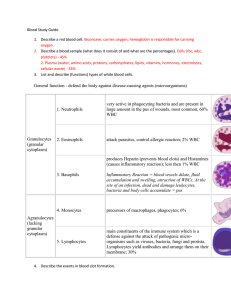
The Circulatory System: The Blood Blood is the fluid in the body that is pumped from the heart and circulated around the body via blood vessels. It is the means by which important substances are transported throughout the body. The average person has 5 liters of blood. Composition: ● Plasma: 55% This is the liquid portion of blood, which allows cells and platelets to float and easily move through blood vessels. Additionally, it transports antibodies (from immune cells), proteins (albumin and fibrinogen) and clotting factors. Waste from cells are also transported to be removed from the body via the kidneys. ○ Blood plasma is made up mostly of: ■ Water: ~ 90% ■ dissolved substances: ● Food: glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol ● Carbon dioxide (in the form of bicarbonate ion) ● Nitrogenous wastes (urea) ● Hormones ● Mineral salts: Na+, K+, Cl+ ● Blood Cells: 45% ○ White Blood Cells (WBC): also known as leukocytes (immune system cells that protects the body). All the white blood cells are able to move like an amoeba, and can move out of blood vessels into the surrounding tissues anywhere in the body. ■ The five types: Neutrophils, Basophils, Eosinophils, Monocytes and Lymphocytes; ● Protect the human body by: ○ Phagocytosis: engulfs disease causing organisms at the sites of infection. ○ Secretion of antibodies: lymphocytes specifically produce antibodies that kill pathogens. ○ Red Blood Cells: also known as erythrocytes. ■ 1mm3 of blood contains 5million RBCs. 7 - 8μm, in size. ■ Biconcave disc shape: thinnest in the center; ● Increases surface area for diffusion of oxygen in and out of the cell; no nucleus allows the cell to hold a large amount of oxygen, so these cells only live for 3-4mths. ■ Contains the red pigmented protein haemoglobin (contains iron) which attaches to O2. ■ Transports a large amount of oxygen (O2) and a small amount of carbon dioxide (CO2). Oxygen is needed for respiration, which is the process that produces energy. ○ Platelets: ■ These are small pieces of cells that contain no nucleus; formed in the bone marrow. They are disc-shaped and small, about 2 - 4μm in diameter. ■ Helps the blood to clot to prevent significant blood loss and to aid in wound healing. Image from: Khan Academy _Image modified from Components of the blood: Figure 4, by OpenStax College, Biology (CC BY 4.0 (Opens in a new window)