Aldol/Retroaldol reactions Major concepts The aldol addition is the
advertisement

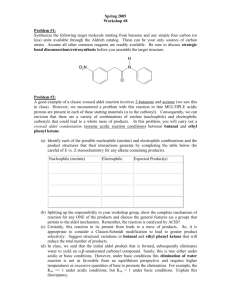
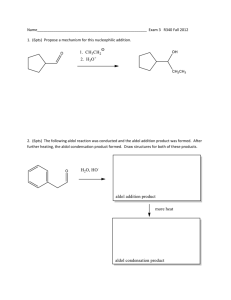
Aldol/Retroaldol reactions Major concepts The aldol addition is the reaction of an enolate nucleophile with an aldehyde/ketone electrophile The product of an aldol reaction is a -hydroxy ketone/aldehyde The aldol condensation occurs after the aldol addition, in which an elimination occurs The product of an aldol condensation is an -unsaturated carbonyl A retroaldol reaction is the aldol reaction with the reaction lying in the opposite equilibrium. Vocabulary Aldol addition Aldol condensation Enolate Retroaldol Students should be able to: Identify the nucleophile and electrophile in an aldol reaction. Predict the aldol addition product Predict the aldol condensation product Predict the products of a retroaldol reaction Daily Problems 1. You already did these reactions last time, but now you recognize them as an aldol reaction. Identify the nucleophile and the electrophile in each reaction, then fill in each box. 2. In the case where an aldehyde is mixed with hydroxide, some of the aldehyde is deprotonated at the alpha position to make the nucleophile, and some remains as the aldehyde and serves as the electrophile. Draw the structure of the nucleophile and electrophile in this reaction. 3. Compare this reaction to the one in problem 2. The difference is that this reaction will not undergo an aldol reaction. What is the problem? Is the problem the nucleophile or the electrophile? 4. Predict the products of these aldol addition reactions. 5. Predict the products of these aldol condensation reactions. 6. Now work backwards. Given this aldol product, indicate which Carbon-Carbon bond was made. Now decide which carbon was the nucleophilic carbon and which was the electrophilic carbon in the starting materials. Finally, draw structures of the starting nucleophile and electrophile. 7. The reaction below is taken from the gluconeogenesis pathway. (This path is the opposite of the glycolysis pathway.) In gluconeogenesis, small carbon molecules are linked together to make glucose, a six carbon sugar through the action of the enzyme aldolase. 1 H2C 2 H H2C C H2C -2 OPO3 O C + OH HC H2C -2 OPO3 C O aldolase O 3 HC OH HC OPO3-2 HC H2C OH 4 5 6 OH OH OPO3-2 A. What type of reaction is this? (Hint: look at the name of the enzyme.) B. The carbons of the product are numbered 1-6. Number the carbons of the two reactants with corresponding numbers 1-6. C. When a carbon/carbon bond is made, it is because one carbon is acting as a nucleophilic center and another carbon is acting as an electrophilic center. Which carbon atom, 1-6, is the nucleophilic center and which is the electrophilic center? D. Draw a mechanism for this reaction. The enzyme first serves as a base to pull a proton off the nucleophilic carbon to make it a nucleophile. In the last step, it acts as an acid to protonate the negatively charged oxygen atom. Cumulative Problems 8. Identify the nucleophile and electrophile in each reaction. Are these reactions nucleophilic substitutions or nucleophilic additions? Predict the products. Extension problem: 9. What is the product if an amine is the nucleophile that adds into an aldehyde?