2. Skeletal Muscle Anatomy WEB
advertisement
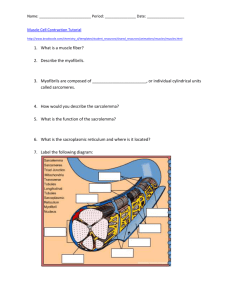
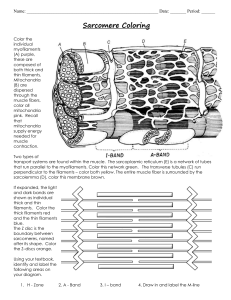
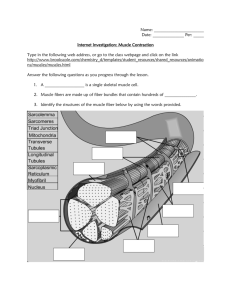
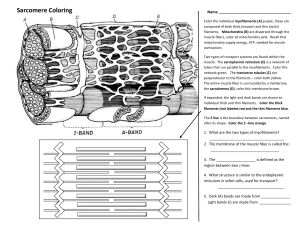
Skeletal Muscle Microscopic Anatomy Chapter 10 Microscopic Anatomy • Muscle fibers = muscle cells: long and multinucleate • Sarcolemma: cell membrane • Sarcoplasm: cytoplasm; rich in oxygen-storing myoglobin protein • Myofibrils: bundles of contractile proteins; fill most of the cytoplasm; 100’s to 1000’s per cell • Sarcomeres: the repeating functional unit of contraction in each myofibril •T tubules (transverse tubules): narrow tubes that are continuous with sarcolemma, conduct impulses • Sarcoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER): stores Ca++ (muscle contraction begins when stored Ca++ ions are released into sarcoplasm) • Mitochondria: provide ATP for contraction Closer Look at Myofibril Composition • thin filaments: actin (plus tropomyosin & troponin) Fig. 10.5 • thick filaments: myosin Sarcomere Structure • Z lines: the boundary between sarcomeres • A band: overlap of thick (myosin) filaments & thin (actin) filaments • I band: thin (actin) filaments only • H zone: thick (myosin) filaments only Fig. 10.3