Dolch Third Grade Vocabulary Words
advertisement

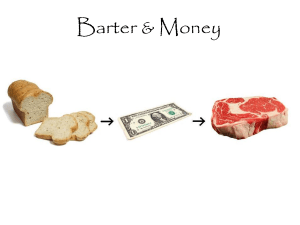
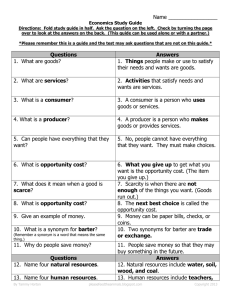
Economics Third Grade Money anything a group of people accept in exchange for goods and services Goods Real items, such as cars, wristwatches, and clothing Goods You need money to buy goods, such as food and clothing. You need money to pay for a place to live or to travel on a bus or a train. You need money to pay for services provided by doctors and dentists. You need money for just about everything. services Work that is done for other people services Services are provided by doctors, lawyers, dentists, teachers, libraries, police, etc… income The money a person gets from salary or wages, interest, investments, and other sources. income Any money that you earn or receive from someone else is called income. Examples: washing the car, babysitting, raking leaves, cutting the grass, etc.. currency any kind of money that is used as a medium of exchange. Budget a plan for using money Costs negative results Benefits Positive results Scarcity A lack of good or services Producer Someone who makes and sells goods or services Consumer Someone who buys the good or services sold by a producer. interdependent To depend on each other Supply The amount producers will make for a certain price. demand The amount consumers are willing to buy for a certain price. Marketplace Where goods may be bought or sold import To buy goods or services from sellers in other countries. export To sell goods or services to people in another country industry All of the people and companies that sell similar goods or services. Common good Whatever helps the most people in the community trade To exchange things with someone else. Barter To trade one item or service for another. In some countries people still barter instead of using money. Some countries even barter with each other. For example, countries that grow wheat can barter with countries that produce sugar. What do you barter? Baseball cards, stickers, snacks? Economy The way that people make, buy, sell, and use things