Video Problem Handout for Extra Test 1 Review Problems
advertisement

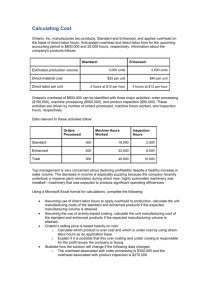
ACG 4361–Cost Accounting – Test 1 Review Problems Problem 1: Hanover manufactures candy bars and uses a normal costing system. It allocates overhead based on direct labor cost. During July, Hanover’s accounts included the following balances and transactions: Factory maintenance & supplies $7,100 Raw materials, beginning $ 7,200 Administrative expenses 26,200 Indirect labor 7,200 Indirect materials transferred to 1,800 Direct labor cost incurred 32,000 production Direct materials used in production 121,000 Work in process, beginning 14,600 Total manufacturing overhead cost 38,700 Sales 331,000 incurred Cost of goods manufactured 186,200 Manufacturing overhead applied 40,100 Cost of materials purchased 127,200 Cost to ship products to customers 4,100 Product advertising costs 18,000 Production supervisor’s salary 22,600 Hanover tracks both direct and indirect material costs in the Raw Materials account. Over and underapplied overhead are considered to be immaterial in amount. Show the calculation of the following amounts and circle your final answer. A. Raw Materials balance at July 31 B. Work in process balance at July 31 C. Total period costs for July D. If the company had used actual costing, what is the amount by which the balance of work in process will differ at July 31 before the adjustment for any over or underapplied amounts? Indicate amount and whether WIP will be greater or smaller than normal costing. Show calculations. E. List any additional information you would need to calculate cost of goods sold Problem 2 - Twellman Enterpirses applies overhead at $11.50 per machine hour. Actual factory overhead was $428,000 and actual machine-hours were 37,500. Budgeted factory overhead was $425,500 and budgeted machine hours were 37,000. The company uses only one control account for factory overhead and deems under or overapplied overhead to be material in amount. Actual year end account balances at December 31 before disposition of the under or over applied amount were as follows: Account Names Account Balances Raw materials $ 24,000 Work in process 72,000 Finished goods 104,000 Cost of goods sold 624,000 Total $824,000 The overhead cost included in each account is not readily determinable. A. Draw and properly name (no abbreviations) the t-account in which any over/underapplied overhead will be found at the end of December. 1) Post all relevant amounts to the account, and 2) display the account balance in its respective place. 3) Circle the account balance. 4) Label as over or underapplied. B. Show the calculation of the balance in cost of goods sold after disposing of any over or underapplied overhead. Circle the balance. C. In addition to allocating/disposing of any material under or overapplied overhead amounts to account balances, on what basis may it be allocated other than that used by Twellman? Problem 3- Radio Flyers produced and sold 400 wagons for $53 each in June. The following information is available for each unit of the finished product produced and sold: Variable manufacturing cost $21 Variable marketing and administrative cost 8 The monthly total fixed manufacturing cost is $3,300 and the total fixed general and administrative cost is $1,100. Show the calculations for each of the following and circle and label each answer. A. Full absorption cost per unit B. Product cost per unit under variable costing C. Gross margin per unit D. Contribution margin per unit E. Total operating profit F. Contribution margin ratio G. Interpret Radio Flyers’ contribution margin ratio, i.e., what specific information does it provide for Radio? Problem 4 Lanahan Freeze produces custom refrigeration units. It applies overhead at a rate of $1.20 per direct labor dollar. At the start of 2011, two jobs were in process with total costs of $1,500 for job 85 and $2,800 for job 86, respectively. In addition, Job 84 was complete with a cost of $1,080 and awaiting shipment at January 1, 2011. During January, the following costs were incurred: Direct Labor Direct Materials Job 85 $650 $240 Job 86 $740 $970 Job 87 $230 $830 Job 88 $610 $540 Job 89 $960 $420 During January, all jobs were completed except job 87. At the end of January, all completed jobs were shipped expect for jobs 88 and 89. 1. Show the flow of jobs by posting ONLY the JOB NUMBERS in the t-accounts below for January. Circle the job numbers that make up the ending balances of work in process, finished goods, and cost of goods sold, respectively. WIP FG CGS 2. Show the calculation of each of the WIP subsidiary account balances for ONLY the jobs that remain in WIP as of the end of January 31. Circle the job totals of each and label by job number. Problem 5- Listed below are effects of various transactions in the manufacturing process using a normal costing system. Identify which account is affected as a result of each action listed in items 1 to 5 by printing the code of the account(s) in the space provided. Accounts RM - Raw Materials Inventory FG - Finished Goods Inventory WIP - Work-in-Process Inventory CGS - Cost of Goods Sold MOH - Manufacturing Overhead X – Some other account Changes 1. Increases when indirect materials are transferred to production 3. Decreases when manufacturing overhead is applied Answers 3. Decreases when goods are sold. 4. Increases when goods are finished. 5. Increases when a factory janitor is paid for work he just performed. Problem 6 –Cinatol uses an actual costing system. It reported the following amounts for July: Work in process, July 1 $26,000 Finished goods, July 1 $25,800 Work in process, July 31 22,000 Finished goods, July 31 25,100 Raw materials, July 1 14,300 Cost of goods manufactured 244,000 Raw materials, July 31 11,800 Direct labor used 61,000 Direct materials used 104,000 Selling costs incurred 43,000 A. In good form, show and properly label which product costs would appear on the balance sheet at the end of July in the space provided. Be sure to label which section they go in (be specific) and show respective amounts. Balance Sheet $ B. Show the calculation of cost of goods sold for the year. Circle your answer. Problem 7: Rock Roofing applies manufacturing overhead based on direct labor hours. Information concerning manufacturing overhead and labor for July follows: Estimated direct labor 5,400 hours @ $14.00 Direct labor incurred 5,500 hours @ $14.70 Estimated manufacturing overhead $122,040 Actual manufacturing overhead $120,350 The production supervisor requisitioned materials for Job 954 totaling $10,500 during July, of which $800 were indirect. Employees worked 270 hours on Job 954 and were paid an average of $14.50 per hour. A. Show the calculation of the total cost of Job 954. Circle the total cost. B. Show the calculation of total prime costs in job 954. Circle the total. Problem 8: Modex, Inc. manufacture headphones and had unit production costs totaling $11.00 for direct materials, $4.50 for direct labor, and $2.40 for variable overhead. During the year, 12,000 headphones were produced and 12,800 of them were sold. The company has annual fixed selling and administrative costs of $31,800 and fixed annual manufacturing overhead costs totaling $48,000. The finished goods inventory at the beginning of the year had 1,500 headphones. Operating income using variable costing is $21,700. In good form, use the reconciliation format we used in class to determine operating income under absorption costing. Problem 9- Radio Flyers has provided the following information the wagons it produces and sells: Wagons produced 14,000 Wagons sold 15,200 Beginning inventory in units 2,700 Selling price per unit $24 Direct material per unit $4.50 Direct labor per unit $3.20 Variable manufacturing overhead per unit $2.50 Variable selling cost per unit $1.00 Annual fixed manufacturing overhead $28,000 Annual fixed operating expenses $16,000 Show the calculations for each of the following in the space provided and circle and label each answer. A. Contribution margin per unit B. Total gross profit D. Operating income using absorption costing E. Product cost per unit using variable costing F. Fixed manufacturing overhead costs that are included on the balance sheet at year end using full costing