AP World History II Midterm Study Guide
advertisement

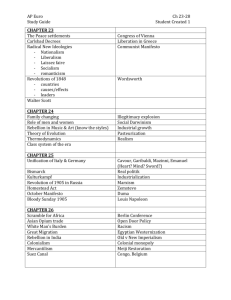
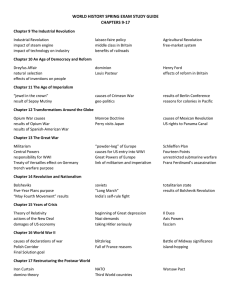
AP World History II Midterm Study Guide Terms to Know: Palace at Versailles Forbidden City Industrialization Seven Years’ War Declaration of Independence Declaration of the Rights of Man and the Citizen National Assembly Congress of Vienna (Convention) Levee en masse Napoleon’s Civil Code Creoles The Demographic Transition (of the 19th century) Serfs Russo-Japanese War People to Know: Qianlong James Watt John Kay John Bessemer Edmund Cartwright Edmund Burke John Locke John Stuart Mil William Wilberforce Voltaire Louis XVI Jean-Jacques Rosseau Maximillen Robespierre Bloody Sunday Massacre of 1905 (Russia) Taiping Rebellion Sepoy Rebellion French Indochina The Berlin Conference The Monroe Doctrine The Spanish-American War The Roosevelt Corollary Social Darwinism Nationalism Imperialism The Twenty-One Demands The February Revolution The Bolshevik/Russian Revolution Napoleon Bonaparte Simon Bolivar Elizabeth Cady Stanton Karl Marx Benito Juarez Emillano Zapata Cecil Rhodes David Livingston William Gladstone Rudyard Kipling Woodrow Wilson V. Lenin Czar Nicholas II Themes to Consider: 1 - Trade between East and West (China, Japan, Europe, America) 2 - Society and Art in the Muslim World (Ottomans, Safavids, Mughals, etc.) 3 - The Industrial Revolution (Where it started, why/how it started, and its immediate impact on society) 4 - The impact of technology on society and the emerging global commerce 5 - The Atlantic World Revolutions (American, French, Haitian, Latin-American, etc.) 6 - The “Isms” from the Industrial Revolution (Capitalism, Utilitarianism, Socialism, Marxism, Communism, etc.) 7 - The rise of female right and suffrage 8 - The Crumbling British Empire (as loss of colonies like Canada, etc.) 9 - The Industrialization of Russia and Japan 10 - Japanese militaristic aggressions 11 - Imperialism 12 - The rise of Nationalism before WWI in the Balkans and the Ottoman Empire 13 - The Causes of WWI 14 - WWI (its start, what happened, and how it ended)