Study Guide/Guide Notes
advertisement

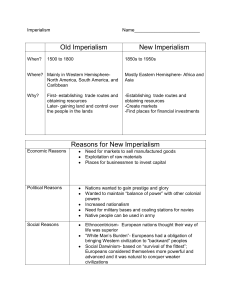
Name:_____________________________________ World History: Hoffmeyer Hour:_________________ Unit 8: Industrialization and Imperialism Study Guide/Guide Notes Chapter 19: Industrialization and Nationalism Section 1: The Industrial Revolution SG1: What three factors led to the Industrial Revolution beginning in Great Britain? SG2: What was the enclosure movement? How did it affect migration of people in Great Britain? SG3: Describe the process of making cotton cloth under the cottage industry system. SG4: What were four key inventions (be sure to include who invented or improved them where possible) that increased the speed of cotton manufacturing? SG5: In the 1780s Henry Cort developed a process that created a better quality or iron. Name the process and briefly describe how it worked. SG6: What were conditions for workers like in factories during the Industrial Revolution? SG7: How did railroads help foster the process of Industrialization? SG8: Describe economist Robert Malthus’s theory on population growth. SG9: What was Industrial Capitalism? What two classes did it create? What were the effects? SG10: Define socialism and explain why it grew in strength as a political movement as result of the Industrial Revolution. SG11: Robert Owen was a proponent of utopian socialism. Who was he and how did he attempt to carry out utopian socialism? Section 2: Reaction and Revolution SG12: What was the goal of the Congress of Vienna? Why was it held? Who was the most influential leader? SG13: Define conservatism. SG14: What was the principle of intervention? SG15: Define liberalism. SG16: What was the effect of Nationalism on Europe during the 19th century? SG17: What four revolutions made up the Revolutions of 1848? What were the outcomes of each? Section 3: National Unification and Nationalism SG18: What was the Concert of Europe? What led to its breakdown? SG19: How did Italian unification occur, beginning in 1849? SG20: How did German Unification occur, beginning in the 1860s? SG21: What reforms were made in Russia by Tsar Alexander II? Why were these reforms made? Chapter 21: The Height of Imperialism Section 1: Colonial Rule in Southeast Asia SG22: Define Imperialism. What were the motives for imperialism? SG23: Define racism and Social Darwinism. How did these beliefs affect Imperialism? SG24: What territories did Great Britain takeover in Asia? How was it accomplished? SG25: What territories did France takeover in Asia? How was it accomplished? SG26: What territories did the United States takeover in Asia? How was it accomplished? SG27: Define indirect and direct rule. SG28: Describe the economic policy of colonial powers. SG29: How did many Asian colonies resist colonial rule by European powers? Section 3: Empire Building in Africa SG30: What does it mean for a country or territory to be annexed? SG31: How and why did Egypt come to be a protectorate of the British Empire? Who were the important figures during this period? SG32: Who were Livingston and Stanley? What was their goal in Africa? SG33: Why was the Berlin Conference held? How did it affect Africa? SG34: What were the Boer Republics? How did the Boer War start and how was it resolved? SG35: How was did colonial rule in Africa differ from Asia? How was it the same? Section 3: British Rule in India SG36: How did the British East India Company use sepoys to protect their interests in India? SG37: What conditions led Indians to revolt against the British in 1857? What was the result of this revolt? SG38: What were the benefits of British rule in India? SG39: What were the costs of British rule in India? SG40: How did Indian nationalism arise? What were the effects of nationalist newspapers? SG41: Who was Mohandas Gandhi? Where did his movement against British rule begin? What ideal was his movement for Indian independence based on? SG42: Who was Rabindranath Tagore? What was his life mission?