Nervous: Neurons
advertisement

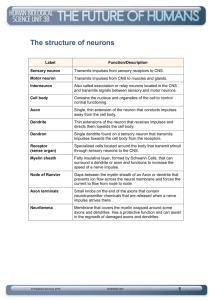
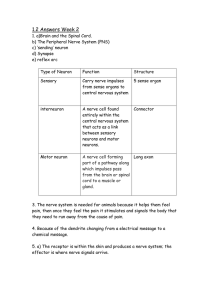
Neurons: The Nerve Cells Our Goals Today • Identify and give functions for each of the following: dendrite, cell body, axon, axoplasm, and axomembrane • Differentiate among sensory, motor, and interneurons with respect to structure and function • Relate the structure of a myelinated nerve fibre to the speed of impulse conduction, with reference to myelin sheath, Schwann cell, node of Ranvier, and saltatory transmission • Describe the structure of a reflex arc (receptor, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, and effector) and relate its structureto how it functions Neuron • Dendrite: conducts impulses towards a cell body • Cell Body: contains the nucleus (maintains the cell) • Axon: conducts impulses away from a cell body • Axomembrane: cell membrane surrounding the axon • Axoplasm: cytoplasm inside the axon • Within each neuron the impulse travels in the following sequence: • Dendrite → Cell Body → Axon Neuron Types of Neurons • Sensory Neurons • Association or Interneurons • Motor Neurons Sensory Neurons • Long dendrite, short axon • Cell body and dendrite are located outside the spinal cord • Conduct impulses to the spinal cord Motor Neurons • Short dendrite , long axon • Long axon between the cell body and an effector (muscle or gland) • Axon is located outside of the spinal cord • Dendrite and cell body are located within the spinal cord Interneurons • Interconnect nerve cells – Sensory neurons with motor neurons • Entirely in the CNS Nerves • Grouping of nerve cells (neurons) • Mixed nerves: dendrites of sensory neurons and axons of motors neurons located in the same nerve • May contain hundreds of long fibers • Covered with a myelin sheath – Fatty tissue – Composed of Schwann cells wrapped around each nerve fiber – Areas between Schwann cells are called nodes of Ranvier • Myelin sheath has two functions – Prevents cross-communication between neurons – Allows impulses to travel faster Nerves Spinal Nerves: connected to the CNS at either the dorsal or ventral side of the spinal cord (mixed nerves) Sensory Nerves • Connected through a dorsal root • Sensory neurons - cell bodies are located in the dorsal root ganglion Motor Nerves • Connected through a ventral root • Motor neurons - cell bodies are located in the spinal cord • Cell bodies of motor neurons along with interneurons makes inner part of the spinal cord dark in colour (grey matter) White Matter: outer regions of the spinal cord Reflex Arc • No thought required, protective mechanism • Involves all 3 types of neurons 1) Receptor (eg. Pain receptor) detects a stimuli that exceeds the threshold and initiates an impulse 2) Impulse travels through a sensory neuron 3) To an interneuron 4) To a motor neuron 5) Axon of the motor neuron sends the impulse to the effector – Muscle (to cause movement) – Gland (cause a secretion) • Synapse: connections between 2 nerve cells • Brain will be alerted by other interneurons that reflex took place Reflexive Arc Remember Our Goals... • Identify and give functions for each of the following: dendrite, cell body, axon, axoplasm, and axomembrane • Differentiate among sensory, motor, and interneurons with respect to structure and function • Relate the structure of a myelinated nerve fibre to the speed of impulse conduction, with reference to myelin sheath, Schwann cell, node of Ranvier, and saltatory transmission • Describe the structure of a reflex arc (receptor, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, and effector) and relate its structureto how it functions