Photography Terms: Shutter, Aperture, Exposure Explained
advertisement

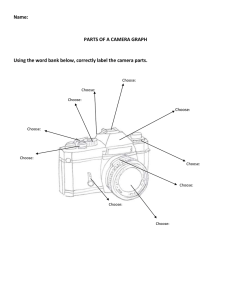
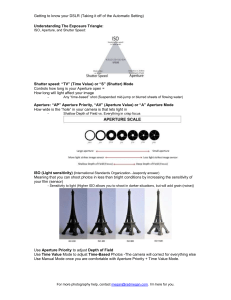
Shutter: a mechanical device for opening and closing the aperture of a camera lens to expose film or the like. Automatic mode: digital cameras have automatic mode that sets focus and exposure, all needed to do is frame the image and push the shutter button. Aperture: an opening, usually circular, that limits the quantity of light that can enter an optical instrument. Scene modes: default setting, camera guesses at the best exposure, adjusting the aperture and shutter speed. Programmed mode: a method of transferring data to and from a storage device (hard disc or CD device). Exposure: the image resulting from the effect of light rays on a photosensitive surface. Overexposure: to expose a film, Plate, or paper for too long a period or with too bright light. Underexposure:1. Inadequate exposure, as of photographic film. 2. A photo negative or print that is imperfect because insufficient exposure. Shutter-priority mode: setting on some cameras that allows to choose a specific shutter speed while the camera adjusts the aperture to ensure correct exposure. Aperture-priority mode: setting on some cameras that allows the user to choose a specific aperture value while the camera selects a shutter speed to match. Manual mode: the photographer has more control over the final image. image sensor: a device that converts an optical image to an electric signal, it is used mostly in digital cameras and other imaging devices. ISO: numerical exposure of index of a photographic film under the system adopted by the International Standardization Organization, used to indicate the light sensitivity of the film emulsion. Depth Of Field: the range of distances along the axis of an optical instrument, usually a camera lens, through which an object will produce relatively distinct image. Sharpness: clearly defined; distinct: a sharp photographic image. f-stops: the setting of an adjustable lens aperture, as indicated by an f number. lens: a piece of transparent substance, usually glass, having to opposite surfaces either both curved or one curved and one plane, used in an optical device in changing the convergence of light rays, as for magnification, or in correcting defects of vision.