measurement
advertisement
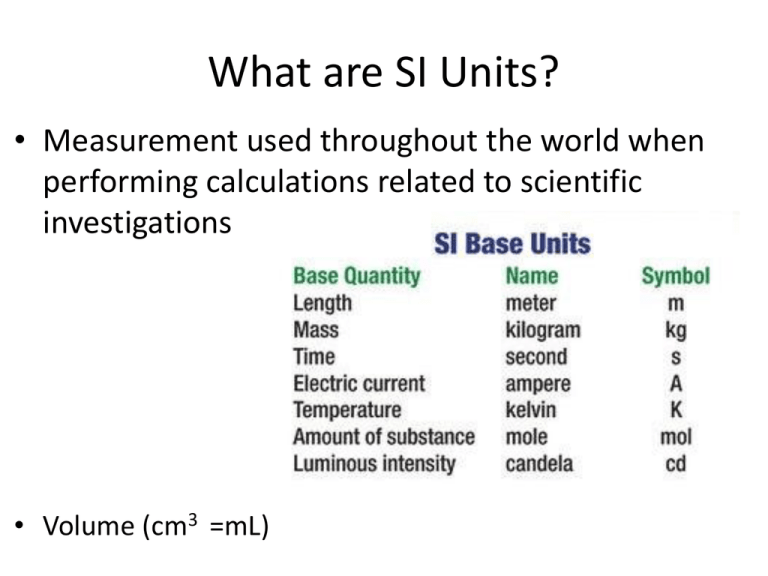
What are SI Units? • Measurement used throughout the world when performing calculations related to scientific investigations • Volume (cm3 =mL) Choose from: Centimeters, ounce, grams, °C, milliliters 1.) Which unit of measurement would you use to record the mass of 10 sunflower seeds? 2.) Which unit of measurement would you use to record the volume of 10 sunflower seeds? 3.) Which unit of measurement would you use to record the temperature of a chemical reaction? 4.) Which unit of measurement would you use to measure the length of 1 sunflower seed. Why is it important for scientific measurements to be reproducible and accurate? • If you are able to take measurements of an object and get the same result each time, you increase your accuracy. • All experiments should be reproducible. You should be able to do them again and get the same exact results • What does it tell you if you don’t get the same results the second or third time? Three important points that you should keep in mind when you record scientific measurements 1.) You need both the measurement (for ex: 2.0, 3.4, 5.0) and the unit (g, mL, s, m) because each scientific measurement has a very different meaning. *Need to know what you measured 2.) Units need to be apart of an agreed upon system or measurements would not be accurate 3.) Write the measurement in proper form. This usually means using a decimal. You want your scientific measurement to be as accurate as possible. • • • • 1 inch = 2.54 cm I L = 33.8 fl oz 1000 mm = 1 m 100 cm = 1 m You need to know SI unit prefixes Base scale of 10 kilo x1000 hecto x 100 deca x10 BASE (meter, gram, liter, second) deci 1/10 centi 1/100 milli 1/1000 For example: kilometer (1000x more than 1 meter) hectometer (100 times more than 1 meter) decameter (10 times more than 1 meter) meter (1 meter) decimeter (there are 10 decimeters in 1 meter) centimeter (there are 100 decimeters in 1 meter) millimeter (there are 1000 millimeters in 1 meter) • Density = how much matter is occupying a certain amount of space • = the measure of how closely packed matter is within a given space • If an object sinks it is DENSER than the liquid it is placed in • If an object floats it is LESS dense than the liquid it is placed in • Convert 80 °F to °C • Convert 65 °F to C • Convert 60 °C to °F • Convert 20 °C to K • Convert 55 °C to K • Convert 100 K to °C