Pregnancy
advertisement

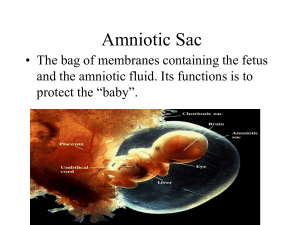
Pregnancy The Beginning of the Life Cycle Fertilization/Conception The process of sperm meeting with an egg in the Fallopian tube Once an egg is fertilized it becomes a zygote Zygote = fertilized egg (sperm meeting the egg) The zygote travels through the fallopian tube and begins to divide The Beginning of the Life Cycle The zygote divides many times and becomes a blastocyst (hollow cluster of cells) by the time it gets to the uterus Implantation occurs. Implantation is the process in which the blastocyst attaches itself to the wall of the uterus Zygote is now called an embryo (occurs 7-10 days after fertilization) Development of the Uterus After implantation, development continues in the uterus Three structures form from the dividing cells: the amniotic sac, placenta, and umbilical cord (All three serve to protect and nourish the developing embryo, and later the fetus) Development in the Uterus Amniotic Sac Fluid filled bag of thin tissue. The sac continues to grow in size as the embryo grows. Inside the sac, the embryo floats in amniotic fluid Placenta The structure that holds the embryo to the wall of the uterus Within the placenta, oxygen and nutrients move from the mother’s blood into tiny blood vessels that lead to the embryo Development of the Uterus Umbilical Cord A ropelike structure that connects the embryo to the placenta This cord is the embryo’s lifeline It carries nutrients and oxygen from the placenta to the embryo and wastes from the embryo to the placenta Development of a Uterus WEEK 1-8 = Embryo Week 9-Birth = Fetus Pregnancy term= lasts between 38-40 weeks Pregnancy Calendar (kids health) Development of the Uterus Trimesters 0-13 weeks = 1st Trimester 2nd Trimester 27-40 weeks = 3rd Trimester 14-26 weeks = Conception Developing Embryo (4 weeks) Developing Embryo (7 weeks) Developing Fetus (14 weeks) Developing Fetus (24 weeks) Developing Fetus (30 weeks) Week by Week Pregnancy http://kidshealth.org/parent/pregnancy_calendar/pregnancy_cale ndar_intro.html?tracking=79986_G%20-%20cat32 Birth (3 stages) Stage One (Labor) Dilation- stretching of the cervix (10cm) May last for a few hours Contractions to shorten the uterus Longest most difficult part of labor Near the end of this stage, the amniotic sac breaks and the cervix becomes softer and wide enough (10 cm) for the fetus to pass through Birth (3 Stages) Stage Two (Delivery of the Baby) Birth: muscles of the uterus contract and push baby out of the body Umbilical cord is clamped and cut Appearance of the head first, known as crowning Stage Three (After Birth) Afterbirth: contractions continue and push placenta and umbilical cord out of the mother Complications during Birth Premature birth Delivery of a live baby before the 37th week of pregnancy Low birth weight A newborn that weighs less than 5.5 pounds at birth. *Premature and low birth weight babies face an increased risk of health problems Still Birth * occurs when a fetus dies and is removed from the body after the 20th week of pregnancy. Complications during Birth Cesarean Section This method can be the family’s choice of delivery or what is called an emergency “cesarean section” or “C-Section”. The doctor makes an incision in the lower abdomen into the uterus. The baby and placenta are then removed. Complications during Birth Jaundice • A common condition in newborns. • Refers to the yellow color of the skin and whites of the eyes caused by excess bilirubin in the blood. Miscarriage • the death of an embryo or fetus in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy. Having a Healthy Pregnancy Avoid alcohol (Fetal Alcohol Syndrome) Causes physical, mental and behavior problems FAS babies are: -Shorter & lighter -Speech problems -Slow growth -Facial abnormalities - Poor coordination - Heart defects - Mental retardation Having a Healthy Pregnancy Avoid drugs (tobacco, OTC, prescription, and illegal drugs) = Low birth weight/possible premature birth Exercise Eat a variety of healthy foods (avoid uncooked meats, deli meats, fish, seafood, caffeine) Signs of Pregnancy Appear a few weeks or 1-2 months after conception/fertilization “Morning Sickness” Nipples darken Increased fatigue Menstruation usually stops PMS - type symptoms Increased urination Pregnancy Test Reveals hormone HCG in urine about 2 weeks after missed period - about 95% accurate A blood test also detects HCG Home tests give false negatives and positives. Should be followed up by a doctor visit