Examples - Chem-is
advertisement
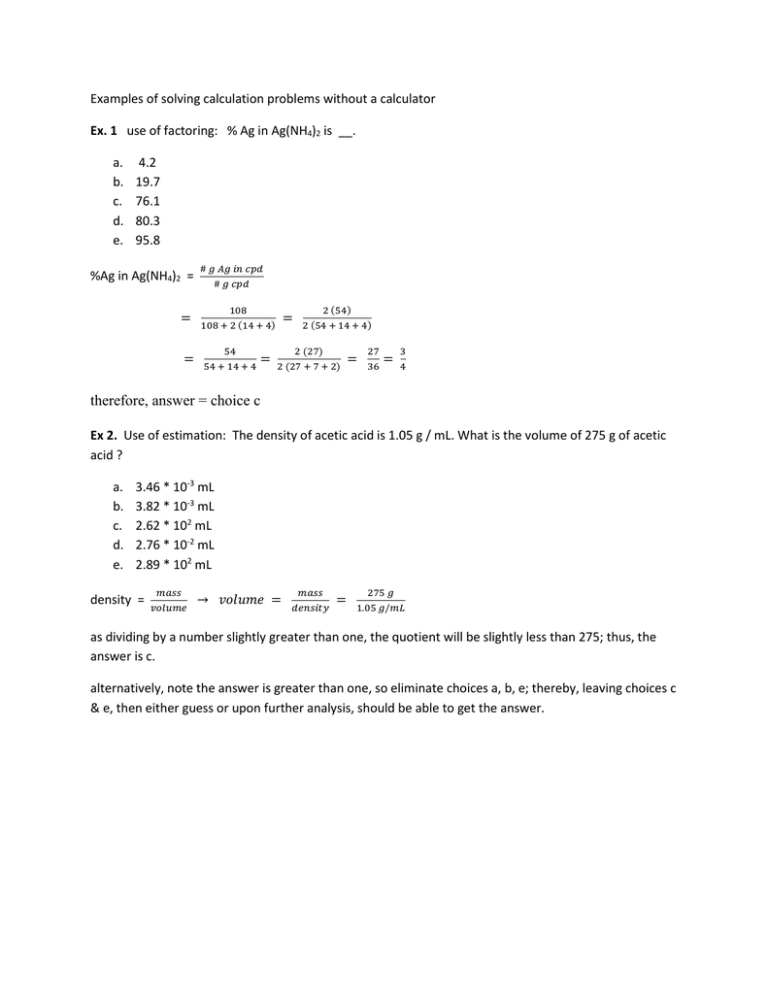
Examples of solving calculation problems without a calculator Ex. 1 use of factoring: % Ag in Ag(NH4)2 is __. a. b. c. d. e. 4.2 19.7 76.1 80.3 95.8 %Ag in Ag(NH4)2 = = = # 𝑔 𝐴𝑔 𝑖𝑛 𝑐𝑝𝑑 # 𝑔 𝑐𝑝𝑑 108 108 + 2 (14 + 4) 54 54 + 14 + 4 = = 2 (54) 2 (54 + 14 + 4) 2 (27) 2 (27 + 7 + 2) = 27 36 = 3 4 therefore, answer = choice c Ex 2. Use of estimation: The density of acetic acid is 1.05 g / mL. What is the volume of 275 g of acetic acid ? a. b. c. d. e. 3.46 * 10-3 mL 3.82 * 10-3 mL 2.62 * 102 mL 2.76 * 10-2 mL 2.89 * 102 mL density = 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 → 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 = 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑦 = 275 𝑔 1.05 𝑔/𝑚𝐿 as dividing by a number slightly greater than one, the quotient will be slightly less than 275; thus, the answer is c. alternatively, note the answer is greater than one, so eliminate choices a, b, e; thereby, leaving choices c & e, then either guess or upon further analysis, should be able to get the answer. Ex. 3 use of estimation: When 12 copper pennies are submerged in water ,the pennies displace 4.13 cm3 of water. If the combined mass of the pennies is 36.93 g, what is the density of copper ? a. b. c. d. e. 0.745 g / cm3 3.49 g / cm3 8.94 g / cm3 32.8 g / cm3 153 g / cm3 𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑦 = 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 = 36.93 𝑔 4.13 𝑐𝑚3 ≅ 37 4 =9 1 4 = 9.25 Notice that the answer choices are somewhat different, where the nearest value is given by choice c and that the number of pennies, 12, is extraneous. Ex 4. Use of estimation: copper has two naturally occurring isotopes. A typical sample consists of 69.17% 63Cu (62.939598 amu) and 30.83% 65Cu (64.927793 amu). Calculate the atomic mass of copper. a. b. c. d. e. 62.93 amu 62.33 amu 62.45 amu 63.55 amu 63.93 amu Average mass = ∑ 𝑚𝑖 𝑝𝑖 ≈ 69% 63 + 31% 65 The pi values maybe viewed as a “’weighing factor”. Notice that the answer is between 63 & 65, so eliminate choices a, b, c, since they are less than 63. As such, so your remaining choices are d & e, where both choices are between 63 and 64. If the isotope distribution were 50%, the answer would be 64. As 63Cu is 69%, which is greater than 50%, the answer should be closer to 63 than 64, so the answer is choice d. Ex 5. Use of estimation. At its boiling point of - 10 °C, 20.7 kJ of heat is required to vaporize 53.2 g of sulfur dioxide. What is the enthalpy of vaporization of SO2 ? a. b. c. d. e. 5.39 kJ/mol 17.2 kJ/mol 20.7 kJ/mol 24.9 kJ/mol 38.9 kJ/mol 20.7 𝑘𝐽 ΔHvap = 53.2 𝑔 𝑆𝑂 ∗ (32+32)𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙 2 ≅ 21 64 53 > 21 So the answer is D; choice E is too big, while choices a, b, & c are too small. The boiling point is extraneous information. Ex 6. Use of estimation. Dinitrogen trioxide, a blue solid, dissociates to form nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide gases. What mass of nitrogen dioxide is formed from the decomposition of 12.8 g of N2O3 ? a. b. c. d. e. 5.05 g 6.40 g 7.75 g 12.8 g 21.1 g The chemical equation is N2O3 NO + NO2. i.e. 12.8 g N2O3 = __ g NO2 # g NO2 = 12.8 𝑔 𝑁2 𝑂3 ∗ ≅ 13∗46 75 ≅ 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁2 𝑂3 75 𝑔 𝑁2 𝑂3 13∗50 75 So the answer is choice C. = ∗ 13 ∗ 2 3 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑂2 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁2 𝑂3 = 26 3 ≤9 ∗ 46 𝑔 𝑁𝑂2 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑁𝑂2








