Cells Part 1
advertisement
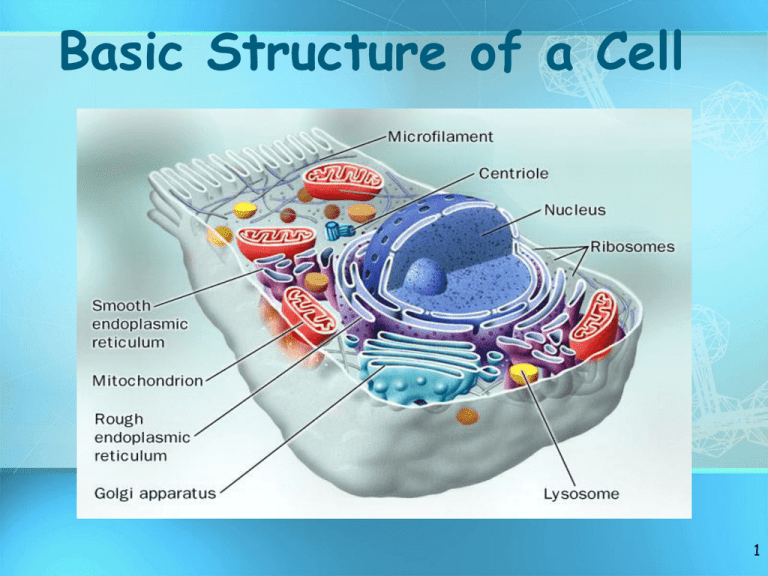
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 I. Modern Cell Theory A. Main Characteristics of Organisms 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5. ORGANIZED 6. RESPOND to environment 7. GROW and DEVELOP 8. EXCHANGE materials with surroundings (water, wastes, gases) 2 B.CELL THEORY 1.All living things are made of cells 2.Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) 3. Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division) 3 C. Robert Hooke 1. First to view cells 2. Robert Hooke (1665): microscope to examine a slice of cork (dead plant cell walls) 3. Saw small boxes, and called them “CELLS” because they looked like the small rooms that monks lived in called Cells. 4 D. Other Scientists Contributed to the Cell 1.Matthias Schleiden: (1838) plants made of cells; cofounder of cell theory 2.Theodore Schwann: (1839) animals made of cells; cofounded the cell theory 3.Rudolph Virchow: (1855) observed cells dividing using a microscope; all cells come from other pre-existing cells by cell division 5 E. Discoveries Since the Cell Theory 1.Endosymbiotic theory: One organism begins to live within another organism and both organism benefit. Eventually, the two organisms evolve to become one new single organism. 2.Lynn Margulis (1970): evidence that some organelles within cells were at one time free living cells themselves. 3.Examples: Chloroplast and Mitochondria (have their own DNA) 6 7 II. Modern Cell Theory A. Cell Size and Types 1. Cells can only be observed under microscope 2. Cell range: 5 – 50 micrometers (microns; 1 cm = 10,000 microns) in diameter 3. Three basic types of cells include (Biggest to smallest: plant, animal, bacteria): i.Plant Cell ii.Animal Cell iii.Bacterial Cell 8 B. Number of Cells 1. Although ALL living things are made of cells, organisms may be: a. Unicellular – composed of one cell b. Multicellular - composed of many cells that may organize into tissues, etc. 9 C. Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic 1.Prokaryotes include bacteria & lack a nucleus or membrane-bound structures called organelles 2. Eukaryotes include most other cells & have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles (plants, fungi, & animals) 10 D. Prokaryotes 1. The first cells 2. Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles 3. Includes bacteria 4. Simplest type of cell 5. Single, circular chromosome 11 D. Prokaryotes 6. Nucleoid region (center) contains the DNA 7. Surrounded by cell membrane & cell wall (peptidoglycan) 8. Contain ribosomes (no membrane) in their cytoplasm to make proteins 12 E. Eukaryotic Cell 1. Contain 3 basic cell structures: a. Nucleus b. Cell Membrane c. Cytoplasm with organelles 2. Two main types of eukaryotic cells a. Plant cells b. Animal cells 13 E. Eukaryotic Cell 3. Organelles a. b. c. d. e. Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound Examples: i. Golgi Bodies – wrap & export proteins ii. Nucleolus – makes ribosomes iii. Lysosomes – digests & gets rid of wastes iv. Ribosomes – makes proteins 14