Financial accounting
advertisement

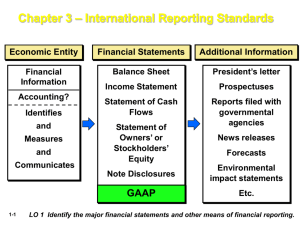
StIce | StIce |Skousen Financial Reporting Chapter 1 Intermediate Accounting 16E COPYRIGHT © 2007 Thomson South-Western, a part of The Thomson Corporation. Thomson, the Star logo, and South-Western are trademarks used herein under license. Learning Objectives 1. Describe the purpose of financial reporting and identify the primary financial statements. 2. Explain the function of accounting standards and describe the role of the FASB in setting those standards in the United States. 3. Recognize the importance of the SEC, AICPA, AAA and IRS to financial reporting. Learning Objectives (cont.) 4. 5. 6. Realize the growing importance and relevance of international accounting issues to the practice of accounting in the United States and understand the role of the IASB in international accounting standard setting. Understand the significance of the FASB’s conceptual framework in outlining the qualities of good accounting information, defining terms such as asset and revenue, and providing guidance about appropriate recognition, measurement, and reporting. Identify career opportunities related to accounting and financial reporting and understand the importance of personal ethics in the practice of accounting. Definition of Accounting “Accounting is a service activity. Its function is to provide quantitative information, primarily financial in nature, about economic entities that is intended to be useful in making economic decisions—in making reasoned choices among alternative courses of action.” (Statement of the Accounting Principles Board No. 4, p. 8) Key Features Accounting: • Provides a vital service in today’s business environment. • Uses quantitative financial information in conjunction with qualitative evaluations to help make decisions. • Helps in decision making for scarce resources. • Impacts economic decisions about the future by analyzing past information. Users of Accounting Information • Stakeholders are all parties interested in the financial health of a company. • Internal users make decisions that directly affect the internal operations of the company. • External users make decisions concerning their relationship to the enterprise. Branches of Accounting • Management accounting deals with financial reporting for internal usersespecially management. • Financial accounting focuses on creating and communicating financial information for external users. Financial Reporting The income The statement of The balance sheet statement reports, cash flows reports, reports, as of a forina specified for a specified time certain point Accounting estimates interval, the net period, theand amount time, the resources assets of cash of a company (the judgments aregenerated outlined ingenerated the notes and consumed by a assets), thethrough business to financial statements. company through company’s operations theoperating, net financing, obligations (revenues), (the assets and(the investing liabilities), and theconsumed expenses), andactivities. the equity of the net income. owners. Auditor’s Role • Auditors working independently of a company’s management and internal accountants examine the financial statements • They issue an auditor’s opinion about the fairness of the statements and their adherence to proper accounting principles. Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) • 1929 stock market crash blamed on nonstandard accounting. • 1933 Securities Act established SEC to standardize accounting. • Created to protect the interests of investors by ensuring full and fair disclosure. • Granted legal authority to dictate GAAP. • Has tended to defer setting GAAP to the accounting profession. Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) • • • • • A private sector body responsible for the US accounting standards (also known as GAAP). Seven full-time members comprise this independent body. Issues Statements of Financial Accounting Standards. Determines GAAP by “due process.” Works within the Conceptual Framework. American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) • Professional organization of practicing CPAs in the United States • Responsibilities include: – – – – certification continuing education quality control standard setting Internal Revenue Service • The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has the primary goal of equitable collecting revenue. • Although not the same, there are many areas where tax and financial accounting are related. International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) • Formed in 1973 to harmonize conflicting worldwide standards. • Similar to FASB, IASB develops pronouncements after feedback sessions. • Board members are representatives from the US, UK, France, Germany, Sweden, Canada, Australia, South Africa and Japan. • IASB standards are called International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs). Conceptual Framework • Concepts guide the field in developing new accounting policies for a changing business world. • When accountants face issues not covered by GAAP, they are to look to the conceptual framework as a guide. • This framework can be traced to early AAA publications in 1936. Objectives of Financial Reporting • Usefulness. • Understandability. • Target audience: investors and creditors. • Assessing future cash flows. • Evaluating economic resources. • Primary focus on earnings. Qualitative Characteristics of Accounting Information • Benefits greater than cost • Relevance • Reliability • Comparability • Materiality Recognition • Recognition- Taking all the estimates and judgments into one number and using that number to make a journal entry. • Recognition Criteria- For an item to be formally recognized, it must meet one of the definitions of the elements of the financial statements. – For example, revenue must meet the definition of revenue to be recorded and reported on the income statement. • Disclosure- Skipping the journal entry and just relying on the note to convey the information to users. Measurement • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Five attributes of measurement: Historical cost Current replacement cost Current market value Net realizable value Present (or discounted) value Reporting • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. To meet the objectives of financial reporting, a full set of financial statements should include: Financial position at the end of the period Earnings (net income) for the period Cash flows during the period Investments by and distributions to owners during the period Comprehensive income for the period Traditional Assumptions • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Underlying assumptions not addressed in the framework: Economic entity Going concern Arm’s-length transactions Stable monetary unit Accounting period Careers in Financial Accounting 1. Public Accounting 2. Corporate Accounting 3. User (analyst, banker, consultant