PowerPoint - Minority Student Achievement Network
advertisement

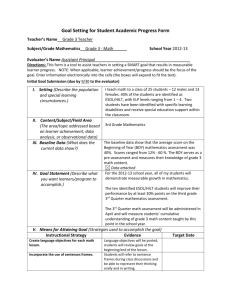
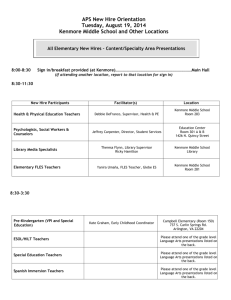
Analia Almada, LPC, LMFT, NCC Francesca Reilly-McDonnell, MA Lourdes Rubio LPC, NBCC, DAPA Israel Salas, MA Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 1 Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 2 Language Development Social and Cultural Processes Cognitive Development Academic Development Language Acquisition for School, by Virginia P. Collier, 1994 3 Special Qualifications: Bilingual and Bicultural MA in Counseling, Psychology, Social Work Extensive experience counseling families and working with adolescents Knowledgeable about the diverse community Knowledgeable about community resources Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 4 1.Highly educated, literate newcomers 2.Under -schooled newcomers 3.Long term ELLs with 6+ years of US schooling 4.ELLs progressing successfully through a developmental sequence 5.Struggling ELLs failing to make expected progress in the mainstream Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 5 One: What I value most about my culture… Two: What would I miss the most about my culture if I had to immigrate Three: What strengths from your culture would you like to bring to the new culture? Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 6 Acculturation is …the process that occurs when two cultures come into long-term contact, which produces changes in the language, behaviors, and values of individuals in both cultures. “Explaining the Gender Disparity in Latino Youth’s Education: Acculturation and Economic Value of Education”. Colón and Sanchez, 2010. Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 7 Family separation English proficiency/ Reason education immigration for Factors Influencing Acculturation SES Culture Language Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 8 Acceptance or Rejection of Dominant Culture Maintenance or Rejection of Original Culture Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 9 Immigration Integration (Acculturation) Elation Model of Acculturation Recovery and Optimism Culture Shock (Resistance) From “Teaching and Learning in Multicultural Schools”, Elizabeth Coelho, 1998; and http://www.helium.com/items/2168437-processes-of-culture-change-acculturation 10 School/ Community Family Stress Immigration of Parent Child Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 11 Healthy vs. Unhealthy Acculturation Adaptation/Integration Assimilation Marginalization Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 12 Rejection of new culture Rejection Rejection ofhome home of culture culture Denialof of Denial previous previous identity identity COMPLETE Complete Assimilation ASSIMILATION Family Family and and social social difficulties difficulties Discard Discardof of native native language language Exclusion from new society MARGINALIZATION Rejection of new language Family and social difficulties Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 13 Issues of Acculturation Attachment Separation Resentment Grief Anger Reunification New family units Differences in expectations Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 14 Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 15 Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 16 Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 17 Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 18 Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 19 Reunification: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Separation Attachment Anger Grief Adaptation ◦ From excitement to frustration to anger Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 20 Resentment Commitment to family in their country. Expectations ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Fit into the new family Care for siblings School attendance Contribute to household expenses Work Newly arrived ◦ Work vs. study ◦ Condition for staying in the USA ◦ Adult life in their countries Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 21 Children that come without adults Older relatives take them in Expectations to work School is temporary Expectation to be independent Little or poor supervision Transient students Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 22 Newly arrived students: Issues of acculturation Reunited students: Issues of acculturation, separation, resentment, reunification Selected According to Student Needs: 1. Skills– Empowerment, cohesiveness. 2. Academic and/or Attendance Groups 3. Relationships 4. Coping with trauma 5. Career exploration 6. Anger and stress management Grade level groups Support groups Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 23 Bullying Dating Parental control Gender roles in society Religion Domestic Violence History of political tensions Clothing Eating habits School system Substance abuse Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 24 Students are able to process the impact of the immigration experience Students are able to concentrate in the academics during classes, instead of acting out their desperation Students find a place where others share their experiences and find solutions together Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 25 Academic Language and Skills for Success (ALAS) Parent Leadership Facilitation Latino Youth Leadership Conference and other Leadership Opportunities Multicultural Parent Conference Clubs: Latin American Student Association, Hispanic Student Association, International Club, Latinos for Excellence Lunch Bunch Community Partnerships The Dreamers Project Parenting Workshops Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 26 “Their conversational ability in English is similar to that of a native speaker. Nevertheless, they have not developed academic English, and their school performance is well below average. They need academic support from teachers who are knowledgeable about second-language issues but they do not need the kind of support designed for special education students.” (Freeman & Freeman 2002, p. 29) Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 27 7 years+ Oral English proficiency vs. Academic English Proficiency Low Literacy in 0wn language Below grade level achievement Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT, 2015 False perception of their academic achievement Low test scores 28 Need support from staff who are knowledgeable about the Need support from staff knowledgeable about the process of English language acquisition process of acculturation Experience conflicting cultural identification: -they are Americans but see themselves as marginalized Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 29 Resources: For information and specific ways of addressing the issues of Immigrant Reunification visit Silvia’ Burwell’s Blog: THE IMMIGRANT FAMILY: HEALING THE LOST BOND MPI (Migration Policy Institute) Free Webinars on Regions: · Africa (sub-Saharan) · · · · · · · · · · Asia and the Pacific Central America & the Caribbean Europe European Union Middle East & North Africa North America United States Canada Mexico South America Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 30 Reunifed Family Video Bridge Manual for research and assessment information regarding ELLs Email Francesca.reilly@apsva.us for more information For Descriptor of each English Language Proficiency Level visit WIDA Website: www.wida.com Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 31 Arlington Public Schools, ESOL/HILT Counselors, 2015 32