Chapter 7 Study Guide
advertisement

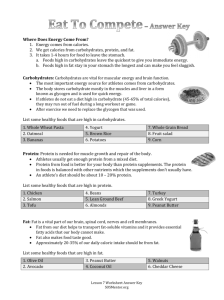
Chapter 7 “Nutrition: The Nutrients” Study Guide The recommended percentage of carbohydrates in a healthy diet is 60%. There are 9 calories of fat in a gram. A potato is an example of a starch. The major source of fuel for the body is fat. A can of orange soda is an example of empty calories. A total vegetarian would not eat eggs, poultry, or milk products. Working cell parts are made from proteins. 60% of the body’s weight is water. Sucrose, fructose and lactose are sugars, and cholesterol is a fat. Because the body can turn alcohol into fat, alcohol has to be considered an energy source. Too much fiber can cause diarrhea. Carbohydrates supply one of the main fuels of the body, a sugar called glucose. Amino acids are the building blocks for protein. The body can tolerate small quantities of toxins, such as alcohol. A calorie is a unit used to measure energy. The main carbohydrate in vegetables and grains is starch. Most kinds of fiber move through the digestive tract almost unchanged. Saturated fats are derived mainly from animal sources. Amino acids are simple forms of protein normally used to build tissues. Nutritional deficiencies and under nutrition are both forms of malnutrition. The major substance of which bodies are made is water. Lactose is the sugar found in milk. High blood pressure is also called hypertension. Three nutrients-carbohydrates, fats, and protein-provide energy the body can use. Carbohydrates important in the diet are starch, fiber, and sugars. The average person will consume about 50 tons of food in a lifetime. Over nutrition is considered a form of malnutrition. Sodium chloride is ordinary table salt, a much-loved food seasoning. Nutrients are divided into six classes: carbohydrates, fat, protein, vitamins, minerals, and water. Fat supplies the body with another main fuel, fatty acids. Peanut butter contains over 70% fat. The body can tolerate alcohol in small quantities but in larger quantities is poisoned by it. Glucose is stored in the liver and muscles are glycogen. In a balanced meal, fat provides most of the meal’s calories. Another form of carbohydrate in foods-fiber-is not digestible by human beings and so provides no calories, however, it helps to maintain the health of the digestive tract. Constipation is a result of not enough fiber in the diet. A healthy diet contains more unsaturated fats than saturated fats. A set of 20 different amino acids form proteins. Nutrients are compounds in food that the body requires for proper growth, maintenance, and functioning. Three minerals –sodium, chloride, and potassium-serve as electrolytes, minerals that dissolve in body fluids and carry electrical charges, Protein: a class of nutrients that builds body tissues and supplies energy. Vitamins: essential nutrients that do not yield energy, but that are required for growth and proper functioning of the body. Minerals: elements of the earth needed in the diet, which perform many functions in body tissues. Glucose: the body’s blood sugar a simple form of carbohydrate. Digestion: the breaking down of food into nutrients the body can use. Balanced meal is a meal that contains many kinds of food that offer carbohydrate, fat, and protein all together.