Module 1 Notes and Assignments
advertisement

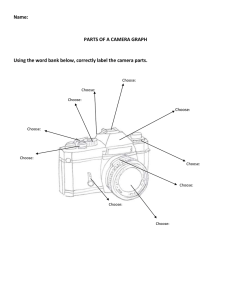
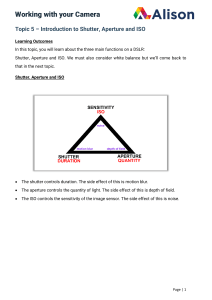
Module One: Digital Camera Basics IMAGE CAPTURE Instead of film, a digital camera uses a device called a ____________________________________. This device is a light-sensitive chip that converts _________________________ into a _______________________ signal. The sensors are also known as ___________________. CCD SENSITIVITY The higher the number or ISO setting, the______________________ the sensor's sensitivity to light. Using lower numbers means that the sensor needs more light to reach it in order to record a properly exposed shot. In general, use: IMAGE RESOLUTION Resolution is explained as the number of horizontal pixels multiplied by the number of vertical pixels. The more pixels there are, the __________________ the resolution. In addition, the higher the resolution the more space (memory) your image requires. dpi = dots per inch ppi= pixels per inch Screen resolution is _________ dpi. Printing resolution is be _____________ dpi or more. METERING Correct exposure happens when your photograph has the same range and intensity of tone as the scene being photographed. Underexposure occurs when the sensor ________________________________________________, and overexposure occurs when the sensor receives ___________________________________________________. Sensors on the camera measure the amount of light reflecting back off the subject(s), then the camera uses this information to calculate the exposure – a process known as metering. __________________________________ ________________________ _________________________ APERTURE AND SHUTTER SPEED Proper exposure also depends on finding the right combination of aperture and shutter speed. shallow DOF deep DOF Aperture controls the amount of __________________________ entering the camera, much like the iris of a human eye-widening and constricting to let in more or less. Apertures are shown in _______________________________. The bigger the number, the _______________________ the aperture opening is. This is tricky!! Aperture controls the Depth of Field, which we will talk about in another module. Shutter Speed at 1/250, ½, and 1 second Shutter Speed refers to how much time the light is allowed to enter the camera and is measured in fractions of a second. Think of a door opening to the outdoors: if you take your time to open and close the door, more light will be let in than if you open and slam the door quickly. For example 250 is 1/250th of a second, 2 is ½ (half) a second and 1 is a full second. Shutter Speed can be manually controlled to alter how motion (a moving subject) is captured in your photographs. FILE FORMATS The _______________ is the standard image file format for the Internet. Subsequently most digital cameras create this file format for each image taken. It’s best to set your camera to the __________________________ image size and the ____________________ compression option, this will give you the highest quality image, however it will also means you can store fewer photos on your memory card. TRANSFERING AND STORING FILES Memory cards initially store your images. Using either a USB cord or a Memory Card Reader you can transfer your images to a computer. MODULE 1 ASSIGNMENTS 1-3. Set up a FlickR account and add a “Buddy Icon” of your face. 4. Create Gallery 1 of four photos that describe what you are looking forward to this spring. In the description field, tell me what you are looking forward to and why you like/chose this particular photo. 5. Draw and label your camera parts with the worksheet. 6. On several letter scavenger hunts, spell your name with letters that you see through your viewfinder.