Blood Study Guide
advertisement

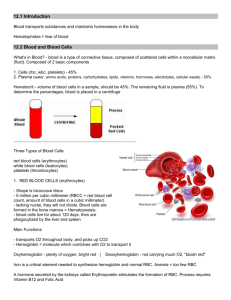
Blood Study Guide 1. Describe a red blood cell. Biconcave, carries oxygen, hemoglobin is responsible for carrying oxygen. 2. Describe a blood sample (what does it consist of and what are the percentages). Cells (rbc, wbc, platelets) - 45% 2. Plasma (water, amino acids, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, vitamins, hormones, electrolytes, cellular waste) - 55% 3. List and describe (functions) types of white blood cells. General function - defend the body against disease-causing agents (microorganisms) Granulocytes (granular cytoplasm) 1. Neutrophils very active in phagocyting bacteria and are present in large amount in the pus of wounds, most common, 60% WBC 2. Eosinophils attack parasites, control allergic reaction; 2% WBC produces Heparin (prevents blood clots) and Histamines (causes inflammatory reaction); less then 1% WBC 3. Basophils Inflammatory Reaction = blood vessels dilate, fluid accumulation and swelling, attraction of WBCs. At the site of an infection, dead and damage leukocytes, bacteria and body cells accumulate = pus 4. Monocytes precursors of macrophages, phagocytes; 6% 5. Lymphocytes main constituents of the immune system which is a defense against the attack of pathogenic microorganisms such as viruses, bacteria, fungi and protista. Lymphocytes yield antibodies and arrange them on their membrane; 30% Agranulocytes (lacking granular cytoplasm) 4. Describe the events in blood clot formation. Hemostasis - the process of stopping bleeding. 3 Key Events - Coagulation causes the formation of a blood clot. 1. Blood vessel spasm - damaged or broken vessels stimule muscle tissue in the walls of the blood vessels to contract. This slows or stops blood flow, lasts for several minutes. Also, platelets release serotonin, a vasoconstrictor which maintains the muscle spasm even longer. 2. Platelet plug formation - platelets stick to surfaces of damaged blood vessels and to each other to form a "plug" 3. Blood coagulation - most effective, forms a blood clot (hematoma). Injury causes an increase in the release of coagulants. Main event - conversion of fibrinogen into long protein threads called fibrin. 5. List the 4 blood types and what antigens and antibodies those blood types would have. 6. What is plasma and what is it composed of? the liquid portion of the blood, 92% water - transport nutrients, gases, vitamins, maintain fluid and electrolyte balance, and pH Plasma Proteins 1. Albumins - made in liver, maintain osmotic pressure and blood volume (blood pressure) 2. Globulins - 3 groups: alpha, beta, gamma a. alpha & beta globulins - from liver, transport lippids and fat-soluble vitamins b. gamma globulins - from lymphatic tussies, antibodies for immunity 3. Fibrinogen - from liver, largest molecules of plasma proteins - important for blood clotting. Major event in blood clotting is the changie of fibrogen into fibrin 7. What are platelets? (thrombocytes) - help initiate formation of blood clots, close breaks in damaged blood vessels 8. Describe how antibodies and antigens work (related to a blood transfusion). Blood that has antibodies on it that is not recognized by the body will be attacked by your immune system 9. What is the Rh factor? How does it affect blood transfusions? A person can have surface Rh antigens (and be Rh +) or no antigens (and be Rh - ) Rh factor is caused by a dominant allele and is inherited like any other trait. Problem: When a fetus is Rh+ and the mother is Rh-, this can cause the mother's immune system to attack the fetus. There are drugs that will suppress this reaction. 10. What is sickle cell anemia? Genetic Disorder, Abnormally shaped blood cells Parents can be carriers (asymptomatic) 11. What is leukemia? LEUKEMIA o Type of cancer o Overproduction of immature white blood cells o They take the place of RBCs o Treatable with bone marrow transplants, chemothemotherapy, radiation 12. What is hemophilia? Difficult time blood clotting, genetic 13. What is septicemia? BLOOD POISONING - SEPTICEMIA o An infection enters the blood stream, can be deadly o Treated with antibiotics 14. 15. 16. 17. What is jaundice? What organ removes damages or old blood cells? liver List the plasma proteins. See question 6 What element is included in hemoglobin molecules to allow oxygen uptake? iron