Introduction
advertisement

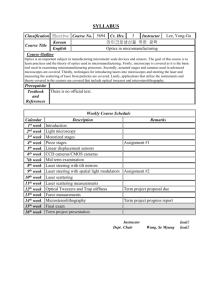
Optics in micromanufacturing Prof. Yong-Gu Lee Email: lygu@gist.ac.kr Phone: 062-715-2396 Course web site: https://210.107.176.1/wiki/pages/V0b5M5F/optics_in_micromanufacturing.html Password for protected zip files: xxxx 1 Motivation • Silicon manufacturing was a great success leading to integrated circuits, sensors (ex: gyroscopes, accelerometers), actuators (ex: DMD) • Normally, manufacturing is done in batch processes without visual monitoring • Optics allows real time monitoring of objects comparable to the wavelength of light (400nm~800nm) • Sophisticated sensing, manipulation and manufacturing can be realized using optics 2 Micromanufacturing, micromanipulation and sensing Sun et al, Elastic force analysis of functional polymer submicron oscillators, 3 Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 3173 (2001); http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1418024 Course Outline • Optics is an important subject in manufacturing micrometer scale devices and sensors. The goal of this course is to learn practices and the theory of optics used in micromanufacturing. Firstly, microscopy is covered as it is the basic tool used in examining micromanufacturing processes. Secondly, actuated stages and cameras used in advanced microscopes are covered. Thirdly, techniques for introducing lasers into microscopes and steering the laser and measuring the scattering of laser from particles are covered. Lastly, applications that utilize the instruments and theory covered in the courses are covered that include optical tweezers and microsterolithography. 4 Course focus • • • • • • • • • Light microscopy (2 weeks) – basic light microscopy – phase contrast and darkfield microscopy – properties of polarized light and polarization microscopy – DIC, fluroscence, confocal microscopy Microscope stages (2 weeks) – Motorized stages – Piezo stages – Linear displacement sensors – SW control Microscope image acquisition (2 weeks) – CCD, CMOS cameras – SW control Laser steering in microscope (2 weeks) – Laser safety – Tilt mirrors – Spatial light modulators – SW control Laser scattering in microscope (2 weeks) – Theory – Quadrant Photo Diodes – SW control Force measurements (2 weeks) – Particle tracking – Optical Tweezers and Trap stiffness Microstereolithorgraphy Final examination (1 week) Term project presentations (1 week) 5 Syllabus Weekly Course Schedule Calendar Remarks Description 1st week Introduction 2nd week Light microscopy 3rd week Motorized stages 4th week Piezo stages Assignment #1 th 5 week Linear displacement sensors 6th week CCD cameras/CMOS cameras 7th week Mid term examination 8th week Laser steering with tilt mirrors 9th week Laser steering with spatial light modulators Assignment #2 10th week Laser scattering 11th week Laser scattering measurements 12th week Optical Tweezers and Trap stiffness 13th week Force measurements 14th week Microstereolithography 15th week Final exam 16th week Term project presentation Term project proposal due Term project progress report 6 Understandings • Grades Assignments 10 Term project 30 Mid exam 20 Final exam 30 Class attendance 10 _____________________ 100 • A,B,C,F A B C,F ~40% ~40% ~20% *Subject to change If you fail to attend more than 1/3 of the classes, you disqualify for taking any examinations further scheduled. Regulations on Courses, ART 25 (3) 7 Understandings • Attendance –No excuses for absence •Business trip •Sick –Attendance credit • Assignments –Penalties for late submissions –No credit for copied submissions, (original and copies) •Not to be later than 15 minutes •No early leave 8