Chromatography - Miss Fogg's science
advertisement

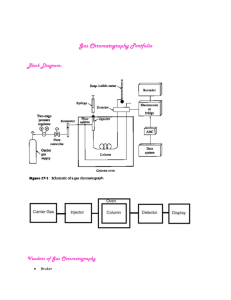
Miss Fogg 2015 Chromatography Chromatography (from Greek word for chromos for color) is a laboratory technique for the physical separation of a mixture into its individual components Mixtures & Compounds A mixture = a collection of 2 or more pure substances that are physically close together but not chemically combined A compound = 2 or more elements that are chemically combined Types of mixtures Solutions Solutions have 2 parts: solute & solvent Solute: the substance that is dissolved Solvent: the substance that does the dissolving Solutions Identify the solute and solvent in each solution… Lemon juice, sugar Water Sugar, coloring… Water Salt, ions… Water Solubility Solubility = a measure of how much of a given substance will dissolve in a liquid. A substance that does not dissolve in water is called insoluble results in a suspension A substance that does dissolve in water is called soluble results in a dissolved solution How Chromatography Works Parts of a mixture will be separated based on their affinity to the solvent AFFINITY: Does the solute “like” the solvent? Chromatography We can separate the components of a mixture in a variety of ways… Types of Chromatography: Liquid Thin-layer Gas Paper Liquid Chromatography Used to identify unknown plant pigments & other compounds Thin-Layer Chromatography Uses thin plastic or glass trays to identify the composition of pigments, chemicals, and other unknown substances. Gas Chromatography Used to determine the chemical composition of unknown substances, such as the different compounds in gasoline shown by each separate peak in the graph below. Paper Chromatography Can be used to separate the components of inks, dyes, plant compounds (chlorophyll), make-up, and many other substances How Chromatography Works Check your understanding… Can chromatography procedures be used to separate… A mixture? It depends – only homogeneous mixtures A compound? NO – this would require a chemical change A dissolved solution? Yes – into solute and solvent Use of Chromatography Chromatography can be used to Separate the different colored components that make up black ink Detect tiny amounts of drugs or certain chemicals in urine samples Chromatography Lab Forensic scientists can determine whether a document contains 2 or more different kinds of ink Different types of water-soluble ink pens vary in their compositions (the mixtures are unique to the brand that manufactures them) Unique mixtures will separate differently on the chromatograph Check your understanding What type of chromatography procedure is shown below: Paper Chromatography Chromatography Lab We will use paper chromatography to investigate the components of inks The final product is called a “chromatograph” RF value How chromatography works Why solvent moves up the paper Affinity