Nuclear Reactions
advertisement

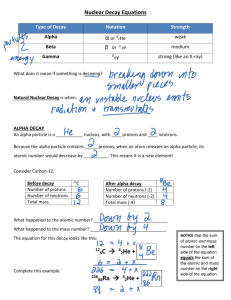
Nuclear Reactions Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Decay Objectives : State what is meant by alpha, beta and gamma decay. Identify the processes occurring in nuclear reactions written in symbolic form. The Atom The atom consists of two parts: 1. The nucleus which contains: protons neutrons 2. Orbiting electrons. The Atom •All matter is made up of elements (e.g. carbon, hydrogen, etc.). •The smallest part of an element is called an atom. •Atom of different elements contain different numbers of protons. •The mass of an atom is almost entirely due to the number of protons and neutrons. Nuclear Symbol Mass number A X Z Atomic number Element symbol • Chlorine - 35 Nuclear Symbol Hyphen notation: carbon -14 Nuclear symbol: Mass # Atomic # 14 6 C PEN from nuclear symbol • Chlorine-37 atomic #: 17 mass #: 37 # of protons: 17 # of electrons: 17 # of neutrons: 20 37 17 Cl Practice • Write the nuclear symbol for each isotope below: Sodium - 25 Uranium – 235 Gold – 197 Practice • Identify the PEN for each od the previous isotopes 25 11 #p Na #e #n 235 92 U #p #e #n 197 79 Au #p #e #n There are many types of uranium: 235 U 92 238 U 92 Mass # Mass # Atomic # Atomic # Number of protons Number of protons Number of neutrons Number of neutrons There are many types of uranium: 238 235 U 92 U 92 Mass # 235 Mass # 238 Atomic # 92 Atomic # 92 Number of protons 92 Number of protons 92 Number of neutrons 143 Number of neutrons 146 Isotopes have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. Nuclear Reactions •Most isotopes that occur naturally are stable. •Few naturally occurring isotopes & all man-made isotopes are unstable. •Unstable isotopes become stable by releasing different types of particles. •This process is called radioactive decay and the elements which undergo this process are called radioisotopes. Radioactive Decay Radioactive decay results in the emission of either: • an alpha particle (a), • a beta particle (b), • a gamma ray(g). Alpha Decay • Is identical to that of a helium nucleus • Contains two protons and two neutrons 4 2 He Alpha Decay A X Z A-4 4 Y He + Z-2 2 unstable atom alpha particle more stable atom Alpha Decay 222 226 Ra 88 Rn 86 4 He 2 Alpha Decay A A-4 4 226 222 4 X Z Ra 88 Y + Z-2 Rn + 86 He 2 He 2 Alpha Decay Copy the following equation and write the correct answer 222 Rn 86 222 Rn 86 A 4 Y He + Z 2 218 Po + 84 4 He 2 Alpha Decay Copy the following equation and write the correct answer A 230 4 234 230 4 X Z U 92 Th He + 90 2 Th He + 90 2 Alpha Decay Copy the following equation and write the correct answer 230 Th 90 230 Th 90 A 4 226 4 Y He + Z 2 Ra He + 88 2 Alpha Decay Copy the following equation and write the correct answer A 214 4 218 214 4 X Z Po 84 Pb He + 82 2 Pb He + 82 2 Beta Decay • A beta particle is a fast moving electron which is emitted from the nucleus of an atom undergoing radioactive decay. • Beta decay occurs when a neutron changes into a proton and an electron. Beta Decay • A result of beta decay, the nucleus has one less neutron, but one extra proton. • The atomic number increases by 1 and the mass number stays the same. 0 -1 e Beta Decay 218 218 Po 84 At 85 0 e -1 Beta Decay A X Z 218 Po 84 A 0 218 0 e Y + Z+1 -1 At + 85 e -1 Beta Decay 234 A 234 234 Th 90 Th 90 Y + Z Pa + 91 0 e -1 0 e -1 Beta Decay A 210 e -1 210 210 0 X Z Tl 81 Pb + 82 Pb + 82 0 e -1 Beta Decay 210 A 210 210 Bi 83 Bi 83 Y + Z Po + 84 0 e -1 0 e -1 Beta Decay A 214 e -1 214 214 0 X Z Pb 82 Bi + 83 Bi + 83 0 e -1 Gamma Decay Gamma rays are not charged particles like a and b particles. Gamma rays are electromagnetic radiation with high frequency. When atoms decay by emitting a or b particles to form a new atom, the nuclei of the new atom formed may still have too much energy to be completely stable.