Metric System & Scientific Measurement Presentation

SCIENTIFIC MEASUREMENT
Metric System
(international system of units or SI)
- A decimal system (based on 10) that scientists and everyone else in the world uses, except the U.S.
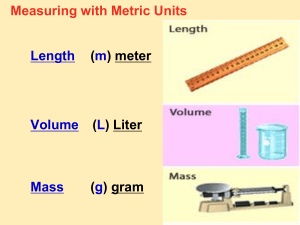
LENGTH
Meter - basic unit of length. A little more than 3 feet. Use to measure a room.
Kilometer - = 1000 meters. Use to measure long distances. About 2/3 of a mile.
Centimeter - 100 cm = 1 meter. Use to measure smaller objects, like a bird.
Millimeter - 1000 mm = 1 meter. Use to measure even smaller objects, like the pupil of an eye.
Micrometer - 1 million = 1 meter. Use to measure microorganisms.
Nanometers - 1 billion = 1 meter. Use to measure very small organisms, like viruses.
VOLUME
The amount of space an object takes up is called its volume.
Liter - (L) the basic unit of volume in the metric system, slightly larger than the quart.
Milliliter-(mL) 1/1000 of a liter: 1000 mL= 1 L
Use L and mL to measure liquids and gases.
MASS AND WEIGHT
Kilogram - (Kg): a little more than 2 lbs.
Gram - (g): 1/1000 of a Kg. 1000 g = 1
Kg
Milligram - (mg): 1/1000 of a gram
MASS VERSUS WEIGHT
Mass is not equal to weight
Mass - the measure of the amount of matter in an object. Is constant
Weight - is a measure of the force of attraction between objects due to gravity.
Is not constant.
DENSITY
The measurement of how much mass is contained in a given volume of an object.
Density=Mass/Volume
Every substance has its own characteristic density.
TEMPERATURE
Scientist use the Celsius scale
0 degrees = the freezing point of water.
100 degrees = boiling point of water.
QUICK QUIZ
1. What are 2 benefits of using the
International System of Units?
2. What is the basic unit for length? For mass? For volume?