Cell Theory: Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes Presentation
advertisement

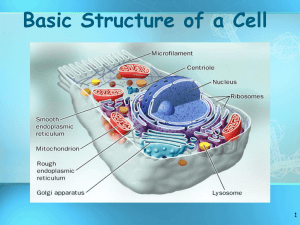
CHAPTER 3 CELLS 3.1 Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life. Discovery of Cells • The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. • A cell is the smallest unit capable of carrying out life functions • More was learned about cells as microscopes improved. • The cell theory is a concept of biology. Examples of Cells Amoeba Proteus Plant Stem Bacteria Red Blood Cell Nerve Cell Wacky theory of cell history • Cell Theory Discovery of Cells • Zacharias Jannsen • Man who invented the compound microscope Discovery of Cells • Robert Hooke • In 1665 he used a microscope to look at a thin slice of cork • Responsible for naming cells after looking at cork • Named them after the chambers that monks lived in Discovery of Cells • Anton van Leeuwenhoek • In 1674, first scientist to observe and describe living cells from looking at pond water • Called them Animalcules The Cell Theory • Matthias Schleiden • German Scientist • 1838, concluded all plants are made of cells • Cofounded the Cell Theory The Cell Theory • Theodore Schwann • German Zoologist • 1839, concluded all animals were made of cells • Cofounder of cell theory The Cell Theory • Rudolph Virchow • German Scientist • 1855, concluded all cells come from other cells • Cell Division Cell Theory • 3 major principles of the Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made of cells 2. All existing cells are produced from other living cells 3. The cell is the most basic unit of life • There are two types of cells: Prokaryote and Eukaryote • All cells share certain characteristics. • Cells tend to be microscopic. • All cells are enclosed by a membrane which regulates the flow of materials into and out of the cell. • All cells are filled with cytoplasm – a jelly like cell membrane substance containing dissolved molecules like proteins and minerals. cytoplasm Bacterium (colored SEM; magnification 8800x) There are two types of Cells: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes • Prokaryotes • Do not have a nucleus. • DNA in cytoplasm • Do not have membrane-bound organelles • Single celled organisms • Less complex Ex Bacteria cell membrane cytoplasm There are two types of Cells: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes • Eukaryotes • Have a nucleus. nucleus • DNA in nucleus • Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles. • Single or Multicellular organelles • More complex and Specialized cell membrane Ex. Most plant and animal cells