw a circle Shoulder: Circumduction • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • MOV Video plays about 2 sec Wrist: Circumduction • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • MOV Video plays about 2 sec Special Movements • Dorsiflexion ex: flexion of ankle to elevate sole • Plantar flexion ex: flexion of ankle to elevate heel • Inversion ex: twisting sole inward • Eversion ex: twisting sole outward Ankle: Plantar Flexion & Dorsiflexion • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • MOV Video plays about 3 sec Ankle: Inversion & Eversion • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • MOV Video plays about 2 sec Special Movements • Opposition ex: movement of thumb toward palm • Protraction ex: movement anteriorly in horizontal plane • Retraction ex: movement posteriorly in horizontal plane • Elevation ex: movement in a superior direction • Depression ex: movement in an inferior direction • Lateral flexion ex: movement of vertebral column laterally Nice Schnozz, eh? Elevation Hand/Thumb: Opposition • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • MOV Video plays about 2 sec Synovial Joint Classification • Gliding (planar) joints flat articular surfaces biaxial – permit linear motion ex: intercarpal & intertarsal joints; sacroiliac; tibiofibular joints • Hinge (ginglymus) joints monaxial – permit angular motion ex: humeroulnar (elbow) joint; interphalangeal joints Synovial Joint Classification • Pivot (trochoid) joints monaxial – permit rotation ex: atlas-axis joint • Ellipsoidal (condylar) joints oval face articulates w/ depression biaxial – permits any angular movement including circumduction ex: radius & proximal carpals; proximal phalanges & metacarpals Synovial Joint Classification • Saddle (sellaris) joints faces w/ concave & convex regions biaxial – permits angular & circumduction; no rotation ex: carpometacarpal joint of thumb • Ball & Socket joints round head w/ cup-shaped depression triaxial – permits any angular movement including circumduction & rotation ex: shoulder & hip joints Synovial Joint Movements • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • MOV Video plays about 36 sec Representative Articulations • • • • • Intervertebral Articulations The Shoulder Joint The Elbow Joint The Hip Joint The Knee Joint Learning Objectives • Articular Features: Describe the articulations btw/ the vertebrae of the vertebral column Describe the articular features of the shoulder, elbow, hip, & knee • Joint Mobility: Explain the relationship btw/ joint strength & mobility Intervertebral Articulations • Gliding amphiarthroses • Structural factors: Intervertebral discs btw/ vertebrae nucleus pulposus – soft, gelatinous, elastic core of disc • Stabilizing factors: intervertebral ligaments – anterior longitudinal; posterior longitudinal; ligamentum flavum; interspinous; supraspinous Vertebral Movements • flexion – bending forward • extension – bending backward • hyperextension – bending beyond anatomical position • lateral flexion – bending to the side • rotation – atlas & axis joint (only pivot diarthrosis in vertebral column) The Shoulder Joint (Glenohumeral or Scapulahumeral) • Ball & socket diarthrosis • Structural factors head of humerus w/in shallow glenoid cavity of scapula • Stabilizing factors: interlocking bones ligaments – glenohumeral; coracohumeral; coracoacromial; coracoclavicular rotator cuff muscles – supraspinatus; infraspinatus; subscapularis; teres minor Shoulder Joint – Detail • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • MOV Video plays about 32 sec Widest range of movement of any joint Shoulder Movements • flexion – elevating humerus & moving horizontally across chest • extension/hyperextension – elevating humerus & moving horizontally away from chest • abduction – moving arm laterally (outward) in vertical plane • adduction – moving arm medially (inward) in vertical plane • circumduction – moving extended arm to trace a circle • rotation – twisting extended arm dorsally & ventrally The Elbow Joint (Olecranal) • Hinge diarthrosis • Structural factors troclear surface of humerus interlocks w/ troclear notch of ulna (stabilizing factor) • Stabilizing factors interlocking bones thick articular capsule ligaments – radial collateral; annular; ulnar collateral Elbow Movements • flexion – bending forearm forward toward upper arm • extension – bending forearm away from upper arm The Hip Joint (Coxal) • Ball & socket diarthrosis • Structural factors head of the femur lies w/in deep acetabulum of the coxal bone • Stabilizing factors interlocking bones dense articular capsule ligaments – iliofemoral; pubofemoral; ischiofemoral; transverse acetabular; femoral head ligament muscular padding Coxal Articulation Note stabilizing effect of muscles nd 2 Widest range of Hip Movements movement of any joint • flexion – elevating femur & moving horizontally toward pubis • extension/hyperextension – lowering femur & moving horizontally away from pubis • abduction – extending leg laterally (outward) in vertical plane • adduction – moving leg medially (inward) in vertical plane • circumduction – moving extended leg to trace a circle • rotation – twisting leg dorsally & ventrally The Knee Joint (Femurotibial) • Hinge diarthrosis – complex • Structural factors actually 3 separate joints 2 - btw/ lateral & medial condyles of femur & tibia 1 btw/ patella & femur no unified joint capsule no common synovial cavity medial & lateral menisci The Knee Joint Note• Stabilizing factors fat pads stabilizing ligaments – patellar; 2 popliteal; effect of pads, anterior cruciate & posterior cruciate; tibial collateral; fibular menisci,collateral & ligaments medial & lateral menisci Knee Joint – Detail • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • MOV Video plays about 18 sec Knee Movements • flexion – bending lower leg backward • extension – bending lower leg forward • rotation – extremely limited Locking of the knee – in extended – somewhat hyperextended – position permits standing for long periods w/out use of muscles that extend the leg Review of Important Joint Movements • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • ASF Video plays about 2-1/4 min