Revolutionary War Study Guide 2015

Revolutionary War Study Guide 2015
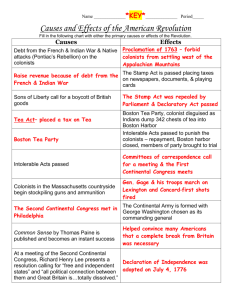
1. Patrick Henry - He used fiery speeches to criticize the British such as "give me liberty or give me death"
2. Cavalry - Horse mounted soldiers used by the army. They usually act as the eyes and ears monitoring the enemy movements
3. Battle of Yorktown - This battle led to the British capturing the important port city of
New York.
4. Committees of Correspondence - a group of colonists whose members regularly wrote letters and pamphlets, reporting on events.
5. Siege - a strategy used by Washington and the French at Yorktown to force Charles
Cornwallis into surrendering.
6. George Rogers Clark - Patriot leader who captured British forts of Cahokia, Kaskaskia and Vincennes in the Ohio Valley.
7. Boston Tea Party - To protest the Tea Act, some colonists protested by dumping 342 crates of tea into the Boston Harbor.
8. Blockade - Shutting of a port to keep people and supplies from moving in or out.
9. 1st Continental Congress - a meeting in Philadelphia of delegates from 12 of the 13 colonies. It was a reaction to the Intolerable Acts.
10. 2nd Continental Congress - They met in Philadelphia after the Battles of Lexington and
Concord. They sent the Olive Branch Petition to the King.
11. John Paul Jones - He is the most famous American Naval Captain of the war. His
Bonhomme Richard defeated the H.M.S Serapis.
12. Common Sense - This pamphlet from Thomas Paine persuaded many colonists to support independence.
13. Olive Branch - The petition that was sent to the King from the Second Continental
Congress asking for peace.
14. French and Indian War - British and American colonists fought this nine year war against their French and Native allies
15. Ally - A nation that works with another nation to reach a common goal.
16. Trenton and Princeton - These victories in New Jersey during the winter were important in giving Americans hope. Washington crossed the icy Delaware River attacking German mercenaries.
17. Treaty of Paris (1783) - This document officially ended the war and forced the British to officially recognize the United States as an independent country.
18. Boston Massacre - British panicked when faced with an angry mob and opened fire.
Five colonists were killed.
19. Boycott - to refuse to buy certain good and services.
20. American Advantages - George was a strong leader, defending their homes, and experienced in firing rifles.
21. Stamp Act - This act passed in 1765, placed a tax on almost all printed material in the colonies-everything from newspapers and pamphlets to wills and playing cards.
22. The Cowpens - Daniel Morgan scored a victory against Cornwallis' best troops at this place in South Carolina.
23. Thomas Jefferson - He wrote most of the Declaration of Independence himself.
24. Lexington and Concord - Outside of Boston, the first shots of the revolution were fired.
Revere, Dawes and others rode to warn the militias.
25. Albany Plan of Union - Ben Franklin's plan to unify the colonists during the French and
Indian War. Colonial governments rejected his plan.
26. Guerilla - Francis Marion the "Swamp Fox" used these types of hit and run tactics to wear down the British in South Carolina.
27. Mercy Otis Warren - She wrote plays criticizing British officials.
28. Intolerable (Coercive) Acts - The British passed these laws to punish Massachusetts for the destruction of tea.
29. Proclamation of 1763 - British government's response to Pontiac's War and other fighting that was occurring with the Natives.
30. Valley Forge - Washington's troops suffered hardships here during the winter of 1777 -
1778.
31. George Washington - The Second Continental Congress appointed him to lead the
Continental Army.
32. British Advantages - A well trained army, powerful navy and money to hire mercenaries from other countries.
33. Samuel Adams - He worked behind the scenes organizing the Sons of Liberty and protests.
34. Treaty of Paris 1763 - This treaty ended the French and War. France lost nearly all of their land in North America.
35. Battle of Saratoga - This battle was a major turning point for the Americans. General
Gates and Arnold kept the British from gaining control of the Hudson River. The French agreed to help the Americans after this victory.
36. Declaration of Independence - This document declared the 13 colonies to be free from
British Rule. It states the natural rights of life, liberty and pursuit of happiness. It also lists 27 wrongs committed by Britain.
37. Bunker Hill - This battle took place on Breed's Hill outside of Boston. The Americans lost because of lack of supplies but proved they could fight bravely. It was a costly victory for the British because they lost more than 1,000 men. Americans lost 400.
38. Tea Act - Act passed in 1773 that made tea less expensive. Colonists viewed this as a trick to get them to pay the tax.
39. Marquis de Lafayette - French noble who volunteered to help Americans.
40. Women - They tended businesses and farms, helped supply troops, cared for the wounded and a few took part in battle.
41. Loyalists - Did not consider unfair taxes a good reason for rebellion.